Abstract
The advancement in extraterrestrial exploration has highlighted the crucial need for studying how the human cardiovascular system adapts to space conditions. Human development occurs under the influence of gravity, shielded from space radiation by Earth’s magnetic field, and within an environment characterized by 24-hour day-night cycles resulting from Earth’s rotation, thus deviating from these conditions necessitates adaptive responses for survival. With upcoming manned lunar and Martian missions approaching rapidly, it is essential to understand the impact of various stressors induced by outer-space environments on cardiovascular health. This comprehensive review integrates insights from both actual space missions and simulated experiments on Earth, to analyze how microgravity, space radiation, and disrupted circadian affect cardiovascular well-being. Prolonged exposure to microgravity induces myocardial atrophy and endothelial dysfunction, which may be exacerbated by space radiation. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress emerge as key underlying mechanisms along with disturbances in ion channel perturbations, cytoskeletal damage, and myofibril changes. Disruptions in circadian rhythms caused by factors such as microgravity, light exposure, and irregular work schedules, could further exacerbate cardiovascular issues. However, current research tends to predominantly focus on disruptions in the core clock gene, overlooking the multifactorial nature of circadian rhythm disturbances in space. Future space missions should prioritize targeted prevention strategies and early detection methods for identifying cardiovascular risks, to preserve astronaut health and ensure mission success.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Since the inception of the Mercury program more than six decades ago, over 600 astronauts have participated in space missions lasting up to 438 d. The International Space Station (ISS) has been operating within Low Earth Orbit (LEO) for more than twenty years as global space agencies aim for extended lunar and Martian expeditions. Nevertheless, deep-space missions present unique challenges compared to those experienced within LEO such as microgravity, radiation exposure, and circadian rhythm disruptions, which require thorough evaluation and management [1, 2]. Microgravity and low gravity on lunar or Martian surfaces can lead to adaptive changes in cardiovascular physiology, including myocardial atrophy and arterial wall thickening [3]. Conversely, microgravity may trigger gene expression similar to early developmental stages in cardiovascular cells, potentially facilitating myocardial regeneration [4]. Furthermore, astronauts face heightened exposure to intense space radiation comprising high-energy heavy ions [known as high charge and energy nuclei (HZE particles)] as well as protons due to lack of Earth’s magnetic shield, leading to potential vascular dysfunction along with ischemic cardiac remodeling [3]. Moreover, disturbances in the circadian rhythm caused by changes in daily schedules, lack of sleep, and other factors can collectively lead to alterations in cardiac morphology, structure, and function [5, 6].
Regardless of mission duration, evaluations of relevant physiological parameters and the implementation of risk mitigation strategies, including those associated with exercise, have been widely adopted. This review outlines the potential mechanisms driving cardiovascular structural and functional changes during spaceflight and discusses possible interventions for managing the space environment and promoting cardiovascular recovery.
Microgravity-induced degenerations in cardiovascular structure and function
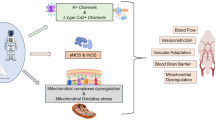
Over the past few decades, a multitude of cardiovascular abnormalities associated with microgravity have been identified, including myocardial atrophy [7], systolic and diastolic dysfunction [8], and vascular dysfunction [9]. Headward fluid shifts mediated by unloading in microgravity are correlated with enhanced systolic function during short-term or early stages of long-term spaceflight [10]. However, prolonged exposure to microgravity can induce cardiac atrophy through alterations in ion channel expression or activity and downstream signaling pathways in cardiomyocytes, as well as myofiber and extracellular networks, accompanied by oxidative stress, ultimately resulting in impaired cardiac function (Fig. 1a) [11,12,13]. Moreover, microgravity can induce changes in vascular structure and function, and endothelial cells (ECs) are particularly sensitive to hemodynamic variations [14, 15]. Microgravity may trigger vascular wall inflammation by modulating gene expression related to cell adhesion and oxidative stress in ECs and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), leading to arterial wall thickening and stiffness that contribute to vascular dysfunction (Fig. 1b) [16, 17]. Furthermore, microgravity can enhance the expression and activity of EC nitric oxide synthase (NOS), thereby augmenting vascular relaxation [18]. Table 1 [7, 10,11,12, 17, 19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50] compares the potential differences in the cardiovascular system at the functional, structural, and molecular levels between short- and long-term spaceflight.
Molecular mechanisms of cardiovascular dysfunction induced by microgravity and possible countermeasures. a Cardiac change under microgravity. Microgravity leads to cardiac atrophy and myofibril change, with the Ca2+-CaMKII-HDAC4 axis playing a central role. Increased intracellular Ca.2+ activates CaM and CaMKII, leading to HDAC4 phosphorylation. Phosphorylated HDAC4 translocates to the cytoplasm, relieving its inhibitory effect on MEF2C and causing cardiac atrophy. Furthermore, oxidative stress is increased in mitochondria and cytoskeleton. Potential countermeasures include SGLT2 inhibitors that suppress CaMKII phosphorylation, as well as compounds like I3C and Ivabradine targeting WWP1 and PP2A, respectively. b Vascular alterations in microgravity. Microgravity induces arterial thickening as well as EC and VSMC dysfunction. ROS generation is a key mediator, with NOX enzymes contributing to oxidative stress. Mitochondrial dysfunction further amplifies ROS production, leading to cellular damage and mitophagy. Therapeutic strategies such as DPP-4i, GLP-1RA, and MitoQ. β-AR β-adrenergic receptor, CaM calmodulin, CaMKII calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase II, cAMP cyclic adenosine monophosphate, CKIP-1 casein kinase 2 interacting protein-1, DPP-4i dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, DVL2 dishevelled segment polarity protein 2, EC endothelial cell, ECM extracellular matrix, ER endoplasmic reticulum, GLP-1RA glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, HDAC4 histone deacetylase 4, HDAC4-NT N-terminal proteolytic fragment of HDAC4, I3C indole-3-carbinol, ICAM-1 intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1, LTCC L-type calcium channels, MEF2C myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C, MitoQ mitoquinone, NOX NADPH oxidase, PKA protein kinase A, PP2A protein phosphatase 2A, ROS reactive oxygen species, SGLT2i sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, VCAM-1 vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1, VSMC vascular smooth muscle cell, WWP1 WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1
Insights into cardiac functional changes: atrophic remodeling
Extensive degenerative changes in cardiac structure caused by microgravity have been extensively documented. Initial research conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) using chest X-rays revealed a decreased cardiothoracic ratio in 80% of Apollo astronauts [51]. However, the limitations of X-ray diagnostics, such as sensitivity to body position and respiration, and the inability to detect alterations in cardiac systolic and diastolic function, constrain their utility in evaluating cardiac health and heart failure (HF) [52]. Subsequent use of echocardiography offered a more precise assessment of left ventricle (LV) morphology and function in Skylab astronauts, demonstrating reductions in left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVEDD), stroke volume (SV), and mass upon return to Earth [53]. Perhonen et al. [7] confirmed similar findings using cardiovascular magnetic resonance, observing a decrease in LV mass among astronauts and bed-rest patients, suggesting that morphological atrophy of the heart occurs under the influence of microgravity.
