Abstract
Background
The “International Hip Outcome Tool 12” (iHOT12) is a self-administered patient-reported outcome tool for measuring health-related quality of life and physical functioning in young and active patients with hip pathology. Since the iHOT12 has become widely used, we sought to translate and validate it for Hebrew-speaking populations. The aims of this study were: (1) To translate and culturally adapt the iHOT12 into Hebrew using established guidelines. (2) To test the new Hebrew version for validity, and (3) reliability.
Methods
The iHOT12 was translated and culturally adapted from English to Hebrew (iHOT12-H) according to the COSAMIN guidelines. For validity, the iHOT12-H and Western Ontario and McMaster universities osteoarthritis index (WOMAC) were completed by 200 patients with hip pathology. Exploratory factor analysis was used to assess structural validity. Subsequently, 51 patients repeated the iHOT12-H within a 2-week interval. Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC), Cronbach alpha, and Standard Error of Measurement (SEM) were calculated to assess reliability.
Results
Construct validity: iHOT12-H correlated strongly to the WOMAC scores (r = -0.82, P < 0.001, Spearman). Factor analysis revealed a two-factor structure. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.953 confirming internal consistency to be highly satisfactory. Test–retest correlation of the iHOT12-H was excellent with an ICC = 0.956 (95% CI 0.924–0.974). There was no floor or ceiling effect.
Conclusion
The iHOT12 Hebrew version has excellent reliability, good construct validity and can be used as a measurement tool for physical functioning and quality of life in young, physically active patients with hip pathology. This study will serve Israeli researchers in evaluating treatment effectiveness for these patients. Moreover, it will also enable multinational cooperation in the study of hip pathology.
Highlights
• The International Hip Outcome Tool 12 was translated into Hebrew (iHOT12-H).
• The iHOT12-H showed comparable psychometric properties to the original version.
• The iHOT12-H is a valid and reliable questionnaire for people with hip-related pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Background
Hip-related pain is known to be a major contributor to years lived with disability [1], causing functional loss and low patient-reported outcomes scores in many young and active people [2, 3]. In recent years, as hip arthroscopic technology has evolved, there has been a significant increase in diagnosis and surgical management for different hip pathologies in younger populations around the world [4, 5].
To assess the impact of hip pathologies and to measure the effect of hip arthroscopic surgery and conservative management, it is important to use health related patient reported outcome measurements (HR-PROM’s) [6]. HR-PROM’s are questionnaires completed by patients to measure their subjective perception of their health, pain and function about a specific condition. Thus, they have been recognized as important tools in assessing conservative and surgical management effects on different Musculoskeletal conditions [6].
Several HR-PROM’S have been developed over the years to evaluate different lower limb and hip-related disorders [7, 8]. However, most of these questionnaires were originally developed to assess older patients with osteoarthritis or undergoing hip arthroplasty [7,8,9,10]. As young and active patients undergoing hip arthroscopy have different expectations and goals, Throborg et al. recommended to reconsider their applicability for this population [11, 12]. The 33-item International Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT33) developed by Mohtadi et al. has addressed this limitation as it was developed to assess young active patients with hip joint disorders [13]. This questionnaire showed high validity and reliability in measuring physical functioning and quality of life among young, physically active patients with hip-related pain. Based on the iHOT33, Griffin et al. [14] developed a shorter version (iHOT12), which has proved to have good validity, reliability, and responsiveness to change [14]. Due to its high psychometric properties, the iHOT12 has been translated into many languages, including Portuguese [15], Swedish [16], Dutch [17], German [18], Japanese [19], Turkish [20, 21], Greek [22], and French [23]. The iHOT12 has not yet been translated and culturally adapted into Hebrew. The aims of this study were to: 1) to translate the English version of the iHOT12 into Hebrew and to adapt it culturally to a Hebrew speaking population; 2) to test the new Hebrew version for validity and reliability.
