Abstract
Background
The existing Z-test for uncertainty events does not give information about the measure of indeterminacy/uncertainty associated with the test.
Methods
This paper introduces the Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics. The test statistic of the existing test is modified under the philosophy of the Neutrosophy. The testing process is introduced and applied to the Covid-19 data.
Results
Based on the information, the proposed test is interpreted as the probability that there is no reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19 is accepted with a probability of 0.95, committing a type-I error is 0.05 with the measure of an indeterminacy 0.10. Based on the analysis, it is concluded that the proposed test is informative than the existing test. The proposed test is also better than the Z-test for uncertainty under fuzzy-logic as the test using fuzz-logic gives the value of the statistic from 2.20 to 2.42 without any information about the measure of indeterminacy. The test under interval statistic only considers the values within the interval rather than the crisp value.
Conclusions
From the Covid-19 data analysis, it is found that the proposed Z-test for uncertainty events under the neutrosophic statistics is efficient than the existing tests under classical statistics, fuzzy approach, and interval statistics in terms of information, flexibility, power of the test, and adequacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The Z-test is playing an important role in analyzing the data. The main aim of the Z-test is to test the mean of the unknown population in decision-making. The Z-test for uncertainty events is applied to test the reduction in the uncertainty of past events. This type of test is applied to test the null hypothesis that there is no reduction in uncertainty against the alternative hypothesis that there is a significant reduction in uncertainty of past events. The Z-test for uncertainty events uses the information of the past events for testing the reduction of uncertainty [1]. discussed the performance of the statistical test under uncertainty [2]. discussed the design of the Z-test for uncertainty events [3]. worked on the test in the presence of uncertainty [4]. worked on the modification of non-parametric test. The applications of [5], [6], [7] and [8].
[9] mentioned that “statistical data are frequently not precise numbers but more or less non-precise also called fuzzy. Measurements of continuous variables are always fuzzy to a certain degree”. In such cases, the existing Z-tests cannot be applied for the testing of the mean of population or reduction in uncertainty. Therefore, the existing Z-tests are modified under the fuzzy-logic to deal with uncertain, fuzzy, and vague data [10]., [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19] worked on the various statistical tests using the fuzzy-logic.
Nowadays, neutrosophic logic attracts researchers due to its many applications in a variety of fields. The neutrosophic logic counters the measure of indeterminacy that is considered by the fuzzy logic, see [20] [21]. proved that neutrosophic logic is efficient than interval-based analysis. More applications of neutrosophic logic can be seen in [22], [23], [24] and [25] [26]. applied the neutrosophic statistics to deal with uncertain data [27]. and [28] presented neutrosophic statistical methods to analyze the data. Some applications of neutrosophic tests can be seen in [29], [30] and [31].
The existing Z-test for uncertainty events under classical statistics does not consider the measure of indeterminacy when testing the reduction in events. By exploring the literature and according to the best of our knowledge, there is no work on Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics. In this paper, the medication of Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics will be introduced. The application of the proposed test will be given using the Covid-19 data. It is expected that the proposed Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics will be more efficient than the existing tests in terms of the power of the test, information, and adequacy.
Methods
The existing Z-test for uncertainty events can be applied only when the probability of events is known. The existing test does not evaluate the effect of the measure of indeterminacy/uncertainty in the reduction of uncertainty of past events. We now introduce the modification of the Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics. With the aim that the proposed test will be more effective than the existing Z-test for uncertainty events under classical statistics. Let \({A}_N={A}_L+{A}_U{I}_{A_N};{I}_{A_N}\epsilon \left[{I}_{A_L},{I}_{A_U}\right]\) and \({B}_N={B}_L+{B}_U{I}_{B_N};{I}_{B_N}\epsilon \left[{I}_{B_L},{I}_{B_U}\right]\) be two neutrosophic events, where lower values AL, BL denote the determinate part of the events, upper values \({A}_U{I}_{A_N}\), \({B}_U{I}_{B_N}\) be the indeterminate part, and \({I}_{A_N}\epsilon \left[{I}_{A_L},{I}_{A_U}\right]\), \({I}_{B_N}\epsilon \left[{I}_{B_L},{I}_{B_U}\right]\) be the measure of indeterminacy associated with these events. Note here that the events ANϵ[AL, AU] and BNϵ[BL, BU] reduces to events under classical statistics (determinate parts) proposed by [2] if \({I}_{A_L}={I}_{B_L}\) =0. Suppose nN = nL + nUIN; INϵ[IL, IU] be a neutrosophic random sample where nL is the lower (determinate) sample size and nUIN be the indeterminate part and INϵ[IL, IU] be the measure of uncertainty in selecting the sample size. The neutrosophic random sample reduces to random sample if no uncertainty is found in the sample size. The methodology of the proposed Z-test for uncertainty events is explained as follows.