Prolonged spaceflight has been associated with reduced cardiac systolic and diastolic functions [54]. Shibata et al. [30] utilized photoplethysmography to record 24-hour finger blood pressure waveforms and estimate SV and total cardiac output (CO), reporting a decrease in SV and 24-hour total CO after 4–6 months of spaceflight. However, these values did not differ significantly from pre-flight levels. In contrast, Herault et al. [20] observed a significant reduction in CO at 1, 3, and 5 months of flight using echocardiography and calculations based on heart rate (HR). These discrepancies may arise from different measurement methods, highlighting the necessity for more precise techniques to monitor cardiac performance. The left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), early to late diastolic transmitral flow velocity (E/A), and early diastolic transmitral flow velocity to early diastolic mitral annular tissue velocity (E/E’) serve as crucial indicators of ventricular diastolic function [55, 56]. A prospective observational study employing tilt tests to simulate varying gravity conditions revealed an increase in LVEDV with decreasing gravity, while the E/A and E/E’ ratios remained constant [8]. Conversely, long-term spaceflight resulted in a 13% decrease in LVEDV [22], a trend also observed in a prolonged bed-rest study [57].
Studies involving rodents in spaceflight and simulated microgravity have demonstrated that, despite maintaining body weight, there is a decrease in the ratio of cardiac mass to body weight, interventricular septal mass, ventricular mass, and wall thickness [58, 59]. Histological analyses revealed a reduction in the cross-sectional area of myofibers, thinning of sarcomeres, irregular morphology, and a decreased quantity of cardiomyocyte mitochondria, indicating cardiac atrophy [34, 60]. Further investigations using tail suspension (TS) and hindlimb unloading (HU) models have confirmed that microgravity significantly diminished cardiac mass as well as the ratio of cardiac mass to body weight. It also affects ejection fraction (EF), fractional shortening (FS), LVEDD, and left ventricular end-systolic dimension (LVESD) across various species [31, 37], suggesting a consistent pattern of cardiac atrophy leading to functional deterioration. Table 2 [61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68] summarizes changes observed in animal and human models mimicking conditions during spaceflight.
Calcium handling and downstream signaling pathways
Kohn et al. [69] proposed that microgravity induces changes in ion channel activity by altering cell membrane fluidity. This change has been associated with calcium handling abnormalities, contributing to cardiac structural and functional impairments [70]. Echocardiography conducted after 28 d of HU treatment in mice revealed cardiac enlargement and compromised systolic function. Ventricular cardiomyocytes from these mice exhibited increased spontaneous calcium release and sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) calcium leakage. The underlying mechanism may involve the activation of calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) under simulated microgravity, leading to enhanced phosphorylation of ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) and phospholamban, thereby disrupting normal SR calcium regulation. Additionally, parabolic flight-induced microgravity activated L-type calcium channels (LTCC) in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hCMs), potentially increasing SR calcium release through calcium-induced calcium release [71]. Conversely, simulated microgravity impaired isoproterenol-stimulated L-type calcium currents in cardiomyocytes [72]. This effect was attributed to disrupted β-adrenergic receptor signaling, resulting in reduced cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production, attenuated protein kinase A (PKA) activation, LTCC dysfunction, and decreased L-type calcium currents, ultimately leading to reduced cardiac contractility [72]. These variations may be due to rapid shifts between hypergravity and microgravity during parabolic flight, affecting LTCC activity in hCMs. These findings underscore the significant role of SR calcium handling anomalies in the decline of cardiac function induced by microgravity.
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) serves as a link between the modulation of intracellular calcium concentration and cardiac remodeling by inhibiting myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C) [73]. Phosphorylation of HDAC4 at Ser467 and Ser632, which relieves the suppression of transcription factors by binding to 14-3-3 proteins and relocating to the cytoplasm, is pivotal for modulating MEF2C activity [74]. Liu et al. [11] demonstrated that simulated microgravity reduced HL-1 cell volume, increased spontaneous calcium oscillations, and elevated cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations, leading to activation of the CaMKII/HDAC4 signaling pathway and upregulation of cardiac remodeling genes such as ANP and BNP. This finding suggests that microgravity-induced cardiac atrophy potentially involves the Ca2+-CaMKII-HDAC4 axis. Notably, cardiovascular remodeling may exacerbate cardiac reloading. Following 28 d of HU in mice, HDAC4 phosphorylation in the LV remained unchanged; however, an increase was observed after 7 d of hindlimb reloading (HLR), consistent with changes in LVESD and LVEDD. Conversely, post-HU RV exhibited increased HDAC4 phosphorylation, which normalized after 14 d of HLR. The RV end-diastolic dimension decreased post-HU but recovered post-HLR [75], indicating differential responses in cardiac remodeling between the LV and RV.
Recent studies have revealed the crucial roles of WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (WWP1) and casein kinase 2 interacting protein-1 (CKIP-1) in cardiac remodeling [76, 77]. WWP1, through catalyzing K27-linked polyubiquitination, stabilizes dishevelled segment polarity protein 2 (DVL2), thereby enhancing the CaMKII-HDAC4-MEF2C axis and promoting cardiac remodeling [78]. Simulated microgravity induced by TS resulted in elevated expression of WWP1 and DVL2. WWP1 knockout alleviated cardiomyocyte volume reduction, cardiac atrophy, and functional decline [37]. By facilitating the interaction between the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and HDAC4, CKIP-1 promotes HDAC4 dephosphorylation and nuclear retention, thereby dose-dependently inhibiting MEF2C transcriptional activity and influencing cardiac remodeling [79]. In murine hearts subjected to microgravity simulations, decreased CKIP-1 expression was observed, while CKIP-1 overexpression countered cardiomyocyte volume reduction and cardiac atrophy [31]. These findings suggest that targeting the Ca2+-CaMKII-HDAC4-MEF2C pathway and its associated regulatory proteins may hold promise as a therapeutic approach for addressing microgravity-induced cardiac atrophy and dysfunction.
Assembly and degradation of contractile proteins
In comparison to specimens subjected to ground control conditions, Drosophila exposed to 30 d of spaceflight exhibited significant reductions in end-diastolic diameter and FS, leading to decreased CO. Microgravity exposure resulted in the reorientation of cardiac myofibrils from circumferential to longitudinal orientation, with a more relaxed arrangement, increased interstitial spacing, and a notable decrease in sarcomere count [12]. Simultaneous downregulation of human actin homologs, such as Actin88F (hACTB) and Actin79b (hACTA/B), along with upregulation of genes encoding proteasome subunits, suggests compromised protein folding or increased degradation in the Drosophila heart [12]. Similar findings were observed in mouse studies, indicating downregulation of genes crucial for cardiac actin stabilization, polymerization, actomyosin assembly, and focal adhesion, implying alterations in the function and assembly of myocardial proteins [80]. Interestingly, species-specific differences were noted in the extracellular matrix (ECM) changes. Drosophila exhibited a significant reduction in the collagen network associated with myofibers alongside downregulation expression of genes involved in collagen cross-linking and ECM formation, such as plod and lox, as well as genes related to collagen degradation like matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) associated with myofibril remodeling. In contrast, mice displayed limited changes related to ECM gene transcription except for the downregulation of Col4a5 and the upregulation of Itgb1, highlighting species-specific responses within the myofibril-associated network under microgravity conditions. Overall, these studies underscore the role of microgravity in cardiac remodeling through gene regulation affecting myofibril assembly or stabilization while influencing protein degradation processes that may lead to cardiac atrophy.
