Abstract
Background
Membrane proteins represent over 25 % of human protein genes and account for more than 60 % of drug targets due to their accessibility from the extracellular environment. The increasing number of available crystal structures of these proteins in the Protein Data Bank permits an initial estimation of their structural properties.
Description
We have developed two web servers—TMalphaDB for α-helix bundles and TMbetaDB for β-barrels—to analyse the growing repertoire of available crystal structures of membrane proteins. TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB permit to search for these specific sequence motifs in a non-redundant structure database of transmembrane segments and quantify structural parameters such as ϕ and ψ backbone dihedral angles, χ1 side chain torsion angle, unit bend and unit twist.
Conclusions
The structural information offered by TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB permits to quantify structural distortions induced by specific sequence motifs, and to elucidate their role in the 3D structure. This specific structural information has direct implications in homology modeling of the growing sequences of membrane proteins lacking experimental structure. TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB are freely available at http://lmc.uab.cat/TMalphaDB and http://lmc.uab.cat/TMbetaDB.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Membrane proteins represent over 25 % of all proteins in sequenced genomes and mediate the interaction of the cell with its surroundings, including selective molecular transport, signalling, respiration and motility [1]. Because of their accessibility from the extracellular environment, membrane proteins are targets of over 60 % of currently marketed drugs [2–4]. Due to the difficulty in over-expressing, purifying and crystallizing membrane proteins [5], only 2 % of the structures deposited in Protein Data Bank are membrane proteins [6, 7]. Membrane proteins display specific features that differ from those of water-soluble ones, due to their different environment [8]. For instance, the number of folds that membrane proteins can adopt is limited to α-helix bundles and β-barrels due to the physical constraints imposed by the lipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer, where the transmembrane (TM) regions are located, is predominantly lipophilic, lacks hydrogen-bonding potential, and provides little screening of electrostatic interactions. Thus, α-helix and β-sheets secondary structure elements maximize the hydrogen bond interactions among backbone atoms, whereas hydrophobic side chains are preferentially oriented toward the membrane lipids. This results in significant differences in amino acid composition [9] and in the probabilities of amino acid substitutions during evolution [10, 11] relative to globular proteins.
Biological function of membrane proteins involves conformational rearrangement of the TM regions. For example, activation of the G protein-coupled receptor family requires the binding of the C-terminal α-helix of the G protein to the intracellular cavity that is opened by the conformational rearrangement of TM6 [12]. Similarly, multidrug transporters are flexible proteins that switch from outward-open to inward-open conformations, facilitating the release of the substrate [13]. Such conformational changes require local flexibility or distortions in the TM regions, which can be provided by specific structural motifs. For instance, our laboratory has shown that serine or threonine, either alone [14] or in combination with proline [15], induces distinctive TM distortions to accommodate the structural needs of specific protein functions [16, 17]. To address this issue we have developed two non-redundant databases of 3D structures of TM segments consisting on α-helix bundles and β-barrels that are accessible through the TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB web servers, respectively. The main advantage of these servers is their ability to systematically survey sequences of TM regions and provide to the users main structural parameters, such as backbone ϕ and ψ dihedral angles and side chain χ1 angle, as well as helix bend and twist angles. This structural information allows to quantify distortions induced by residues or motifs and to elucidate their role in the structure and function of membrane proteins.
Construction and content
TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB are web-based servers that combine a MySQL database management system and Python programs with a dynamic web interface based on PHP.