Suppose that the probability that an event ANϵ[AL, AU] occurs (probability of truth) is P(AN)ϵ[P(AL), P(AU)], the probability that an event ANϵ[AL, AU] does not occur (probability of false) is \(P\left({A}_N^c\right)\epsilon \left[P\left({A}_L^c\right),P\left({A}_U^c\right)\right]\), the probability that an event BNϵ[BL, BU] occurs (probability of truth) is P(BN)ϵ[P(BL), P(BU)], the probability that an event BNϵ[BL, BU] does not occur (probability of false) is \(P\left({B}_N^c\right)\epsilon \left[P\left({B}_L^c\right),P\left({B}_U^c\right)\right]\). It is important to note that sequential analysis is done to reduce the uncertainty by using past events information. The purpose of the proposed test is whether the reduction of uncertainty is significant or not. Let ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] be neutrosophic test statistic, where ZL and ZU are the lower and upper values of statistic, respectively and defined by.
Note that P(B+kN| AN) = P(BN| AN) at lag kN, where P(BN| AN)ϵ[P(BL| AL), P(BU| AU)] denotes the conditional probability. It means that the probability of event P(BN)ϵ[P(BL), P(BU)] will be calculated when the event ANϵ[AL, AU] has occurred.
The neutrosophic form of the proposed test statistic, say ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is defined by.
The alternative form of Eq. (2) can be written as.
The proposed test ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is the extension of several existing tests. The proposed test reduces to the existing Z test under classical statistics when IZN =0. The proposed test is also an extension of the Z test under fuzzy approach and interval statistics.
The proposed test will be implemented as follows.
Step-1: state the null hypothesis H0: there is no reduction in uncertainty vs. the alternative hypothesis H1: there is a significant reduction in uncertainty.
Step-2: Calculate the statistic ZNϵ[ZL, ZU.]
Step-3: Specify the level of significance α and select the critical value from [2].
Step-4: Do not accept the null hypothesis if the value of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is larger than the critical value.
Results
The application of the proposed test is given in the medical field. The decision-makers are interested to test the reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19 when the measure of indeterminacy/uncertainty is IZNϵ[0,0.10]. The decision-makers are interested to test that the reduction in death due to Covid-19 (event AN) with the increase in Covid-19 vaccines (event BN). By following [2], the sequence in which both events occur is given as
where nNϵ[12, 12], kNϵ[1, 1], P(AN) = 6/12 = 0.5 and P(BN) = 6/12 = 0.5.
Note here that event AN occurs 6 times and that of these 6 times BN occurs immediately after AN five times. Given that AN has occurred, we get
(B+kN| AN) = P(BN| AN) = 5/6 = 0.83 at lag 1. The value of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is calculated as
\({Z}_N=\left(1+0.1\right)\frac{0.83-0.50}{\sqrt{\frac{0.50\left[1-0.50\right]\left[1-0.50\right]}{\left(12-1\right)0.50}}}=2.42;{I}_{ZN}\epsilon \left[\mathrm{0,0.1}\right]\). From [2], the critical value is 1.96.
The proposed test for the example will be implemented as follows
Step-1: state the null hypothesis H0: there is no reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19 vs. the alternative hypothesis H1: there is a significant reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19.
Step-2: the value of the statistic is 2.42.
Step-3: Specify the level of significance α = 0.05 and select the critical value from [2] which is 1.96.
Step-4: Do not accept the null hypothesis as the value of ZN is larger than the critical value.
From the analysis, it can be seen that the calculated value of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is larger than the critical value of 1.96. Therefore, the null hypothesis H0: there is no reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19 will be rejected in favor of H1: there is a significant reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19. Based on the study, it is concluded that there is a significant reduction in the uncertainty of Covid-19.
Simulation study
In this section, a simulation study is performed to see the effect of the measure of indeterminacy on statistic ZNϵ[ZL, ZU]. For this purpose, a neutrosophic form of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] obtained from the real data will be used. The neutrosophic form of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is given as
To analyze the effect on H0, the various values of IZNϵ[IZL, IZU] are considered. The computed values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] along with the decision on H0 are reported in Table 1. For this study α = 0.05 and the critical value is 1.96. The null hypothesis H0 will be accepted if the calculated value of ZN is less than 1.96. From Table 1, it can be seen that as the values of IZNϵ[IZL, IZU] increases from 0.01 to 2, the values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] increases. Although, a decision about H0 remains the same at all values of measure of indeterminacy IZNϵ[IZL, IZU] but the difference between ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] and the critical value of 1.96 increases as IZU increases. From the study, it can be concluded that the measure of indeterminacy IZNϵ[IZL, IZU] affects the values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU].