Oxidative stress and cytoskeleton collateral damage
Mitochondrial stress is a key factor contributing to the physiological changes observed during spaceflight [13]. Microgravity-induced oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes leads to cardiac dysfunction. Rats exposed to microgravity for 6 d exhibited a notable increase in both the activity and mRNA levels of myocardial malate dehydrogenase (MDH), as well as elevated mRNA and protein levels of subunits III, IV, and VIc of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase (CytOx). Despite this observation, overall myocardial CytOx activity remained unaltered [81]. Conversely, skeletal muscle did not exhibit changes in MDH or CytOx expression but displayed a 41% reduction in CytOx activity. Transcriptomic analysis conducted on hCMs after spaceflight revealed significant enrichment of genes related to mitochondrial metabolic pathways, electron transport chain function, mitochondrial respiratory chain activities, and myocardial contraction [36], indicating that the adaptive response within mitochondria following short-term exposure to microgravity was more prominent in myocardium compared to skeletal muscle. Nevertheless, the upregulation of stress-related pathways and redox-related genes in hCMs did not correspond to the upregulation of aerobic respiration-related pathways or genes [36, 82], implying oxidative damage to cardiomyocytes. Acharya et al. [82] reported that microgravity led to an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) in hCMs, resulting in loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and diminished ATP synthesis. Following 48 h of exposure to microgravity, cardiomyocytes showed impaired calcium transients, reduced LTCC function, and decreased expression of RyR2 and phospholamban, leading to a significant slowing contraction and relaxation speeds [82]. These findings highlight a strong link between microgravity-induced oxidative stress and subsequent cardiac functional impairment.
Oxidative stress also impacts the cytoskeleton of cardiomyocytes. hCMs exposed to microgravity exhibited characteristic changes in the cell membrane, including stress fibers and caveolae, as well as increased ROS levels [82]. H9C2 cells subjected to simulated microgravity for 24 to 48 h showed a notable increase in cell height. After 96 h, there was a significant increase in the average length of microfilaments despite stable expression of cytoskeletal components such as β-tubulin and β-actin [39]. These structural alterations were concurrent with heightened intracellular ROS, mitochondrial superoxide anion levels, and protein carbonylation. Interestingly, treatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) mitigated the effects of microgravity on cardiomyocyte morphology in H9C2 cells. This suggests that while microgravity may not cause irreversible damage to the cytoskeleton, it disrupts oxidative balance and potentially hinders cellular proliferation.
Liang et al. [42] used a murine TS model to investigate how calpain activation and oxidative stress contribute to diminishing cardiomyocyte volume, heart mass, and myocardial function. Their study on cultured mouse cardiomyocytes exposed to simulated microgravity demonstrated that calpain facilitated the phosphorylation of p47 via the extracellular regulated protein kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and p38 pathways, triggering NADPH oxidase (NOX) activation with resultant myocardial abnormalities [42]. These findings suggest the potential use of calpain inhibitors as a therapeutic approach for alleviating microgravity-induced cardiac issues [41]. Notably, peak ERK1/2 and p38 activity induced by simulated microgravity occurred on day 14 but diminished on day 28. Despite inhibiting ERK1/2 and p38 activity, incomplete blockade of p47 phosphorylation implies that these kinases act as early mediators of NOX induction, while other mechanisms might drive NOX stimulation leading to cardiac atrophy during later stages of microgravity exposure [42].
Insights into vascular alterations: EC and VMSC dysfunction
The effects of microgravity on vascular structure and function during spaceflight are significant. The transition to space results in a shift of bodily fluids towards the head, leading to changes in peripheral and shear stress, which in turn impact blood pressure and flow, respectively [54]. Studies conducted by NASA and the European Space Agency have revealed an increase in intima-media thickness (IMT) and arterial stiffness after long-duration ISS missions [17, 29, 83], aligning with the prediction that the walls of arteries above the heart would thicken in response to elevated pressure [3]. However, measurements of femoral artery IMT in astronauts have shown an unexpected increase, contradicting predictions of atrophy below the heart [29], suggesting additional factors at play beyond microgravity during spaceflight. Both humans and rodents have demonstrated a time-dependent rise in IMT, media cross-sectional area, and arterial stiffness under simulated microgravity [84, 85]. Given that IMT and carotid artery stiffness are indicators of cardiovascular disease risk, these findings imply that spaceflight-associated microgravity may heighten astronauts’ susceptibility to cardiovascular events [86, 87]. Furthermore, Li et al. [88] conducted a study on the impact of the microgravity-induced headward fluid shift on the pulmonary circulation. They observed hypertrophy of the VMSCs in the media, arterial wall thickening and stenosis, as well as vascular hyperplasia in the pulmonary arterioles. The microvasculature displayed changes similar to those of the arteriola, including varying degrees of broadening, uneven intimal thickness, hyperplasia, degeneration, and detachment of the ECs, along with VSMC hypertrophy. The remodeling of the pulmonary vascular structure resulted in increased vascular resistance, potentially heightening susceptibility to pulmonary vascular disease such as pulmonary arterial hypertension, and exacerbating RV dysfunction and remodeling in astronauts [89].
Endothelial inflammation and metabolic disorder
The endothelium, essential for maintaining vascular homeostasis, releases vasoactive factors, inhibits platelet aggregation and leukocyte adhesion, and modulates VSMC proliferation [90]. ECs act as mechanoreceptors and are highly sensitive to changes in blood fluid dynamics [14, 15]. Versari et al. [16] observed differential expression of 1023 genes involved in cell adhesion, oxidative phosphorylation, stress response, cell cycle, and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to microgravity for 10 d. Moreover, exposure to simulated microgravity for 24 h increased E-selectin expression in HUVECs [91]. Upon microgravity stimulation, intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1low (ICAM-1low) ECs upregulated ICAM-1, vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and VE-cadherin, and these effects were further enhanced by tumor necrosis factor stimulation [91]. E-selectin, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 are pivotal for slowing leukocyte rolling and promoting leukocyte adhesion and inflammation [92], while VE-cadherin is crucial for maintaining vascular integrity [93]. These findings suggest that microgravity may exacerbate inflammation by modulating EC adhesion molecules, and pre-existing inflammatory conditions could intensify this effect [94].
Microgravity induces mitochondrial autophagy in ECs to counteract the metabolic challenges of mechanical unloading. Research linking the cytoskeleton to mitochondrial autophagy has shown that treating HUVECs with cytochalasin D leads to actin cytoskeletal and mitochondrial changes similar to those observed under microgravity [49]. Microgravity exposure increased the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2/adenovirus E1B 19 kD protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3), a marker of mitochondrial autophagy, while decreasing mitochondrial content, oxygen consumption, and maximal respiratory capacity. These effects were partially reversed by chloroquine, an autophagy inhibitor [49]. Furthermore, microgravity disrupted endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein homeostasis in HUVECs, leading to ER stress and Ca2+ transfer to mitochondria, resulting in mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, reduction in membrane potential, mitochondrial fission, and activation of the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)-Parkin pathway, further inducing mitochondrial autophagy [50]. Mitochondrial dysfunction increased ROS production and activated the NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome; these processes can be attenuated by MitoTempo treatment and PINK1 knockout [50]. Thus, microgravity may promote mitochondrial autophagy through disruption of the cytoskeletal and ER stress mechanisms that facilitate cellular adaptation for maintaining essential functions and ensuring survival [66]. Additionally, exposure to microgravity could induce endothelial inflammation and apoptosis via ER stress [95]. Microgravity upregulated ER stress-related proteins such as C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) and glucose-regulated protein 78, and pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-8, and IL-1β, followed by activation of inducible NOS (iNOS)/NO-nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and NLRP3 signaling pathways, resulting in endothelial inflammation and apoptosis. This ER stress was confirmed using inhibitors for iNOS/NO, NF-κB, or small interfering RNA targeting NLRP3 [95].
