Abstract
Background
Supportive care and dental treatment for older adults are crucial in addressing the global emergency of population aging, requiring specialized healthcare services and knowledge-based practices.
Methods
This cross-sectional content analysis study was conducted on 150 general dentists in Kerman in 2021. The participants were selected using cluster sampling. The data were collected using a questionnaire with four sections assessing the participants’ demographic characteristics, knowledge, attitudes, and performance. The data were analyzed with SPSS-26 software using the t-test, ANOVA, and linear regression analysis.
Results
The dentists’ mean age was 36.10 ± 7.60 years. The mean knowledge score of the participants was 5.29 ± 1.49 (out of 9). The mean attitude score was 59.42 ± 11.6 (out of 85), and the mean performance score was 24.13 ± 4.96 (out of a maximum of 35). The data showed a positive relationship between the dentists’ knowledge, attitudes, and performance. However, the participants’ gender had no significant correlation with their knowledge, attitudes, or performance. It was also shown that 50% of dentists had adequate experience treating elderly patients with complex medical problems.
Conclusions
The participants had an adequate level of knowledge and performance and a positive attitude toward dental care for older adults. Health officials and administrators need to organize and hold effective training and refresher courses on geriatric dentistry to promote dentists’ knowledge and performance.
Trial registration
Ethics code IR.KMU.REC.1401.007.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Population aging is one of the biggest global accomplishments and the outcome of technological growth, improved healthcare, diagnosis, and treatment, and increased life expectancy [1]. Improving public health and safety is one of the important missions of the health system, and this system can adopt a new approach to replacing unwanted care and services with goals and plans that value old age. Besides, the health system should follow integrated strategies to improve older adults’ health and well-being [2]. Given the current increasing trend of the elderly population, the population of this group in developing countries will make up 80% of the world’s elderly population by 2050 [3]. Currently, 2.8% of Iran’s population is made up of older adults over 60 years old, and this figure is predicted to reach 26% in less than 4 decades [4].
Aging is associated with the occurrence of some chronic diseases, most of which have oral manifestations that may lead to chewing and swallowing problems [5]. Furthermore, aging is associated with many physiological changes in the oral cavity, including the loss of tooth translucency and surface details and dental wear and erosion [6]. A study showed that oral and dental health is somewhat neglected in older adults because these people need care for their daily activities such as eating, taking medication, dressing, bathing, general healthcare, and physical therapy. As a result, less time is spent on activities that are usually less important to older adults, including oral care [7]. Moreover, financial restrictions, a lack of family support or transportation problems, and the unavailability of dental services can have harmful effects on the comfort, beauty, speech, chewing, and consequently the quality of life of older adults [8].
The World Health Organization has emphasized older adults’ need for adequate access to quality dental services [9]. However, dentists, who are responsible for maintaining the public’s oral health, have problems providing services to older adults. One of the most important issues is the lack of knowledge and practice in similar situations. Moreover, it has been shown that some factors, such as gender, age, and experience of the dentist, as well as the number of patients over 75 years of age visited by each dentist, can play a major role in reducing these problems [10]. The difficulties of performing dental treatment for older adults and treating various systemic diseases in these patients require adequate knowledge about correct behavior and an effective treatment plan for these patients. Accordingly, the present study aims to explore the knowledge, attitudes, and performance of dentists in providing care to elderly patients in Kerman in 2021.
Methods
Study design
This descriptive-analytical cross-sectional study was conducted on the dentists working in healthcare centers in five central, eastern, western, northern, and southern urban districts in Kerman in 2021. The dentists who had work experience of less than one year, dental students, and those who were not willing to participate in the study were excluded from the study.