Methods
Study design
The translation to Hebrew and the validation process of the translated iHOT12 were conducted between September 2020 to December 2021. The process consisted of two steps: 1) translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the English iHOT12 into Hebrew; 2) evaluation of the psychometric properties of the iHOT12-Hebrew version (iHOT12-H): internal consistency, test–retest reliability, standard error of measurement (SEM), floor and ceiling effects, and construct validity of the iHOT12-H with the Western Ontario and McMaster universities Osteoarthritis index (WOMAC). The study was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of Assuta Medical Center (23.8.2020/0007–20-ASMC)”.
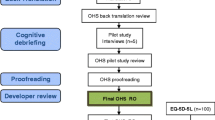
Translation of the iHOT12
The translation was performed with the permission of the original author of the iHOT12 [14]. The iHOT12 was translated into Hebrew and culturally adapted according to the Consensus-based Standards for the selection of health measurement instruments (COSMIN) guidelines for best practice in questionnaire translation including five stages [24]. In stage 1 (translation), the English version of the iHOT12 was translated to Hebrew by two Hebrew native speakers (two independent versions) who were also fluent in English; an orthopedic surgeon (with over 20 years of experience) and a physiotherapist with a PHD degree (with more than 15 years of experience). A third translator was a professional translator, meeting the need for a translator who is not a health provider, naïve to the questionnaire’s concepts. Backward translation was performed by two bilingual native English speakers, who independently translated the Hebrew version of the iHOT12 back into English. Both were naïve to the questionnaire’s concepts. An expert committee consisted of an orthopedic doctor specializing in musculoskeletal conditions (and their measurement) in pain population research (MD, MHA), a physiotherapist and pain researcher experienced with a cross-cultural adaptation of questionnaires (PhD, PT), and a physiotherapist with over 20 years’ experience in the public and private sector. Subsequently, the investigator and the same experts team came to an agreement on the pre-final version of the iHOT12-H.
The pre-final version of the iHOT12-H was tested on a group of patients with various hip pathologies (N = 30). As no changes were found necessary, the pre-final version was chosen as the final version of the iHOT12-H (Additional file 1).
Participants
Patients attending hip clinics of the 3rd and 4th authors were asked to participate in the study. Inclusion criteria were: men and women, between 18 and 60 years of age, who suffered from hip pain. Following informed consent, they completed the iHOT12-H and WOMAC questionnaires.
Measurement instruments
The iHOT12-H
The English iHOT12 is a valid and reliable disease-specific questionnaire that measures physical function and health-related quality of life in a younger patient population with hip pathology [14]. The iHOT12 consists of 12 questions with a 100-mm visual analog scale. Each question has equal weight and is scored between 0 (maximum limitation) and 100 (full function). The final score is calculated as the mean of all questions ranging from 0 to 100. Higher scores reflect better physical functioning and better health-related quality of life [14]. Missing values are ignored, and the score is the mean of the existing values. The validation evaluation of the iHOT12 showed good agreement between the iHOT12 to the iHOT33, with regression analysis showing that the iHOT12 accounted for 95.9% (95% CI, 95.0% to 96.8%) of the variation in the iHOT33. The test–retest reliability was found to be good, with an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.89 (95% boot-strapped CI, 0.83 to 0.93) [14].
The WOMAC
The WOMAC is a 24-item questionnaire. A valid and reliable Hebrew version is available [25]. Subjects rate their level of suffering using a visual analogue scale (10 cm VAS) where 0 represents no suffering while 10 represents high level of suffering. The results were standardized to a scale of 0 to 100 and the final scores were the mean of the 24 items. The validation evaluation of the WOMAC showed significant correlations (p < 0.01) between the WOMAC items and visual analog scale (VAS) of pain and handicap. The test–retest reliability Pearson’s correlation coefficients for the WOMAC items ranged from 0.55 to 0.78 (p < 0.01), and the Cronbach’s alpha ranged between 0.97 (time 1) and 0.98 (time 2) [25].
Procedures
Validity
Construct validity is the extent to which the results of the translated questionnaire correlate with results of other questionnaires that measure the same construct [24]. In this study, we evaluated the magnitude of relationships between the iHOT12-H and the WOMAC questionnaires.