NOS-dependent vascular dysfunction
Nitric oxide (NO) plays a crucial role in maintaining vascular health. However, exposure to microgravity may lead to endothelial dysfunction related to NO [18]. Simulated microgravity exposure resulted in a significant upregulation of endothelial NOS (eNOS) and iNOS in rat carotid and thoracic arteries, while the expression levels decreased in the mesenteric artery, indicating tissue-specific responses [96]. Sangha et al. [97] reported that 20 d of simulated microgravity reduced vasoconstriction response to norepinephrine. This effect was reversed by endothelial removal or iNOS inhibition, suggesting that enhanced iNOS expression or activity under microgravity might augment arterial dilation dependent on the endothelium. Activation of eNOS may also contribute to hyporesponsiveness under microgravity [98]. Specifically, phosphorylation at Ser1177 increased, and phosphorylation at Ser495 decreased after 3 d of simulated microgravity, resulting in increased eNOS activity, enhanced downstream NO and cGMP signaling along with heat shock protein 90, subsequently leading to decreased vasoconstriction [98]. In contrast, one study has shown that HU can induce enhanced vasoconstriction and reduced endothelium-dependent relaxation through angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated decrease in iNOS content [99]. These discrepancies may be attributed to variations in arterial locations: the former two studies employed femoral and aortic arteries below or parallel to the heart, whereas the latter study focused on basilar and common carotid arteries above the heart. The impact of microgravity on pulmonary circulation has been elucidated. Sun et al. [100] observed that the contraction of the pulmonary artery in response to phenylephrine was markedly diminished, while vasodilation in response to acetylcholine was significantly enhanced. These distinct responses could be eliminated by endothelium removal. Nyhan et al. [101] further investigated the reactions of pulmonary arterial endothelium to microgravity at the molecular level. eNOS and soluble guanylyl cyclase expressions were significantly increased in both pulmonary artery and lung tissue from HU rats, which could account for varied responses to vasoactive agents. These findings imply the remodeling of pulmonary vasculature might affect right ventricular function, potentially leading to right heart strain or failure if significant changes occur.
Mitochondrial stress and phenotypic transformation of VSMCs
Microgravity has been associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to oxidative stress in VSMCs. Research on the correlation between mitochondrial dysfunction and NOX has revealed that exposure to simulated microgravity for 4 weeks resulted in elevated levels of mitochondrial ROS, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, increased opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, and altered respiratory control ratio in cerebral artery VSMCs. These changes were accompanied by a significant reduction in the expression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase-1. The administration of apocynin, a NOX inhibitor, ameliorated these effects [102]. Zhang et al. [103] reported that simulated microgravity enhanced superoxide production and NOX activity in cerebral artery VSMCs, leading to a significant upregulation of NOX2 and NOX4. Treatment with the mitochondrial antioxidant MitoTempo mitigated these conditions. These results suggest an interplay between NOX and mitochondria, wherein mitochondria regulate NOX expression and activity under microgravity, while conversely, NOX influences mitochondrial function by modulating superoxide radicals. However, mesenteric artery VSMCs did not respond to microgravity, indicating tissue-specific variability in microgravity-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress [102, 103].
Moreover, oxidative stress not only impacts mitochondrial function but also influences the ER, leading to phenotypic changes in VSMCs [46]. The interaction between mitochondrial oxidative stress and ER stress activates the protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase—eukaryotic initiation factor 2α—activating transcription factor 4—CHOP and phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathways, promoting the transition from a contractile phenotype to a synthetic phenotype in cerebral artery VSMCs. This phenotypic change was characterized by a decrease in the expression of contractile markers and an increase in the expression of osteopontin and elastin. Osteopontin, which is abundant in atherosclerosis (AS) plaques and associated with macrophages and foam cells, impedes EC migration and proliferation, thereby suppressing re-endothelialization and promoting medial VSMC migration as well as AS development [104]. Elastin, linked to AS through the action of elastase and the generation of pro-oxidative elastin-derived peptides, further contributes to the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein and vascular wall calcification [105]. These findings indicate that microgravity may induce VSMC dedifferentiation and exacerbate vascular inflammation, potentially leading to alterations in arterial wall structure.
Potential countermeasures targeting microgravity
Changes in Ca2+-dependent signaling, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ER stress have been identified as significant cardiovascular risk factors for astronauts on extended space missions. The pathophysiological parallels between diabetic cardiomyopathy, characterized by systemic insulin resistance and cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction, and microgravity-induced cardiovascular alterations, particularly with respect to abnormal Ca2+ handling and mitochondrial and ER stress, are noteworthy [106]. These similarities, coupled with the observed elevation of astronauts’ insulin resistance index during prolonged spaceflight [17], underscore the potential of repurposing anti-diabetic medications or other drugs to target the Ca2+-CaMKII-HDAC4-MEF2C signaling pathway and its regulatory proteins, mitigating mitochondrial and ER stress, thereby enhancing cardiovascular function in space.
Empagliflozin (a selective sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor) improves Ca2+ handling by reducing CaMKII autophosphorylation and CaMKII-dependent RyR2 phosphorylation, as well as inhibiting O-GlcNAcylation in cardiomyocytes [107]. Similarly, teneligliptin (a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor) and exendin-4 [glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA)], in combination with endurance training, significantly decrease NOX4-mediated oxidative stress and HDAC4 phosphorylation and expression, thereby enhancing cardiac remodeling [108, 109]. Ivabradine (an If current antagonist) binds to and enhances the catalytic subunit of PP2A, promoting HDAC4 dephosphorylation and improving cardiac remodeling [79, 110]. Indole-3-carbinol (a natural WWP1 inhibitor found in cruciferous vegetables) may attenuate the stabilizing effect of WWP1 on DVL2, resulting in downregulation of the Ca2+-CaMKII-HDAC4-MEF2C axis [78, 111]. For ECs and VSMCs, DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1RAs can reduce ROS production and downregulate NF-κB, NOX, and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. This helps to maintain eNOS phosphorylation, thus reducing EC senescence and apoptosis while inhibiting VSMC migration and promoting apoptosis [112, 113]. Additionally, AKB-9778 (a vascular endothelial protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor) and MitoQ (a mitochondrial antioxidant), improve endothelial function and decrease vascular stiffness by preventing eNOS dephosphorylation, increasing NO production in diabetic patients, as well as reducing mitochondrial ROS generation in elderly individuals [114, 115].