Sample size and sampling method
Given the total number of general dentists working in the offices of health centers in Kerman, 150 dentists were selected using multistage random sampling. To increase the dispersion and accuracy of the data, and to address the cultural and social characteristics of the population of different regions of the city, the city was divided into five central, eastern, western, northern, and southern districts. Then, the dental clinics in each district were selected for sampling. Afterward, the participants were selected randomly based on the number of people under coverage in each clinic. Taking the 95% confidence interval, 0.5 error level, and 0.04 sampling accuracy, the sample size was estimated using the following formula [11]:
Data collection tool
The instrument used for data collection was a questionnaire consisting of two sections: The items in the first section assessed the participants’ demographic information, including gender, age, marital status, working hours, visits to elderly patients, the number of visits to elderly patients in the last week, and whether they had completed the geriatric dentistry course at the college. The second section measured the participants’ attitudes (17 items), performance (7 items), and knowledge (9 items). The items were scored on a 5-point Likert scale (strongly disagree = 1 to strongly agree = 5). Some items were also scored reversely. The minimum and maximum scores for the participants’ attitudes were 17 and 85, respectively. The participants’ performance was measured using items scored on a Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree, in a score range of 7 to 35. The participants’ knowledge was measured using items answered true, false, or I don’t know. A correct answer was scored 1, and the false answers and I don’t know were scored 0. The minimum and maximum scores for the participants’ knowledge were 0 and 9, respectively. The validity and reliability of the items were confirmed in previous studies [12,13,14].
Statistical analysis
The collected data were analyzed using the t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation and regression analysis with SPSS software (version 26). A significance level of 0.05 was considered for data analysis.
Results
Most of the participants were male (60%) and married (66%). Moreover, 66% of them had passed geriatric dentistry courses, and 65.3% of them had an older adult in the family. A majority of the participants (92.6%) stated that they had visited a nursing home, and some of them did not have daily visits from elderly patients (59.3%). In addition, 92.7% of the participants had visited elderly patients in the last week. The participants’ average age was 36.10 ± 7.60 years. Table 1 displays the participants’ demographic data: Table 1.
Geriatric oral health-related knowledge
The participants’ answers to knowledge questions are shown in Table 2. As can be seen, 84% of the participants gave a correct answer to the question “Root decay increases with age”. Besides, the percentage of correct answers to the statement “The prevalence of periodontal diseases increases with aging” was 74%. In addition, 66% of the participants correctly indicated that “most cases of dry mouth in older adults are directly related to the physiological changes of aging”. The least frequent correct answers (38%) were given to the item “Dislocation of the TMJ joint is one of the common complications of old age,” followed by the item “The use of local anesthesia with epinephrine is not restricted for older adults who use digoxin,” with 38.7% of the correct answers (Table 2).
Attitudes toward old age and the oral health of older adults
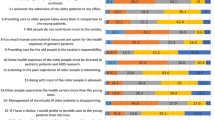
The data showed that 34.7% of the participants strongly agreed with the statement “It is the duty of the community to care for and support older adults” and 27.3% strongly agreed with the statement “In the future, general dentists should have the ability to treat older adults to provide the best possible care for the elderly population”. The participants’ answers to the attitude questions are shown in Table 3.
Performance related to older adults’ oral and dental health
Table 4 shows the participants’ responses to the performance questions. As can be seen, 54.7% of the participants agreed or strongly agreed that they communicate well with older adults. In addition, 66.6% of the participants stated that they could express empathy with and understand elderly patients. The data also indicated that 18.7% of the participants strongly agreed that they had received sufficient education in geriatric dentistry in college (Table 4).
The mean scores for the participants’ attitudes, performance, and knowledge were 59.42 ± 6.11, 24.13 ± 4.96, and 5.29 ± 1.49, respectively. In addition, the total score of the questionnaire was reported as 89.77 ± 8.96.
Pearson’s correction test showed a positive and significant relationship between the participants’ performance and the number of elderly visits. The participants who treated and visited more older adults had a better performance. A significant and positive relationship was observed between the participants’ knowledge, working hours, and graduation time. The total score of the questionnaire did not show a statistically significant relationship with any of the mentioned variables. More details are shown in Table 5.
Based on the results of t-test, Table 6 shows the relationship between the participants’ gender, marital status, taking geriatric dentistry courses in college, having older adults in the family, and visiting nursing homes with knowledge, attitudes, and performance (Table 6).
Based on findings of t-test results, Table 7 shows the relationship between the participants’ demographic variables and the total score on the questionnaire. As can be seen, the married dentists scored significantly higher than the single dentists (Table 7). In other cases, no statistically significant difference was observed.
An analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that the dentists who examined and treated more older adults performed significantly better (P = 0.001). Table 8 shows the results of the regression analysis using the backward method. As the data in this table indicated, higher levels of performance and knowledge and fewer working hours had a statistically significant relationship with more positive attitudes. Being married, having less time passed since graduation, passing dentistry courses, having an elderly person in the family, having a greater number of visits, and having more positive attitudes have significant correlations with better performance. Visiting more older adults, having more working hours, and having more positive attitudes have a significant positive relationship with a higher level of knowledge. The total score on the questionnaire had a statistically significant relationship with marital status, and a greater number of older adults visited (Table 8).