Reliability
To describe reliability of the iHOT12-H we assessed internal consistency, measurement error, and test–retest reliability. For test–retest reliability, 51 patients completed the iHOT12-H twice within a 2-week interval. Participants were also asked whether they had improved or worsened over the past two weeks and were included only if symptoms had not changed. This time interval was considered adequate to prevent the patients from remembering their answers (“recall bias”), and short enough to ensure that clinical change had not occurred.
Sample size
For validity, the input parameters were as follows: assuming a modest effect size of 0.3, α = 0.05 and β = 0.9, considering loss of 10% subjects, the total sample size recommended was at least 126 patients. For test–retest reliability we assumed that the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) score will be more than 0.8, with a power of 0.8, the sample size recommended was of 51 patients.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics software, version 28.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY). Normal distribution of all data was assessed by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Patient characteristics were analyzed by means of descriptive statistics. A P value less than 0.05 (P < 0.05) was used to indicate statistical significance.
Reliability
Reliability is the degree to which the measurement is free from measurement error [24]. To evaluate reliability, internal consistency, test–retest reliability, and measurement error were calculated [26].
Internal consistency
For internal consistency we calculated Cronbach’s alpha, with the following ratings: weak correlation: 0–0.50, medium: 0.50–0.75, very good: 0.75–0.90, and excellent: > 0.90 [26].
Test–retest reliability
For test–retest reliability we used intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), implementing the two-way mixed effect test–retest absolute agreement method. The ICC values were as follows: poor: < 0.40, fair: 0.40–0.59, good: 0.60–0.74, and excellent: 0.75–1.00 [27]. Interpretability and repeatability refer to the degree to which one can assign qualitative meaning to quantitative scores [24]. It was determined by calculating floor and ceiling effects, which are present if more than 15% of respondents have the lowest or highest possible score [26].
Measurement error
The standard error of measurement (SEM) was calculated using the formula \(\mathrm{SEM}=\mathrm{SD}\times \sqrt{1-\mathrm{ICC}}\), where SD = standard deviation [26].
Validity
To validate the Hebrew translation of the iHOT12, it was compared to the WOMAC scores using the Spearman correlation coefficient (not all outcomes were normally distributed). The accepted grading criteria were used: 0 to 0.39 weak correlation, 0.40 to 0.59 medium correlation:, and 0.6 to 1.0 strong correlation [28].
Factor analysis
The structural validity of the iHOT12-H questionnaire was examined using exploratory factor analysis (EFA). This analysis employed a maximum likelihood extraction method with varimax rotation to identify the latent factor structure of the questionnaire. Initially, to assess the appropriateness of the data to factor analysis, Bartlett’s sphericity and the Kaiser–Meyer–Oklin (KMO) tests were applied. Factors with eigenvalues exceeding 1 and items with factor loadings of 0.40 or higher were retained. Additionally, a scree plot was used to determine the optimal number of factors in the questionnaire [29].
Results
Participants
The final data analysis of the cross-cultural translation, adaptation, and validation research of the iHOT12-H provided a total sample size of 200 patients (110 females, 55%). The mean age was 39.8 with standard deviation (SD) of 13.0. Mean scores and standard deviation are shown in Table 1.
Translation and cross-cultural adaptation
During the forward/backward translations, we found only minor linguistic differences: answers for items 1 and 7 (“extreme pain”), and item 4 (“grinding” and “catching”). The answer for items 1 and 7 of “extreme pain” was different between the three forward versions “significant pain”. After discussing this in the expert committee, we agreed that the translation of “significant pain” suited the source better. The translation proposed for item 4 was challenging because not all patients understood the words “grinding” and “catching”. However, during examination of the pre-final version with patients suffering from hip pain it seemed that people without those symptoms, were those who didn’t understand the translated terms of “grinding” and “catching”, but subjects with those feelings immediately understood what the terms meant.