Exercise regimens customized to maintain physical fitness demonstrate the potential to mitigate the cardiac effects of prolonged microgravity. However, it is important to note that the type, duration, and intensity may not completely prevent structural and functional cardiovascular changes, such as cardiac dysfunction, arterial thickening, and stiffness [9, 17, 30]. In diabetic cardiomyopathy, exercise is crucial for combating cardiovascular impairments. The N-terminal proteolytic fragment of HDAC4 (HDAC4-NT) exerts a cardioprotective effect during aerobic activities like running by elevating HDAC4-NT levels in cardiomyocytes through the cAMP-PKA pathway, thereby repressing MEF2C transcription and improving cardiac function [116]. Intriguingly, running also activates myocardial AMP-activated protein kinase, leading to HDAC4 phosphorylation and subsequent MEF2A-mediated repression of glucose transporter 1 expression. This facilitates cardiac function and glucose metabolism in ischemic HF [117]. Aerobic exercise further attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in vascular tissues, while enhancing the bioavailability of antioxidant enzymes and NO. It also improves endothelial function and arterial rigidity [118]. Conversely, resistance exercise may compromise endothelial function due to sustained elevations in blood pressure [119]. Nevertheless, a combination of aerobic and resistance exercise appears to be beneficial for enhancing endothelial function, particularly for individuals with type II diabetes [120]. Notably, individualized exercise prescriptions can be tailored for astronauts, with high-intensity and low-repetition resistance exercise effectively circumventing vascular damage, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear [119]. Blood flow restriction (BFR) training presents a compelling alternative to conventional resistance training by reducing joint stress while yielding comparable gains in muscle strength [121]. However, further exploration to balance the benefits against possible risks associated with BFR training such as alterations in venous wall tension and compliance due to inflatable cuffs applied to the proximal ends of limbs.
Space radiation-induced changes in cardiovascular structure and function
Space radiation, particularly HZE particles, poses a significant risk for cardiovascular structural and functional changes (Fig. 2). Its biological impact is generally more pronounced than that of terrestrial gamma rays and X-rays, highlighting the need for comprehensive protective strategies during long-duration spaceflight [122].
Space radiation-mediated dysfunction of cardiomyocytes, ECs, and VSMCs. a Cardiac response to space radiation. Exposure to space radiation leads to the generation of ROS, which disrupts calcium homeostasis in cardiac cells by inhibiting LTCC and NCX in the cell membrane of cardiomyocytes as well as SERCA in the membrane of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). ROS can also cause DNA damage and oxidative modifications such as 8-oxo-dG, contributing to cardiomyocyte damage and dysfunction. Space radiation induces dephosphorylation of the transcription factor NFATc4, leading to its translocation into the cardiomyocyte nucleus, along with DNA demethylation that potentially activates gene expression related to cardiac remodeling. b Vascular response to space radiation. Space radiation induces oxidative stress in the vascular system, promoting ROS production and resulting in EC and VSMC dysfunction. Increased ROS leads to inflammatory cell migration and disruption of the NOS-NO pathway. The NOS-NO pathway plays an important role in suppressing VSMC proliferation, platelet aggregation, and thrombosis as well as promoting vascular relaxation. Furthermore, DNA DSB induced by radiation activates NF-κB signaling via NEMO, leading to inflammation and apoptosis that further exacerbate vascular integrity damage. DSB double-strand break, EC endothelial cell, LTCC L-type calcium channel, Me methyl, NCX sodium-calcium exchanger, NEMO nuclear factor kappa-B essential modulator, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa-B, NFATc4 nuclear factor of activated T-cell c4, NO nitric oxide, NOS nitric oxide synthase, SERCA SR Ca2+-ATPase, ROS reactive oxygen species, VSMC vascular smooth muscle cell, 8-oxo-dG 8-oxo-deoxy-guanosine
Insights into cardiac diastolic dysfunction: oxidative stress and gene expression
Radiation is intricately associated with cardiac dysfunction, as research has revealed the varying impacts of different types and doses of radiation on cardiac health. In male mice, exposure to 16O resulted in significant declines in EF and FS at 3- and 7-months post-radiation, accompanied by the deposition of α-smooth muscle actin and 75-kD type III collagen within the LV, indicating compromised systolic function and early-stage cardiac remodeling [123]. Conversely, female mice did not exhibit functional changes despite similar biomarker deposition, suggesting a potential sex-related difference in the cardiac response to space radiation [124]. Brojakowska et al. [125] further explored the cardiac ramifications of exposure to simplified galactic cosmic radiation, which included 5 ions (1H, 28Si, 4He, 16O, 56Fe), at doses of 0.5 Gy and 1 Gy in male mice. Within one year, all mice displayed a significant reduction in EF. At 660 d, those exposed to 0.5 Gy showed no change in EF but demonstrated a notable decrease in LV mass and elevated levels of transforming growth factor-β1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, MMP9, and β-myosin heavy chain, indicating increased fibrosis, inflammation, and hypertrophy. Mice exposed to proton radiation initially experienced myocardial hypertrophy and improved systolic function, which subsequently transitioned to cardiac atrophy and fibrosis, resulting in diastolic dysfunction [123]. These findings emphasize the necessity for further exploration into the early effects of space radiation and confirm its role in inducing late-stage diastolic dysfunction, as well as cardiac atrophy, and myocardial fibrosis.
NASA’s investigation into the cardiovascular effects of space radiation revealed that exposure to 1H and 56Fe significantly increased the phosphorylation of H2A histone family member X, a marker for DNA double-strand break, by 2- to fivefold within 2 to 24 h, with detectable levels persisting at 28 d. Concurrently, CD68 (a monocyte-macrophage marker) and 8-oxo-deoxy-guanosine (8-oxo-dG; an indicator of DNA oxidative damage) were elevated in cardiac tissues [126]. The presence of 8-oxo-dG, a byproduct of ROS-induced damage, indicates oxidative stress in failing hearts [127]. Excessive ROS disrupts cardiomyocyte electrophysiology and contraction by impairing critical proteins involved in excitation–contraction coupling, including LTCCs, sodium channels, potassium channels, and sodium-calcium exchangers (NCXs). ROS also inhibits SR Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA), reduces the sensitivity of sarcomeres to Ca2+, and causes energy deficits by targeting metabolic proteins. Furthermore, the generation of ROS-induced DNA damage activates the protein kinase ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, thereby facilitating DNA repair and inhibiting cell cycle-related pathways [128, 129]. Oxidative stress induces an inflammatory response in the heart and recruits monocytes/macrophages to promote timely tissue repair through the synthesis of endogenous lipid mediators, thus preventing chronic inflammation and compromised cardiac repair [130]. The combined effects of microgravity and space radiation may exacerbate oxidative stress, potentially amplifying detrimental impacts on cardiac structure and function.
Subsequent observations revealed an initial increase in NCX and SERCA2a expression at 1-month post-radiation, followed by declines at 3 months. At 10 months, NCX levels increased again in mice exposed to 56Fe, while phosphorylation of the nuclear factor of activated T-cell c4 (NFATc4) progressively decreased from 1 to 10 months [126]. The upregulation of NCX, a hallmark of HF, compensates for compromised contractility; however, NCX dysfunction has been found in ventricular cardiomyocytes of failing hearts [131]. Additionally, SERCA2a, crucial for calcium handling and systolic function enhancement, is downregulated in HF [132]. NFATc4, a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy, remains highly phosphorylated and inactive under baseline conditions, but its dephosphorylation activates itself and contributes to cardiac hypertrophy [133, 134]. Space radiation also impacts cardiac health through decreased DNA methylation levels, particularly within repetitive genetic sequences [135, 136]. Exposure to 56Fe, 16O, and 1H has been shown to reduce the methylation and expression of long interspersed nuclear elements 1 [135, 136]. Subsequent investigations have indicated that space radiation might impair DNA methylation by modifying components related to one-carbon unit and methionine metabolism pathways, consistent with radiation-induced hypomethylation [136]. Importantly, the combined effects of microgravity and space radiation exacerbate this reduction in the potential for DNA methylations [137]. Previous research has established a correlation between reduced promoter region methylation for ANP and BNP with their activation states, indicating a link between radiation-induced hypomethylation and cardiac dysfunction [138].