Data analysis showed that 18% of the participants had positive attitudes, 34% had good performance, and 19.3% had a high level of knowledge. Besides, the overall score was satisfactory for 18.7% of the participants, as shown in Fig. 1.
Discussion
The study found that general dentists in Kerman had poor attitudes, knowledge, and performance, affecting their ability to detect and prevent oral health issues in older adults. Regular visits are crucial for addressing these issues [15].
The present study showed that 19.3% of dentists had a high level of knowledge. A study by Alaei et al. [8] conducted on dentists participating in the Dental Congress in Tehran showed that 11.5% of dentists had an average level of knowledge. Similarly, Sargeran et al. [4] reported an average level of knowledge among dentists. Aldhuwayhi (2021) showed that dental students in Saudi Arabia failed to follow a positive approach to providing primary healthcare despite the rapid growth of the elderly population [16]. In their study in Croatia, Madunic et al. showed that dental studies should highlight higher levels of knowledge and skills in the treatment of older adults [17]. Tahani [14] also found that 2.6% of the dentists had a good level of knowledge. Hatami et al. found dental students have limited knowledge of geriatric dentistry. To improve patient care, geriatric dentistry courses should be developed to address the elderly population’s needs, including rehabilitation services for disabled individuals [13].
The present study indicated that 18% of dentists had positive attitudes toward older adults. Alaei et al. [8] reported that 39.7% of dentists had positive attitudes toward older adults. Moreover, Sargeran et al. [4] reported moderate attitudes among dentists. Other studies also reported similar results [15, 18, 19]. Given the increasing trend of the elderly population, dentists must receive sufficient training so that they can easily treat the oral and dental diseases of older adults. Since most of the problems in this field seem to be due to inadequate training and clinical experiences, it is possible to increase dentists’ positive attitudes and improve performance in oral health and care.
The data in the present study revealed that 34% of dentists had good performance. Sargeran et al. [4] reported that dental students had a moderate performance, and Hatami et al. [13] reported that the performance of dental students was low to moderate. Iran’s population structure changes necessitate examining population aging and raising awareness. Effective communication with older adults is crucial for providing oral and dental health services, emphasizing the importance of oral and dental hygiene.
The data in the present study showed a statistically significant relationship between performance and the completion of geriatric dentistry courses. In contrast, Alaei et al. [8] did not report a statistically significant difference between the attitudes and knowledge of dentists who completed or did not complete geriatric dentistry courses. Kossioni et al. [20] evaluated the status of geriatric dental education in some European dental schools and showed that the majority of universities have special modules and courses dedicated to older adults. Tahani et al. found Iran’s geriatric dentistry programs insufficient; teachers must choose effective teaching methods, with traditional and distance education contributing to dental course goals. Virtual education may replace traditional education in the future [14, 21].
In the present study, no statistically significant difference was observed between the dentists’ gender and their knowledge, attitudes, and performance, possibly due to uniform education in the field of geriatric dentistry. Similarly, Tahani [14] reported no significant difference between dentists’ attitudes and gender. However, a study by Bots-VantSpijker et al. [22] in the Netherlands and Belgium showed that female dentists had more positive attitudes toward older adults. These conflicting findings could be attributed to cultural and social factors governing the countries as well as the differences in the sample size.
The present study found no statistically significant relationship between dentists’ age and their knowledge, attitudes, and performance. In a similar vein, Alaei et al. [8] reported that dentists’ age and gender were not associated with knowledge and attitudes. However, this finding was not consistent with the results reported by Sargeran et al. [4], Bots-VantSpijker et al. [23], and De Visschere et al. [24] who reported a significant correlation between dentists’ gender and knowledge. Inconsistent results may be due to participants’ prior geriatrics courses, family involvement, and frequent visits to nursing homes. Refresher courses should incorporate geriatric dentistry materials.