iHOT12-H psychometric properties: test–retest reliability
Internal consistency for the iHOT12-H was excellent with Cronbach’s α = 0.953. The final test–retest reliability sample included 51 participants. However, for the ICC calculation of question number 9, only 46 participants were included. This question (“how much trouble do you have with sexual activity because of your hip”) was marked “not relevant for me” by 5 participants. Thus, those were excluded from the ICC calculation. The iHOT12-H translated version demonstrated excellent test–retest reliability with ICC = 0.956, 95% Confidence interval (CI) (0.924–0.974). Standard Error of Measurement (SEM) was calculated using the ICC values as described elsewhere [26]. Each item’s ICC and SEM are shown in Table 2. No floor or ceiling effects were found.
Construct validity
Construct validity was evaluated with correlation analysis between the mean results of the iHOT12-H and the WOMAC scores. We used Spearman’s correlation coefficients as most of the questionnaires’ total scores were non-normally distributed. We found a good negative correlation of r = -0.82 (P < 0.001) between the iHOT12-H and the WOMAC scores (these scales are orientated in opposite directions, Fig. 1).
Factor analysis
The Bartlett test of sphericity yielded significant results (Chi square = 1217.73, p < 0.001), affirming the suitability of the data for factor analysis. Additionally, the KMO measure of sampling adequacy stood at 0.92, indicating the dataset’s appropriateness for this analysis. Through the examination, two distinct factors emerged, each with eigenvalues surpassing 1 and item factor loadings ≥ 0.40. Specifically, the first factor accounted for 30.2% of the variance, while the second factor explained 26.5% (with eigenvalues of 3.6 and 3.2, respectively). This two-factor structure was further supported by the scree plot (Fig. 2). Detailed factor loadings can be found in Table 3.
Discussion
This study aimed to translate and culturally adapt the iHOT12 to Hebrew and test its psychometric properties. From this study it can be concluded that the translation procedure of the English iHOT12 was successful. The results of this study show that the iHOT12-H is a reliable, internally consistent, and valid measurement tool to assess physical functioning and quality of life in an Israeli population of young, physically active individuals between 18 to 60 years of age with hip-related pain.
Hip related pain has become one of the most commonly diagnosed musculoskeletal conditions in young and active adults, leading to increased hip arthroscopic surgery rates. However, until recently, there has been a lack of standardized patient-reported outcome measures for this specific population. The iHOT33, and consequently the iHOT12, have addressed this limitation. The favorable psychometric characteristics of the iHOT12 and the relatively short time for application enables it to be used in research as well as in daily clinical practice. Furthermore, a few systematic reviews questioning which patients reported outcome measures are most responsive in this patient population further reinforce the validity of the iHOT12 in assessing outcome for treatment of young and active patients [9, 30, 31].
Study population
Our demographic data included men and women with an average age of 39.8 ± 13.0. Thus, they are comparable with the average age used in the original study of the development of iHOT12 conducted by Griffin et al. [14]. In our study, to have a more heterogenous patient sample, we did not preselect patients according to their diagnosis or intended treatment. Two of the previous translation and validation studies of the iHOT12 evaluated only patients with Femoro-acetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS) [16, 19]. This may have negatively affected the external validity of their study.
Reliability
The overall assessment of the iHOT12-H yielded remarkably high values. These results prove the quality of the iHOT12-H version and confirm the results of previous validation studies on the iHOT12 [9, 13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20, 22, 23]. The iHOT12-H showed good internal consistency, with a Cronbach alpha of 0.953. This result is comparable with the Cronbach alpha values evaluated in prior studies: Swedish (α = 0.89) [16], Dutch (α = 0.96) [17], German (α = 0.94) [18], Japanese (α = 0.90) [19], Turkish (α = 0.93) [20], and Greek (α = 0.92) [22] versions of the iHOT12. The fact that in the present study we found a Cronbach alpha higher than 0.95, may indicate that the items in this questionnaire are almost the same construct [24]. Future studies may look at the possibility of removing some of the items of the iHOT12.