Insights into arterial remodeling: homeostasis disruption and inflammation
Space radiation has a significant impact on arterial structure and function. Mice exposed to 56Fe exhibited intimal thickening in the carotid artery as an indication of potential arterial wall damage associated with compromised vasodilation [139]. ECs and VSMCs exposed to radiation experienced apoptosis, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cellular senescence [140]. EC apoptosis precedes vascular injury and reduced vascular density, with high linear energy transfer (LET) particles posing a greater risk of ischemic damage compared to low LET particles [141]. Vascular tissues showed significant oxidative stress following radiation, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction and endothelial impairment [140]. Exposure to neutrons and 60Co also demonstrated evidence of mitochondrial damage [142]. The bioavailability and signaling of NO are essential for endothelial homeostasis. However, oxidative stress disrupts NO pathways, leading to endothelial dysfunction [143]. Exposure to HZE particles increased ROS production in the aorta, impairing NO signaling and endothelium-dependent vasodilation [144]. HUVECs exposed to 137Cs exhibited premature senescence through double-strand break/NF-κB essential modulator/NF-κB signaling pathways, contributing to AS development [145]. Activation of inflammatory signaling and diminished vascular endothelium integrity promote the adhesion and transmigration of inflammatory cells [146]. The impact of radiation on inflammation during plaque formation includes increased EC permeability and the facilitation of inflammatory cells and VSMC migration or proliferation [147, 148], potentially accelerating age-dependent AS [139]. Moreover, ApoE−/− mice exposed to ionizing radiation at doses of 10 Gy or 56Fe exhibited accelerated plaque formation [139, 149].
Potential countermeasures to space radiation
In the field of radiation therapy, there is an ongoing search for pharmacological agents to mitigate cardiac toxicity. Current strategies focus on identifying and closely monitoring high-risk individuals, coupled with managing resulting complications symptomatically. Nonetheless, dietary regimens and nutritional supplementation have emerged as potential ways to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, offering hope for astronaut health in the context of radiation protection. The Mediterranean diet, which is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, has been linked to reduced arterial stenosis and improved endothelial function [150]. Additionally, a low-fat diet has proven effective in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease [151]. Despite its vascular health benefits, caloric restriction is not recommended for astronauts due to the risk of skeletal and muscular atrophy during spaceflight [152]. It is essential to strategically incorporate functional foods and antioxidant micronutrients for space missions. A summary of promising nutritional supplements can be found in Table 3 [153,154,155,156,157,158,159].
Circadian rhythm disruption-related changes in cardiovascular structure and function
The circadian system is regulated by a central pacemaker clock located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus, which synchronizes physiological rhythms with environmental cues and coordinates peripheral clocks. At the molecular level, circadian oscillations are governed by a transcription-translation feedback loop involving 4 core clock gene families: Bmal1, Clock, Period (Per), and Cryptochrome (Cry), all exhibiting near-24-hour rhythmicity. CLOCK and brain and muscle arnt-like 1 (BMAL1), as part of the positive limb of the loop, stimulate the transcription and translation of Per and Cry, leading to the accumulation of PER and CRY proteins. These proteins form complexes through dimerization that represses the transcription of Clock and Bmal1 [160]. Additional genes, such as Rev-erb-α/β, modulate this feedback loop, contributing to the robustness and precision of the circadian rhythm [161].
The human circadian rhythm, naturally synchronized with Earth’s 24-hour light–dark cycle, is vulnerable to disruption by factors such as microgravity, artificial lighting, shift work, and hypnotic use during missions (Fig. 3). These disturbances pose a threat to the cardiovascular health of astronauts [162, 163]. Studies on the impacts of long-duration spaceflight on human circadian rhythms are rare. A case report from the Space Station Mir investigated the effects of prolonged spaceflight on the endogenous circadian rhythm and sleep [164]. They found that the function of the endogenous circadian pacemaker, as indicated by subjective alertness rhythms and oral temperature, exhibited time-dependent impairment and compromised sleep. Recent behavioral and transcriptomic studies in both human and animal models have revealed that microgravity might exacerbate the asynchrony of clock gene expression between peripheral tissues, consequently leading to disrupted activity and sleep rhythms [165,166,167,168]. Empirical evidence suggests that the space environment can impact the circadian rhythms of blood pressure and HR [169, 170]. Heart rate variability during spaceflight exhibited differences compared to ground missions. Liu et al. [169] documented a notable reduction in HR amplitude, body trunk activity, and rhythmicity among 3 Chinese astronauts during the mission, with 1 experiencing a phase shift in the circadian rhythm of HR. However, the average HR remained unchanged. Long-term observations of 4 Russian astronauts revealed that while the mean systolic blood pressure and HR of astronauts remained stable, their circadian patterns shortened in duration [171]. Notably, Russian astronauts exhibited a significant increase in average systolic blood pressure during sleep. Although isolating the effects of individual factors on the circadian rhythm in space is challenging, overall data underscore the capacity of the space environment to modulate circadian rhythms within the cardiovascular system.
Causes, mechanisms, and possible interventions for cardiovascular alterations induced by circadian rhythm disruption. a The broader environmental and lifestyle factors contribute to circadian disruption and subsequent cardiovascular consequences. b The transcription-translation feedback loop constructed by core components of the circadian clock can be disrupted during spaceflight. c Disruption of BMAL1, CLOCK, and REV-ERB can impair cardiac function and is associated with DCM or HCM phenotypes. d Vascular circadian disorders are shown to influence AS acceleration and inhibition, macrophage lipid disturbances, and endothelial dysfunction. e The potential countermeasures, including hypnotics, medications directly affecting circadian rhythms, and TRE, can fulfill the comprehensive management strategies to mitigate circadian rhythm disturbances in diverse settings. AS atherosclerosis, BAML1 brain and muscle arnt-like 1, CRY cryptochrome, DCM dilated cardiomyopathy, HCM hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, PER period, TRE time-restricted eating
Mechanisms of cardiac structural and functional impairments
Disruption of core clock genes and disturbances in circadian rhythm have been linked to compromised cardiac structure and function [172]. Global Bmal1 knockout mice displayed phenotypes of dilated cardiomyopathy, such as myocardial thinning, chamber dilation, and systolic dysfunction [173]. Conversely, specific ablation of Bmal1 in cardiomyocytes yielded hypertrophic cardiomyopathy characterized by increased cardiomyocyte volume, progressive fibrosis in the interstitial and endocardial regions, and worsening diastolic dysfunction [174]. Clock knockout mice showed age-dependent hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, characterized by increased heart weight, myocardial hypertrophy, chamber dilation, compromised contractility, and reduced myogenic responsiveness. These effects may be associated with disrupted diurnal oscillation of Pten expression and altered phosphorylation of downstream Akt-glycogen synthase kinase 3β-mitogen-stimulated protein kinase p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 [175]. Clock mutant mice were able to attenuate cardiac hypertrophy, LV remodeling, and diastolic dysfunction through the upregulation of cardiac catalase and glutathione peroxidase induced by obesity and metabolic syndrome [176]. Cardiomyocyte-specific Rev-erb-α/β knockout led to progressive deterioration of systolic dysfunction and dilated cardiomyopathy. In the context of obesity with insulin resistance, Rev-erb ablation temporarily ameliorated cardiac dysfunction by relieving the suppression of lipid oxidation genes during the light phase. This was mediated by the downregulation of the transcriptional repressor E4 promoter-binding protein 4, thereby augmenting fatty acid oxidation flux [161]. These observations indicate that while disruptions in circadian rhythm may adversely affect cardiac structure and function, enhancing lipid oxidation and antioxidant mechanisms during extended spaceflight could offer protective effects against cardiac alterations.