Non-redundant databases of transmembrane segments structures of alpha and beta membrane proteins
TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB currently contain 330 structures of α-helix bundles and 107 structures of β-barrels, respectively, with a resolution lower than 3.5 Å. To avoid redundancy, only one structure for each protein is selected (i.e. one structure per UniProt accession code). Among different structures with the same UniProt accession code, the one with best resolution and resemblance to the native state (i.e. without mutations, native pH) is selected. Additionally, for multimeric proteins, only one subunit is extracted. The complete list of structures, together with the unique subunit database, can be downloaded at http://lmc.uab.cat/TMalphaDB/info.php and http://lmc.uab.cat/TMbetaDB/info.php. These databases are regularly and automatically updated, in order to include new solved proteins. Each structure is characterized by the Protein Data Bank identification code (PDBID) [18], protein name, Uniprot accession code [19], family name according to Orientations of Proteins in Membranes [20] and organism. Moreover, because the hydrophobic nature of the lipid bilayer conditions the structure and features of the membrane-embedded regions relative to the water-exposed ones [8, 11], we used PDBTM [7, 21] to download only the coordinates of the domain of the protein that is inserted in the lipid bilayer.
Tools to analyse sequence and structure of membrane proteins
The importance of TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB is their ability to search and analyse specific residues or sequence motifs in TM segments of membrane proteins. The search is performed using the single-letter amino acid code or/and in combination with wildcard characters such as ‘+’ (positively charged, K/R), ‘−’ (negatively charged, D/E), ‘*’ (charged, K/R/H/D/E), ‘@’ (aromatic, F/W/Y/H), ‘~’ (hydrophobic, I/L/V/M/F/A/P), ‘^’ (polar, D/E/N/Q/K/R/H/S/T/C/W/Y), ‘%’ (aliphatic, L/V/I/M), ‘#’ (distorting, P/G), ‘?’ (hydroxylic, S/T/Y), ‘$’ (sulphur-containing, C/M), ‘.’ (tiny, G/A), ‘!’ (aromatic amphipathic, W/Y/H), or ‘x’ (any amino acid). Moreover, the search (advanced options) can be filtered by the proximity of the sequence motif to the beginning/end of the TM domain (as the structural parameters can be highly influenced by the loops) or the presence of certain amino acids within the sequence motif (as, for instance, Pro or/and Gly can distort the secondary structure conformation). The output consists of a list of proteins, identified by the PDBID, Uniprot accession code, the name and identifier of the first residue in the motif, the sequence of the TM segment with the requested motif highlighted and the family name of the protein. The coordinates of the entire protein, the TM segments and/or a unique subunit of the protein can be downloaded for each entry. The user can select all TM segments, unique TM segments (i.e. only one TM segments is select for repeated subunits), or a manually selection can be performed. Average backbone ϕ and ψ angles and side chain χ1 angle for the selected TM segments can be downloaded or/and displayed in a plot. When all the analysed sequences feature the same type of residue (according to the wildcards previously defined), for a specific position, the plot uses this representation. In TMalphaDB, bend and twist angles, two relevant parameters to measure local distortions of TM helices, are also calculated and plotted for the identified/selected TM segments using HELANAL [22]. Local bend angles are calculated as the angle between the axes of the cylinders formed by the Cα atoms of the residues preceding (i-3, i) and following (i, i + 3) a given amino acid i. Unit twist angles are calculated for sets of four consecutive Cα atoms, i.e. one turn, to analyze helical uniformity. An ideal α-helix, with approximately 3.6 residues per turn, has a unit twist of approximately 100° (360°/3.6). A closed helical segment, with <3.6 residues per turn, possesses a unit twist >100°, whereas an open helical segment, with >3.6 residues per turn, possesses an unit twist <100°. A variation greater than 20° in the unit twist angle will result in a change in the orientation of the amino acid side chain. Finally, JSMoL [23] sessions containing the coordinates of the requested motif, and all residues and ligands in its environment can also be displayed.
Utility and discussion
Membrane proteins incorporate in the sequence of their TMs specific residues like Pro and Gly, introducing a flexible point and assisting in helix movements or stabilizing local regions of structural relevance [24]. In order to illustrate the use of TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB, we have surveyed and quantified structural distortions induced by P and PP motifs in TM α-helices and P and G residues in TM β-strands.