The iHOT12-H showed excellent test–retest reliability, with an ICC of 0.956 (95% CI 0.924–0.974), which is comparable with the ICC of the English (ICC = 0.89) [14], Swedish (ICC = 0.88) [16], Dutch (ICC = 0.93) [17], German (ICC = 0.94) [18], Japanese (ICC = 0.89) [19], Turkish (ICC = 0.93) [20] and Greek (ICC = 0.98) [22] versions. The French version of the iHOT12 showed lower values of ICC (ICC = 0.84) [23], but these values are still categorized as good test–retest reliability [27].
Validity
For the evaluation of construct validity, we chose the WOMAC questionnaire, as it was hip-specific and validated questionnaire in the Hebrew language [25]. We found strong correlation between the iHOT12-H and the WOMAC score (r = -0.82, P < 0.001). To our knowledge, these relationships have been investigated previously only by Attila et al. [20], who found a similar correlation between the iHOT12-T and the WOMAC score (r = 0.815, P < 0.001) [20]. All other studies evaluating the validity of the iHOT12 following a procedure of translation used a variability of PROM forms as the gold standard [14, 16,17,18,19, 22, 23]. Li et al. [32] evaluated the correlation between the iHOT33 and the WOMAC score and found similar correlation coefficient (r = 0.812) to our results.
Factor analysis
The factor analysis of the iHOT12-H revealed a two-factor structure: Factor-1 (items 1–5, 7–9) refers to “symptoms and functionality”, while Factor-2 (items 6, and 10–12) refers to “hip related concerns”. The original English version of the iHOT12 has a single factor structure [14]. Likewise, the Dutch and one of the Turkish versions reveled a one-factor structure [17, 20]. However, the Swedish version showed two factors, but with different factor loadings than ours: Factor-1 “Function and symptoms” (items 2–5, 8, 9) and Factor-2 “pain and concern/destruction” (items 1, 6, 7, 10–12) [16]. Another study of a Greak version showed two factors quite similar to our results: factor-1 “symptoms and functionality” (items 1–9) and Factor-2 “hip disorder-related concerns” (items 10–12) [22]. Interestingly, we found a second study validating a Turkish version who revealed 3 factors: “Symptom and functional limitations” (items 1–4), “Social, emotional and lifestyle” (items 8–12), and “Sports and recreational activities” (items 6, 7, 11) [21]. Factor-model variations may result from cross-cultural factors, or from age-related quality of life concerns, as the mean age of the studied population varies among studies [17, 20,21,22]. For the Portuguese, German, Japanese and French versions, no factor analysis has been conducted [15, 18, 19, 23].
Limitations
Despite very good results concerning validity and reliability, there are a few limitations in this study. First, we included patients with different levels of activity but we did not evaluate the exact activity level of our patients using the Tegner Activity Scale as was evaluated in some of the previous studies [17,18,19]. Thus, future research comparing between different levels of activity of patients is therefore necessary to determine whether the iHOT12 is applicable to such a variety of patients. Secondly, the study sample included patients with a variety of hip pathologies. Including a heterogenous population may also increase the external validity of this study. Thirdly, since the iHOT33 questionnaire has not been officially translated into the Hebrew language we were unable to assess the criterion-related validity of iHOT12-H [24]. Finally, responsiveness was not determined in this study, therefore we could not evaluate the exact minimal important change values. Additional research is needed to determine whether the iHOT12-H is a responsive instrument as was shown in previous studies [16, 18, 19, 22]. Further prospective studies are needed to assess the clinical impact of iHOT12 on patients with hip related pain who underwent conservative management or surgical treatment. Such studies will advance our understanding of the therapeutic processes among those patients and will provide benefits both in clinical practice and in research.
Conclusions
The iHOT12-H is a reliable and valid measurement tool for measuring physical functioning and quality of life in young, physically active patients with hip related pain. This is extremely important, as previous tools are less suitable for this young population. We believe that this HR-PROM is beneficial in assessing the condition of Israeli patients with hip related pain.