Mechanisms of vascular structural and functional deteriorations
The disruption of circadian rhythm is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in vascular injury, potentially accelerating the progression of vascular lesions and elevating the risk of vascular diseases in astronauts [177]. APOE*3-Leiden mice exposed to a simulated shift work schedule, characterized by weekly alternating light–dark cycles, showed marked increases in the size and severity of atherosclerotic lesions. This augmentation was attributed to heightened infiltration of macrophages and the upregulation of inflammatory markers, oxidative stress genes, and chemokines within the vascular wall [178]. These findings underscore the direct influence of circadian rhythm disruption on the acceleration of age-dependent AS, a process seemingly independent of plasma lipid concentrations [178]. In LDLR−/− mice, global Bmal1 knockout coupled with a high-fat diet accelerated the onset of AS without concurrent changes in plasma total cholesterol and triglyceride levels [179]. Adult Bmal1 knockout mice demonstrated reduced AS burden and delayed onset when subjected to a high-fat diet [179]. These findings suggest circadian disruption primarily affects the vascular wall locally rather than exerting systemic influences originating from extravascular organs or tissues. The underlying mechanisms for AS acceleration may involve the disconnection of NO synthesis within aortic ECs following Bmal1 deletion. This process is marked by reduced eNOS cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin levels, leading to eNOS uncoupling, diminished NO production, increased superoxide generation, and subsequent endothelial inflammation [180]. Further insights were obtained from VSMC-specific Bmal1 knockout mice, in which downregulation of ARHGDIA transcription and a weakened interaction between the Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate (RAC1) and BMAL1 were implicated in promoting RAC1-driven VSMC migration. These effects were accompanied by an impairment of antioxidant function through the inhibition of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 activity and Bcl2 transcription. This led to a cascade effect involving monocyte migration, elevated ROS levels, and VSMC apoptosis, thereby intensifying the progression of AS [181]. Furthermore, a relationship between microgravity and intrinsic diurnal oscillation of vasoconstriction has been reported [182]. Simulated microgravity attenuated the diurnal variation of myogenic tone in rat cerebral arteries by altering the circadian regulation of the BMAL1/miR-103/CaV1.2 signaling pathway at the post-transcriptional level. These studies highlight the pivotal roles played by ECs and VSMCs in vascular structure and function impairment induced by circadian rhythm disorder.
Mice with a mutation in the Clock gene exhibited hypercholesterolemia when their circadian rhythm was disrupted, which was attributed to enhanced intestinal cholesterol absorption, increased macrophage uptake of modified lipoproteins, and diminished cholesterol efflux. These factors collectively led to accelerated AS [183]. In contrast, Per2 mutant mice showed endothelial dysfunction, potentially expediting AS through reduced production of NO and vasodilatory prostaglandins, and increased levels of vasoconstrictors derived from cyclooxygenase-1, and Akt-dependent EC aging [184, 185]. Moreover, Cry1 overexpression attenuates AS by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and leukocyte adhesion molecules related to the Toll-like receptor/NF-κB pathway, while also reducing plasma cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [186]. These findings indicate the crucial role of an intact circadian rhythm in maintaining vascular structural and functional homeostasis.
Potential countermeasures targeting circadian rhythm disruption
The significant implications of circadian rhythm disruption highlight the necessity for interventions to prevent astronauts’ insomnia and alleviate the impacts of shift work. The current pharmacological approaches primarily involve benzodiazepines, non-benzodiazepine receptor agonists, melatonin, and melatonin agonists [187]. Benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine receptor agonists directly induce sleep by enhancing the activity of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid, thereby amplifying inhibitory signals to arousal-promoting cell groups in the brainstem and hypothalamus [188]. Some studies have indicated that these medications may independently lower mortality rates and reduce rehospitalization in HF patients by ameliorating psychosocial risk factors such as insomnia and psychosocial stress [189, 190]. However, side effects including headaches, dizziness, dry mouth, drowsiness, diarrhea, grogginess, and palpitations, as well as the potential of physiological or psychological dependence and tolerance with long-term use restrict their application in astronauts [191], despite their safety and effectiveness for short-term sleep-promotion [192]. Melatonin is considered to be more effective for treating circadian rhythm disruptions or insomnia in individuals with circadian rhythm disorders than sedatives or hypnotics [191]. Therefore, strategic administration of exogenous melatonin, known to induce fatigue and drowsiness, could rectify circadian rhythm disruptions in astronauts [193]. The use of melatonin before sleep has been shown to assist shift workers in adapting to the day-night cycle, extending both daytime and nocturnal sleep and improving overall sleep quality [194]. Further research is needed to investigate the effects of melatonin on sleep latency, insulin resistance, and diurnal blood pressure rhythms in shift workers. Melatonin agonists similarly influence the circadian clock by binding to melatonin receptors and increasing cerebral melatonin levels [191]. Although benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine receptor agonists are more effective than melatonin and its agonists for short- or long-term treatment of insomnia [195], their superior safety, relevance to circadian rhythm disorder, and relatively mild adverse effects may make them more suitable for astronauts [196]. Drugs directly targeting the circadian system have demonstrated promising potential in correcting disruptions to circadian rhythm. SR9009 and SR9011, which are agonists of REV-ERBα, can promote metabolic homeostasis by reducing fat mass and improving hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in cases of diet-induced obesity [197]. Additionally, SR9011 and SR8278 (a REV-ERBα antagonist) have displayed anxiolytic effects [198, 199], which may help prevent mood vulnerability in shift work settings and anxiety-like mood-associated circadian misalignment [200]. Furthermore, KL001, a compound that stabilizes CRY protein levels leading to extended periods and reduced amplitudes of circadian rhythms, has been found to inhibit glucagon-induced gluconeogenesis [201], potentially improving conditions related to hyperglucagonemia-induced lipotoxicity while delaying the development of insulin resistance and cardiac dysfunction [202].
In addition to pharmacological treatments, improvements in dietary habits and achieving a better work-life balance can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases induced by disruptions in circadian rhythm. Time-restricted eating (TRE), involving the consumption of daily caloric intake within a specific time window followed by fasting without reducing overall caloric intake, has been shown to alleviate circadian rhythm disruption and mitigate cardiovascular aging, thus diminishing the risk of cardiovascular disease in astronauts [203]. A cohort study involving 137 firefighters on 24-hour shifts revealed that a 10-h TRE over 12 weeks significantly reduced very low-density lipoprotein particle size and decreased levels of glycated hemoglobin A1C and diastolic blood pressure, particularly in individuals with elevated baseline cardiometabolic risk. These findings suggest that TRE may improve cardiometabolic health, particularly for populations experiencing circadian rhythm disturbances [204]. The investigation of shift schedules that minimally impact cardiovascular health is of paramount importance. The evidence suggests that limiting consecutive night shifts reduces circadian disruption, and slow rotating shifts exert fewer adverse effects on sleep duration compared to permanent night shifts [205]. Nonetheless, further research is imperative to discern the differential impacts of various shift schedules on cardiovascular health. A proposed schedule aimed at minimizing injury and breast cancer risk may serve as a model for mitigating circadian rhythm disruption in astronauts: (1) ≤ 3 consecutive night shifts, (2) shift intervals ≥ 11 h, and (3) ≤ 9 h of working time [193].