Comparative studies
As mentioned earlier, the proposed Z-test for uncertainty events is an extension of several tests. In this section, a comparative study is presented in terms of measure of indeterminacy, flexibility and information. We will compare the efficiency of the proposed Z-test for uncertainty with the proposed Z-test for uncertainty under classical statistics, proposed Z-test for uncertainty under fuzzy logic and proposed Z-test for uncertainty under interval statistics. The neutrosophic form of the proposed statistic ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] is expressed as ZN = 2.20 + 2.20IZN; IZNϵ[0,0.1]. Note that the first 2.20 presents the existing Z-test for uncertainty under classical statistics, the second part 2.20IZN is an indeterminate part and 0.1 is a measure of indeterminacy associated with the test. From the neutrosophic form, it can be seen that the proposed test is flexible as it gives the values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] in an interval from 2.20 to 2.42 when IZU =0. On the other hand, the existing test gives the value of 2.20. In addition, the proposed test uses information about the measure of indeterminacy that the existing test does not consider. Based on the information, the proposed test is interpreted as the probability that H0: there is no reduction in uncertainty of Covid-19 is accepted with a probability of 0.95, committing a type-I error is 0.05 with the measure of an indeterminacy 0.10. Based on the analysis, it is concluded that the proposed test is informative than the existing test. The proposed test is also better than the Z-test for uncertainty under fuzzy-logic as the test using fuzz-logic gives the value of the statistic from 2.20 to 2.42 without any information about the measure of indeterminacy. The test under interval statistic only considers the values within the interval rather than the crisp value. On the other hand, the analysis based on neutrosophic considers any type of set. Based on the analysis, it is concluded that the proposed Z-test is efficient than the existing tests in terms of information, flexibility, and indeterminacy.
Comparison using power of the test
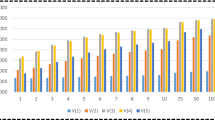
In this section, the efficiency of the proposed test is compared with the existing test in terms of the power of the test. The power of the test is defined as the probability of rejecting H0 when it is false and it is denoted by β. As mentioned earlier, the probability of rejecting H0 when it is true is known as a type-I error is denoted by α. The values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] are simulated using the classical standard normal distribution and neutrosophic standard normal distribution. During the simulation 100 values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] are generated from a classical standard normal distribution and neutrosophic standard normal distribution with mean \({\mu}_N={\mu}_L+{\mu}_U{I}_{\mu_N};{I}_{\mu_N}\epsilon \left[{I}_{\mu_L},{I}_{\mu_U}\right]\), where μL = 0 presents the mean of classical standard normal distribution, \({\mu}_U{I}_{\mu_N}\) denote the indeterminate value and \({I}_{\mu_N}\epsilon \left[{I}_{\mu_L},{I}_{\mu_U}\right]\) is a measure of indeterminacy. Note that when \({I}_{\mu_L}\) =0, μN reduces to μL. The values of ZNϵ[ZL, ZU] are compared with the tabulated value at α =0.05. The values of the power of the test for the existing test and for the proposed test for various values of \({I}_{\mu_U}\) are shown in Table 2. From Table 2, it is clear that the existing test under classical statistics provides smaller values of the power of the test as compared to the proposed test at all values of \({I}_{\mu_U}\). For example, when \({I}_{\mu_U}\) =0.1, the power of the test provided by the Z-test for uncertainty events under classical statistics is 0.94 and the power of the test provided by the proposed Z-test for uncertainty events is 0.96. The values of the power of the test for Z-test for uncertainty events under classical statistics and Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics are plotted in Fig. 1. From Fig. 1, it is quite clear that the power curve of the proposed test is higher than the power curve of the existing test. Based on the analysis, it can be concluded that the proposed Z-test for uncertainty events under neutrosophic statistics is efficient than the existing Z-test for uncertainty events.
Conclusions
The Z-test of uncertainty was introduced under neutrosophic statistics in this paper. The proposed test was a generalization of the existing Z-test of uncertain events under classical statistics, fuzzy-based test, and interval statistics. The performance of the proposed test was compared with the listed existing tests. From the real data and simulation study, the proposed test was found to be more efficient in terms of information and power of the test. Based on the information, it is recommended to apply the proposed test to check the reduction in uncertainty under an indeterminate environment. The proposed test for big data can be considered as future research. The proposed test using double sampling can also be studied as future research. The estimation of sample size and other properties of the proposed test can be studied in future research.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article
References
DOLL H, CARNEY S. Statistical approaches to uncertainty: p values and confidence intervals unpacked. BMJ evidence-based medicine. 2005;10(5):133–4.
Kanji, G.K, 100 statistical tests2006: Sage.