Availability of data and materials
This study contains all of the study data related to these findings. Requests for mor information about data sharing should be directed to the correspondence author via ys3@mail.tau.ac.il.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- COSMIN:
-
Consensus-based Standards for the selection of health measurement instruments
- EFA:
-
Exploratory factor analysis
- FAIS:
-
Femoro-acetabular impingement syndrome
- HR-PROM’s:
-
Health related patient reported outcome measurements
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- iHOT12 :
-
International hip outcome tool 12
- KMO:
-
Kaiser–Meyer–Oklin
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SEM:
-
Standard error of measurement
- VAS:
-
Visual analogue scale
- WOMAC:
-
Western Ontario and McMaster universities Osteoarthritis index
References
Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2163–96.
Griffin DR, Dickenson EJ, O’Donnell J, Agricola R, Awan T, Beck M, et al. The Warwick Agreement on femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI syndrome): an international consensus statement. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(19):1169–76.
Reiman MP, Agricola R, Kemp JL, Heerey JJ, Weir A, Van Klij P, et al. Consensus recommendations on the classification, definition and diagnostic criteria of hip-related pain in young and middle-aged active adults from the International Hip-related Pain Research Network, Zurich. Br J Sports Med. 2018;2020:631–41.
Hale RF, Melugin HP, Zhou J, LaPrade MD, Bernard C, Leland D, et al. Incidence of femoroacetabular impingement and surgical management trends over time. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(1):35–41.
Colvin AC, Harrast J, Harner C. Trends in hip arthroscopy. J Bone Jt Surg - Ser A. 2012;94(4):e23.
Martin RL, Mohtadi NG, Safran MR, Leunig M, Martin HD, McCarthy J, et al. Differences in physician and patient ratings of items used to assess hip disorders. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(8):1508–12.
Nilsdotter AK, Stefan Lohmander L, Klässbo M, Roos EM, Lohmander LS. Hip disability and osteoarthritis outcome score (HOOS) – validity and responsiveness in total hip replacement. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2003;8:1–8.
Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Murray D, Carr A. Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about total hip replacement. J Bone Jt Surg - Ser B. 1998;80(1):63–9.
Kemp JL, Collins NJ, Roos EM, Crossley KM. Psychometric properties of patient-reported outcome measures for hip arthroscopic surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(9):2065–73.
Gasparin GB, Frasson VB, Fritsch CG, Morales A, Vaz MA, Baroni BM. Are the Harris hip score and the hip outcome score valid patient-reported outcome measures for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome? Braz J Phys Ther. 2022;26(4):100422.
Huch K, Müller KAC, Stürmer T, Brenner H, Puhl W, Günther KP. Sports activities 5 years after total knee or hip arthroplasty: the Ulm osteoarthritis study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(12):1715–20.
Thorborg K, Roos EM, Bartels EM, Petersen J, Hölmich P. Validity, reliability and responsiveness of patient-reported outcome questionnaires when assessing hip and groin disability: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(16):1186–96.
Mohtadi NGH, Griffin DR, Pedersen ME, Chan D, Safran MR, Parsons N, et al. The development and validation of a self-administered quality-of-life outcome measure for young, active patients with symptomatic hip disease: the International Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT-33). Arthrosc - J Arthrosc Relat Surg. 2012;28(5):595–610.e1.
Griffin DR, Parsons N, Mohtadi NGH, Safran MR. A short version of the International Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT-12) for use in routine clinical practice. Arthrosc - J Arthrosc Relat Surg. 2012;28(5):611–8.
Polesello GC, Godoy GF, De Castro Trindade CA, De Queiroz MC, Honda E, Ono NK. Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the modified hip outcome tool (mhot) into portuguese. Acta Ortop Bras. 2012;20(2):88–92.
Jónasson P, Baranto A, Karlsson J, Swärd L, Sansone M, Thomeé C, et al. A standardised outcome measure of pain, symptoms and physical function in patients with hip and groin disability due to femoro-acetabular impingement: cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the international Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT12) in Swedish. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(4):826–34.