The findings of the present study confirmed a statistically significant relationship between dentists’ knowledge and attitudes. Likewise, Tahani et al. [14] reported a significant correlation between dentists’ knowledge and attitudes. Rapid demographic changes have necessitated the inclusion of geriatric dentistry in the curriculum of many dental schools. There is a need for a greater focus on special clinical skills and changes in the attitudes of dental students toward caring for elderly patients. Geriatric dental education can be defined as “the part of the pre-doctoral curriculum that deals with the specific knowledge, attitudes, and technical skills required in providing oral healthcare for older adults” [25]. Dental schools should train students in dental management so that they are competent and confident in managing the treatment needs of elderly patients.
The study found a significant relationship between dentists’ attitudes and performance. To improve attitudes and treat older adults more effectively, policies and plans should be developed based on their characteristics and needs [26]. Raising awareness, offering training courses, and incorporating ICT training in online education and remote dentistry should be prioritized by health policymakers. Aging is a global accomplishment, and meeting the needs of older adults is crucial for active aging. Accurate needs assessments are necessary for effective planning, and psychological and physical needs should be considered in policies and programs related to elderly health. Dentists have positive attitudes towards older adults, but with the increasing elderly population, it is necessary to hold more refresher programs or workshops on geriatric dentistry [27].
Since the data in this study were collected using self-report questionnaires completed by dentists, some answers could be influenced by social desirability bias, which was out of the researcher’s control. Since the dentists working in Kerman participated in this research project, the results cannot be generalized to all dentists in Iran.
The department’s practical programs should require the training groups to include specialized instruction in elderly dentistry, and students should be required to treat and oversee this patient population at some time throughout their studies. Government, organization, and other governmental faculties, should work together in this manner. They should also consider to enhance dental care in this community and implement the required policies.
Conclusion
Following the findings of the present study, dentists in Kerman did not have good knowledge, performance, and attitudes toward geriatric dentistry. Thus, since geriatric dentistry courses have a small share in the basic science courses and higher academic levels for dental students, effective training and refresher programs on geriatric dentistry need to be organized to improve the knowledge, attitudes, and performance of dentists.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tayeri S, Jafari M, Alimohammadzadeh K, Hosseini SM, Shahanaghi K. A conceptual model for Iranian older women’s health: a review study. Iran J Ageing. 2021;16(3):304–29.
De Biasi A, Wolfe M, Carmody J, Fulmer T, Auerbach JJIA. Creating an age-friendly public health system. Innov Aging. 2020;4(1):igz044.
Kowal P, Chatterji S, Naidoo N, Biritwum R, Fan W, Lopez Ridaura R, et al. Data resource profile: the World Health Organization Study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE). Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41(6):1639–49.
Sargeran K, Mohebbi SZ, Tajik AJJDM. Evaluation of knowledge, attitude and practice of dentists about oral health of elderly in 2018. J Dent Med. 2021;34:1–10.
Paredes-Rodríguez V-M, Torrijos-Gómez G, González-Serrano J, López-Pintor-Muñoz R-M, López-Bermejo M-Á, Hernández-Vallejo GJJ, et al. Quality of life and oral health in elderly. J clin exp dent. 2016;8(5):e590.
Murray PE, Stanley HR, Matthews JB, Sloan AJ, Smith AJJOS. Age-related odontometric changes of human teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93(4):474–82.
Palati S, Ramani P, Shrelin HJ, Sukumaran G, Ramasubramanian A, Don K, et al. Knowledge, attitude and practice survey on the perspective of oral lesions and dental health in geriatric patients residing in old age homes. Indian J Dent Res. 2020;31(1):22.
Alaee A, Azizi A, Valaie NJJoM. Cultivation. DentistKnowledge and attitude about GeriatricsDentistry in 53rd Iranian Dental Association Congress (IDA). J Med Cultivation. 2017;25(2):57–70.
Mertz E, O’Neil E. The growing challenge of providing oral health care services to all americans. Health Aff. 2002;21(5):65–77.
Bots-VantSpijker PC, Bruers JJ, Bots CP, Vanobbergen JN, De Visschere LM, de Baat C, et al. Opinions of dentists on the barriers in providing oral health care to community‐dwelling frail older people: a questionnaire survey. Gerodontology. 2016;33(2):268–74.
Roshani D, Nouri B, Moradi M. Sample size determination in medical researches. Sci J Kurdistan Univ Med Sci. 2020;25(5):104–12. http://sjku.muk.ac.ir/article-1-5164-fa.html.
Reuben DB, Lee M, Davis JW Jr, Eslami MS, Osterweil DG, Melchiore S, et al. Development and validation of a geriatrics attitudes scale for primary care residents. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998;46(11):1425–30.