Lele SR. How should we quantify uncertainty in statistical inference? Front Ecol Evol. 2020;8:35.
Wang F, et al. Re-evaluation of the power of the mann-kendall test for detecting monotonic trends in hydrometeorological time series. Front Earth Sci. 2020;8:14.
Maghsoodloo S, Huang C-Y. Comparing the overlapping of two independent confidence intervals with a single confidence interval for two normal population parameters. J Stat Plan Inference. 2010;140(11):3295–305.
Rono BK, et al. Application of paired student t-test on impact of anti-retroviral therapy on CD4 cell count among HIV Seroconverters in serodiscordant heterosexual relationships: a case study of Nyanza region. Kenya.
Zhou X-H. Inferences about population means of health care costs. Stat Methods Med Res. 2002;11(4):327–39.
Niwitpong S, Niwitpong S-a. Confidence interval for the difference of two normal population means with a known ratio of variances. Appl Math Sci. 2010;4(8):347–59.
Viertl R. Univariate statistical analysis with fuzzy data. Comput Stat Data Anal. 2006;51(1):133–47.
Filzmoser P, Viertl R. Testing hypotheses with fuzzy data: the fuzzy p-value. Metrika. 2004;59(1):21–9.
Tsai C-C, Chen C-C. Tests of quality characteristics of two populations using paired fuzzy sample differences. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2006;27(5):574–9.
Taheri SM, Arefi M. Testing fuzzy hypotheses based on fuzzy test statistic. Soft Comput. 2009;13(6):617–25.
Jamkhaneh EB, Ghara AN. Testing statistical hypotheses with fuzzy data. In: 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Cognitive Informatics: IEEE; 2010.
Chachi J, Taheri SM, Viertl R. Testing statistical hypotheses based on fuzzy confidence intervals. Austrian J Stat. 2012;41(4):267–86.
Kalpanapriya D, Pandian P. Statistical hypotheses testing with imprecise data. Appl Math Sci. 2012;6(106):5285–92.
Parthiban, S. and P. Gajivaradhan, A Comparative Study of Two-Sample t-Test Under Fuzzy Environments Using Trapezoidal Fuzzy Numbers.
Montenegro M, et al. Two-sample hypothesis tests of means of a fuzzy random variable. Inf Sci. 2001;133(1-2):89–100.
Park S, Lee S-J, Jun S. Patent big data analysis using fuzzy learning. Int J Fuzzy Syst. 2017;19(4):1158–67.
Garg H, Arora R. Generalized Maclaurin symmetric mean aggregation operators based on Archimedean t-norm of the intuitionistic fuzzy soft set information. Artif Intell Rev. 2020:1–41.
Smarandache F. Neutrosophy. Neutrosophic probability, set, and logic, ProQuest Information & Learning, vol. 105. Michigan: Ann Arbor; 1998. p. 118–23.
Broumi S, Smarandache F. Correlation coefficient of interval neutrosophic set. In: Applied mechanics and materials: Trans Tech Publ; 2013.
Abdel-Basset M, et al. A novel group decision making model based on neutrosophic sets for heart disease diagnosis. Multimed Tools Appl. 2019:1–26.
Alhasan KFH, Smarandache F. Neutrosophic Weibull distribution and Neutrosophic Family Weibull Distribution2019. Infinite Study.
Das SK, Edalatpanah S. A new ranking function of triangular neutrosophic number and its application in integer programming. Int J Neutrosophic Sci. 2020;4(2).
El Barbary G, O. and R. Abu Gdairi, Neutrosophic logic-based document summarization. J Undergrad Math. 2021.
Smarandache, F., Introduction to neutrosophic statistic 014: Infinite Study.
Chen J, Ye J, Du S. Scale effect and anisotropy analyzed for neutrosophic numbers of rock joint roughness coefficient based on neutrosophic statistics. Symmetry. 2017;9(10):208.
Chen J, et al. Expressions of rock joint roughness coefficient using neutrosophic interval statistical numbers. Symmetry. 2017;9(7):123.
Sherwani RAK, et al. A new neutrosophic sign test: an application to COVID-19 data. PLoS One. 2021;16(8):e0255671.
Aslam M. Neutrosophic statistical test for counts in climatology. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–5.
Albassam M, Khan N, Aslam M. Neutrosophic D’Agostino test of normality: an application to water data. J Undergrad Math. 2021;2021.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the editor and reviewers for their valuable suggestions to improve the quality of the paper.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
N/A
Consent for publication
N/A
Competing interests
None
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, M. Design of a new Z-test for the uncertainty of Covid-19 events under Neutrosophic statistics. BMC Med Res Methodol 22, 99 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-022-01593-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-022-01593-x