Stevens M, Van Den Akker-Scheek I, Ten HB, Adema M, Giezen H, Reininga IHF. Validity and reliability of the Dutch version of the international Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT-12NL) in patients with disorders of the hip. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2015;45(12):1026–34.
Baumann F, Popp D, Müller K, Müller M, Schmitz P, Nerlich M, et al. Validation of a German version of the International Hip Outcome Tool 12 (iHOT12) according to the COSMIN checklist. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016;14(1):1–10.
Watanabe N, Murakami S, Uchida S, Tateishi S, Ohara H, Yamamoto Y, et al. Exploring the validation of a Japanese version of the international hip outcome tool 12: reliability, validity, and responsiveness. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(4):652–7.
Atilla H. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the turkish version of the international hip outcome tool – 12. SiSli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul / Med Bull Sisli Hosp. 2020;54(4):483–9.
Özge İ, Bayar K, And BB-J of ET, 2019 U. Turkish version of International Hip Outcome Tool (IHOT12T): validity and reliability study. J Exerc Ther Rehabil. 2019;6(3):211–9.
Stasi S, Stamou M, Papathanasiou G, Frantzeskaki P, Kanavas E, Evaggelou-Sossidis G, et al. International Hip Outcome Tool (12-items) as health-related quality-of-life measure in osteoarthritis: validation of Greek version. J Patient-Reported Outcomes. 2020;4(1):41.
Dion MO, Simonyan D, Faure PA, Pelet S, May O, Bonin N, et al. Validation of the French version of the Self-Administered International Hip Outcome Tool-12 Questionnaire and determination of the Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) in the French speaking population. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(8):1–6.
Mokkink LB, Terwee CB. The COSMIN checklist for assessing the methodological quality of studies on measurement properties of health status measurement instruments : an international Delphi study. Qual Life Res. 2010;19:539–49.
Wigler I, Neumann L, Yaron M. Validation study of a Hebrew version of WOMAC in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18(5):402–5.
Terwee CB, Bot SDM, de Boer MR, van der Windt DAWM, Knol DL, Dekker J, et al. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(1):34–42.
Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15(2):155–63.
Mukaka MM. Statistics corner: a guide to appropriate use of Correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med J. 2012;24:69–71.
Feild A. Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics. 5th ed. London: SAGE Publications; 2018.
Stone AV, Jacobs CA, Luo TD, Meadows MC, Nho SJ, Stubbs AJ, et al. High degree of variability in reporting of clinical and patient-reported outcomes after hip arthroscopy. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(12):3040–6.
Thorborg K, Tijssen M, Habets B, Bartels EM, Roos EM, Kemp J, et al. Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) questionnaires for young to middle-aged adults with hip and groin disability : a systematic review of the clinimetric evidence. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49:812.
Li DH, Wang W, Li X, Gao YL, Liu DH, Liu DL, et al. Development of a valid Simplified Chinese version of the International Hip Outcome Tool (SC-iHOT-33) in young patients having total hip arthroplasty. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2017;25(1):94–8.
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend our deepest gratitude to Assuta Medical Center for providing ethical permission for this study. We would also like to thank the translators, supervisors and study participants for their assistance and participation.
Funding
All authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Data collection was done by Itamar Botser, David Morgenstern and Yael Steinfeld Mass. Material preparation and analysis were performed by Noa Ben-Ami, Aharon Finestone and Yael Steinfeld Mss. The first manuscript draft was written by Yael Steinfeld Mass. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was given by the Ethics Committee of Assuta Medical Center (23.8.2020/0007-20-ASMC). All patients had given their written informed consent to participate in this study. Furthermore, the data collectors and investigators ensured the privacy and confidentiality of information.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
The Hebrew version of the iHOT12.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Steinfeld-Mass, Y., Ben-Ami, N., Botser, I. et al. Cross-cultural adaptation, validation and psychometric evaluation of the International Hip Outcome Tool 12 (iHOT12) to Hebrew. Health Qual Life Outcomes 21, 127 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-023-02203-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-023-02203-0