P and PP motifs in TM α-helices
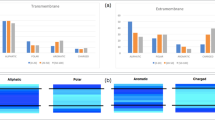
Although Pro presents the smallest helix-forming tendency among naturally occurring amino acids [25], Pro residues are often observed in TM helices [26] where they induce a significant distortion. This is produced to avoid a steric clash between the pyrrolidine ring of Pro and the carbonyl oxygen of the residue in the preceding turn, leading to a bending of the helical structure [27]. Moreover, two consecutive Pro residues are also observed in sequences of membrane proteins. In order to study the distortion induced by the PP motif, relative to P, we scanned TMalphaDB. The search resulted in 349 unique TM helices containing P (search=“P”) and 8 TM helices containing PP (search=“PP”). Figure 1 shows a snapshot of the obtained output for the “P” search, plots for phi and psi dihedrals and unit twist/bend and a Pymol session showing the residues located near “P”. The obtained average bend angle plots for P and PP are shown to compare the structural distortion induced by each sequence motif (Fig. 2a). Clearly, the distortion in bend induced by PP is lower than for P and is not the sum of individual Pro distortions, suggesting a modulating effect.
Snapshots of the TMalphaDB output. The output consists in a list of proteins containing the “P” motif (left panel), average backbone ϕ and ψ angles (top right panel), average bend and twist angles (central right panel), and a JSMol session displaying all residues and ligands at a distance cutoff of 5 Å from the “P” motif (bottom right panel)
P and G in TM β-barrels
The cyclic structure of the side chain of Pro locks the ϕ dihedral angle at approximately -60°, which is incompatible with ϕ values near −130° observed in β-strands. We scanned TMbetaDB in order to calculate the backbone ϕ and ψ dihedral angles of Pro when located in β-barrel domains of membrane proteins. The TMbetaDB search resulted in 172 TM segments containing P whose average ϕ and ψ dihedral angles are plotted in Fig. 3. Relative to the energetically preferred ϕ and ψ dihedral angles near −130° and 130° of β-strands, Pro increases ϕ and triggers a decrease in ψ at position i-1. In contrast to Pro, the absence of a side chain in Gly allows high flexibility in the polypeptide chain as well as dihedral angles. In order to calculate the observed ϕ and ψ dihedral angles of Gly in β-barrel domains TMbetaDB was scanned. The search resulted in 1031 TM segments containing Gly. Figure 3 shows that, on average, Gly increases ϕ and decreases ψ dihedral angles. These results indicate that both Pro and Gly induce a distortion in the conformation of main polypeptide chain in TM β-strands.
Conclusions
The structural data provided by TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB quantify structural distortions induced by specific amino acids or motifs, and elucidate their role in the structure of membrane proteins. This specific structural information can be, for instance, incorporated in the homology modelling of membrane proteins lacking experimental structure. Thus, these servers emerge as valuable tools to fill the growing gap between the pool of known sequences of membrane proteins and the number of experimentally determined structures.
Availability and requirements
TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB are freely available at http://lmc.uab.cat/TMalphaDB and http://lmc.uab.cat/TMbetaDB.
Abbreviations
- TM:
-
Transmembrane segments
- PDBID:
-
Protein Data Bank identification code
References
Fagerberg L, Jonasson K, von Heijne G, Uhlen M, Berglund L. Prediction of the human membrane proteome. Proteomics. 2010;10:1141–9.
Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL. How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:993–6.
Arinaminpathy Y, Khurana E, Engelman DM, Gerstein MB. Computational analysis of membrane proteins: the largest class of drug targets. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14:1130–5.
Bakheet TM, Doig AJ. Properties and identification of human protein drug targets. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:451–7.
Bill RM, Henderson PJ, Iwata S, Kunji ER, Michel H, Neutze H, et al. Overcoming barriers to membrane protein structure determination. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:335–40.
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissing H, et al. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:235–42.
Kozma D, Simon I, Tusnady GE. PDBTM: Protein Data Bank of transmembrane proteins after 8 years. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D524–529.