Hatami B, Ebn Ahmady A, Khoshnevisan M, Lando HA. Senior dental student’s attitudes toward older adults and knowledge of geriatric dental care in the Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J. 2013;19.
Tahani B, Manesh SS. Knowledge, attitude and practice of dentists toward providing care to the geriatric patients. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):1–9.
Wong FMF, Yannies TY, Ng, Leung WK. Oral health and its associated factors among older institutionalized residents—a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(21):4132.
Aldhuwayhi S. A comprehensive evaluation of knowledge and perceptions regarding geriatric dentistry among Saudi Arabian dental students: geriatric dentistry: Saudi students’ perspective. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2021;28(01):35–45.
Madunic D, Gavic L, Kovacic I, Vidovic N, Vladislavic J, Tadin A, et al. Dentists’ opinions in providing oral Healthcare to Elderly people: a questionnaire-based online cross-sectional survey. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(6):3257.
Zuluaga DJM, Ferreira J, Montoya JAG, Willumsen T. Oral health in institutionalised elderly people in Oslo, Norway and its relationship with dependence and cognitive impairment. Gerodontology. 2012;29(2):e420–e6.
McKeown L, Woodbeck H, Lloyd M. A journey to improve oral care with best practices in long-term care. Can J Den Hyg. 2014;48(2):57–62.
Kossioni A, McKenna G, Müller F, Schimmel M, Vanobbergen J. Higher education in Gerodontology in European universities. BMC Oral Health. 2017;17(1):1–12.
Tahani B, Khademi A, Fathollahi S, Promotion H. Status of geriatric education and meeting the standards of facilities in dental schools. J Educ Health Promot. 2019;8(1):163.
Bots-VantSpijker P, Bruers J, Bots C, De Visschere L, Schols J. Dentists’ opinions on knowledge, attitudes and barriers in providing oral health care to older people living independently in the Netherlands and Flanders (Belgium). Br Dent J open. 2017;3(1):1–8.
Bots-VantSpijker PC, Vanobbergen JN, Schols JM, Schaub RM, Bots CP, de Baat C. Barriers of delivering oral health care to older people experienced by dentists: a systematic literature review. Community Dent. 2014;42(2):113–21.
De Visschere L, Van Der Putten GJ, De Baat C, Schols J, Vanobbergen J. The impact of undergraduate geriatric dental education on the attitudes of recently graduated dentists towards institutionalised elderly people. Eur J Dent Educ. 2009;13(3):154–61.
León S, Araya-Bustos F, Ettinger RL, Giacaman RA. Geriatric dentistry content in the curriculum of the dental schools in Chile. Gerodontology. 2016;33(3):373–9.
Samouei R, Keyvanara M. Explaining the challenges of the Iranian Health System in the Face of Future Aging: qualitative study. Iran J Ageing. 2022;16(4):608–23.
Balooch Rafsanjani E, Morowatisharifabad MA, Jambarsang S, Mirzaei M. Health-related needs of older adults in Rafsanjan County, Kerman, Iran. J Ageing. 2022;17:232–45. (2).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all dentists who participate in the study for their warm support of this work.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FN and MK designed the study, FN, MK, MK and HH helped screen and included subjects, HH, FN processed the analysis data, RGH and FN wrote the manuscript, and reviewed and revised manuscript and all authors read and approved the final version of the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The objectives of the study were described to the dentists, and their informed consent to participate in the study was obtained. The present study was conducted based on a research proposal approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences with the ethics code IR.KMU.REC.1401.007.
Ethical considerations
To comply with ethical considerations in this study, the necessary permits were obtained before collecting data and distributing questionnaires. A trained interviewer collected the data. The questionnaires were distributed and collected three days a week at medical centers and clinics. After completing a questionnaire, it was placed in a folder, and if the dentist wished, the answers to the knowledge questions were provided to them. Furthermore, the researchers provided necessary explanations to the dentists regarding their voluntary participation, the freedom to withdraw from the study, the confidentiality of the data obtained from them, and the anonymity of the questionnaires.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Nouri, F.N., Afshar, M.K., Afshar, M.K. et al. Exploring the knowledge, attitudes, and performance of dentists in providing care to elderly patients. BMC Oral Health 24, 62 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-023-03832-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-023-03832-z