Olivella M, Gonzalez A, Pardo L, Deupi X. Relation between sequence and structure in membrane proteins. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:1589–92.
Donnelly D, Overington JP, Ruffle SV, Nugent JH, Blundell TL. Modeling alpha-helical transmembrane domains: the calculation and use of substitution tables for lipid-facing residues. Protein Sci. 1993;2:55–70.
Jones DT. De novo protein design using pairwise potentials and a genetic algorithm. Protein Sci. 1994;3:567–74.
Li SC, Deber CM. A measure of helical propensity for amino acids in membrane environments. Nat Struct Biol. 1994;1:368–73.
Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, Kobilka TS, et al. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature. 2011;477:549–55.
Masureel M, Martens C, Stein RA, Mishra S, Ruysschaert JM, Mchaourab HS, et al. Protonation drives the conformational switch in the multidrug transporter LmrP. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:149–55.
Deupi X, Olivella M, Sanz A, Dolker N, Campillo M, Pardo L. Influence of the g- conformation of Ser and Thr on the structure of transmembrane helices. J Struct Biol. 2010;169:116–23.
Deupi X, Olivella M, Govaerts C, Ballesteros JA, Campillo M, Pardo L. Ser and Thr residues modulate the conformation of pro-kinked transmembrane alpha-helices. Biophys J. 2004;86:105–15.
Sansuk K, Deupi X, Torrecillas IR, Jongejan A, Nijmeijer S, Bakker RA, et al. A structural insight into the reorientation of transmembrane domains 3 and 5 during family A G protein-coupled receptor activation. Mol Pharmacol. 2011;79:262–9.
Boiteux C, Vorobyov I, Allen TW. Ion conduction and conformational flexibility of a bacterial voltage-gated sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:3454–9.
Bernstein FC, Koetzle TF, Williams GJ, Meyer Jr EF, Brice MD, Rodgers JR, et al. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977;112:535–42.
UniProt. Activities at the Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D191–198.
Lomize MA, Pogozheva ID, Joo H, Mosberg HI, Lomize AL. OPM database and PPM web server: resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D370–376.
Tusnady GE, Dosztanyi Z, Simon I. PDB_TM: selection and membrane localization of transmembrane proteins in the protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:D275–278.
Bansal M, Kumar S, Velavan R. HELANAL: a program to characterize helix geometry in proteins. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2000;17:811–9.
Hanson RM, Prilusky J, Renjian Z, Nakane T, Sussman JL. JSmol and the next-generation Web-based representation of 3D molecular structure as applied to proteopedia. Isr J Chem. 2013;53:207–16.
Gonzalez A, Cordomí A, Caltabiano G, Campillo M, Pardo L. Impact of helix irregularities on sequence alignment and homology modelling of G protein-coupled receptors. Chembiochem. 2012;13:1393–9.
O’Neil KT, DeGrado WF. A thermodynamic scale for the helix-forming tendencies of the commonly occurring amino acids. Science. 1990;250:646–51.
Senes A, Gerstein M, Engelman DM. Statistical analysis of amino acid patterns in transmembrane helices: the GxxxG motif occurs frequently and in association with b-branched residues at neighboring positions. J Mol Biol. 2000;296:921–36.
Rey J, Deville J, Chabbert M. Structural determinants stabilizing helical distortions related to proline. J Struct Biol. 2010;171:266–76.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (SAF2013-48271-C2-2-R) to LP and Instituto de Salud Carlos III (CD09/00150) to AC. We thank Víctor Urrea for his help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author’s contributions
LP, XD and MO participated in the research design. IL, MP, EM, AC and MO wrote the required computer software. LP, AC, EM and MO contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Marc Perea and Ivar Lugtenburg contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Perea, M., Lugtenburg, I., Mayol, E. et al. TMalphaDB and TMbetaDB: web servers to study the structural role of sequence motifs in α-helix and β-barrel domains of membrane proteins. BMC Bioinformatics 16, 266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0699-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0699-5