Leveraging microgravity to promote cardiovascular treatment
hCMs and cardiovascular progenitor cells (CPCs) play a pivotal role in unraveling the intricacies of cardiac pathophysiology, development, and regeneration [206]. The ability to culture these cells in space has been confirmed by various studies [207, 208]. A 3-week study on the ISS observed a significant increase in the expression of genes related to cell proliferation, cardiac differentiation, and cardiac function in hCMs, along with a suppression of ECM regulation genes [207, 209]. After 30 d of exposure to microgravity, neonatal and adult CPCs showed upregulated expression of DNA repair genes and paracrine factors, along with enhanced migratory capacity [208]. Intriguingly, differences in gene expression related to cell proliferation, cardiac regeneration, and development were observed between neonatal and adult CPCs [208]. Neonatal CPCs, in particular, exhibited characteristics indicative of early cardiovascular development and enhanced proliferative capacity, alongside a significant downregulation of the Hippo signaling pathway effector gene Yap1. Conversely, adult CPCs showed an upregulation of Yap1 under microgravity, as supported by subsequent studies [210]. The importance of Yap is highlighted in myocardial regeneration post-infarction, where it promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and the expression of genes associated with cardiac regeneration, while simultaneously inhibiting cardiac fibroblast activation and trans-differentiation through the enhancement of noncanonical Wnt signaling to prevent cardiac fibrosis [211]. These findings suggest that spaceflight has the potential to address certain challenges inherent in cardiovascular regenerative medicine. Nevertheless, there are still obstacles to overcome, such as the possible decline in enhanced stemness of hCMs or CPCs upon return to Earth and the feasibility of mass-producing personalized hCMs or CPCs with high quality during spaceflight.
Conclusions
Microgravity, space radiation, and circadian rhythm disruption are recognized as primary risks to cardiovascular health that exacerbate the dangers associated with human space exploration. In the course of spaceflight, there is evidence of accelerated aging-related modifications in the cardiovascular system. After a 6-month mission on the ISS, astronauts exhibit structural and functional changes in their vasculature and heart, including increased thickness and stiffness of blood vessel walls, potentially heightening susceptibility to AS. Numerous aspects necessitate further investigation. Firstly, it is imperative to elucidate the specific mechanisms underlying altered ion channel activity, such as LTCC and RyR, from a structural biology perspective. Subsequently, further research is warranted to comprehensively understand the reversibility of cardiovascular remodeling induced by spaceflight. This necessitates longitudinal studies tracking astronauts’ post-mission to monitor the recovery of cardiovascular function and structure over time; exploration into the molecular mechanisms governing both reversible and irreversible changes for identification of potential therapeutic targets; and advancement in countermeasures development that can be implemented during and after space missions to promote cardiovascular health. Thirdly, there remains a scarcity of information on the molecular connections between the circadian clock and spaceflight-induced circadian disruption leading to cardiovascular malfunction during spaceflight. Therefore, additional evidence is needed in the future. Lastly, given the limitations of diagnostic tools such as echocardiography and photoplethysmography in space, it is crucial to develop more accurate and reliable techniques for monitoring cardiac performance and detecting early signs of cardiovascular dysfunction during space missions. Moreover, continuous monitoring is essential for assessing the potential cardiovascular complications following extended space missions and re-entry to Earth. Careful consideration of these environmental hazards is necessary to accurately evaluate health risks and develop effective countermeasures. The discrepancies between space and simulated terrestrial data underscore the imperative to comprehensively assess the interaction of these complex risk factors. Ongoing and future research efforts are vital for protecting human health during interstellar travel.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- 8-oxo-dG:
-
8-Oxo-deoxy-guanosine
- Ω-3:
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- AS:
-
Atherosclerosis
- BFR:
-
Blood flow restriction
- BMAL1:
-
Brain and muscle arnt-like 1
- BNIP3:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2/adenovirus E1B 19 kD protein-interacting protein
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- CaMKII:
-
Calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase II
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP-homologous protein
- CKIP-1:
-
Casein kinase 2 interacting protein-1
- CO:
-
Cardiac output
- CPCs:
-
Cardiovascular progenitor cells
- Cry:
-
Cryptochrome
- CytOx:
-
Cytochrome c oxidase
- DPP-4:
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
- DVL2:
-
Dishevelled segment polarity protein 2
- E/A:
-
Early to late diastolic transmitral flow velocity
- ECs:
-
Endothelial cells
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- E/E’:
-
Early diastolic transmitral flow velocity to early diastolic mitral annular tissue velocity
- EF:
-
Ejection fraction
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial NOS
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular regulated protein kinases 1 and 2
- FS:
-
Fractional shortening
- GLP-1RA:
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist
- hCMs:
-
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
- HDAC4:
-
Histone deacetylase 4
- HDAC4-NT:
-
N-terminal proteolytic fragment of HDAC4
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- HLR:
-
Hindlimb reloading
- HU:
-
Hindlimb unloading
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- HZE:
-
Particles high-energy heavy ions
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IMT:
-
Intima-media thickness
- iNOS:
-
Inducible NOS
- ISS:
-
International space station
- LEO:
-
Low earth orbit
- LET:
-
Linear energy transfer
- LTCC:
-
L-type calcium channels
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- LVEDD:
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic dimension
- LVEDV:
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic volume
- LVESD:
-
Left ventricular end-systolic dimension
- MDH:
-
Malate dehydrogenase
- MEF2C:
-
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- NAC:
-
N-acetylcysteine
- NASA:
-
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- NCX:
-
Sodium-calcium exchanger
- NFATc4:
-
Nuclear factor of activated T-cell c4
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-B
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NOX:
-
NADPH oxidase
- NR:
-
Nicotinamide riboside
- PER:
-
Period
- PINK1:
-
PTEN-induced putative kinase 1
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PP2A:
-
Protein phosphatase 2A
- RAC1:
-
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RyR2:
-
Ryanodine receptor 2
- SERCA:
-
SR Ca2+-ATPase
- SGLT2:
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2
- SR:
-
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- SV:
-
Stroke volume
- TRE:
-
Time-restricted eating
- TS:
-
Tail suspension
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1
- VSMCs:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells
- WWP1:
-
WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1
References
Patel ZS, Brunstetter TJ, Tarver WJ, Whitmire AM, Zwart SR, Smith SM, et al. Red risks for a journey to the red planet: the highest priority human health risks for a mission to Mars. NPJ Microgravity. 2020;6(1):33.
Afshinnekoo E, Scott RT, MacKay MJ, Pariset E, Cekanaviciute E, Barker R, et al. Fundamental biological features of spaceflight: advancing the field to enable deep-space exploration. Cell. 2020;183(5):1162–84.
Hughson RL, Helm A, Durante M. Heart in space: effect of the extraterrestrial environment on the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(3):167–80.
Scott JM, Stoudemire J, Dolan L, Downs M. Leveraging spaceflight to advance cardiovascular research on Earth. Circ Res. 2022;130(6):942–57.
Malhan D, Schoenrock B, Yalçin M, Blottner D, Relógio A. Circadian regulation in aging: implications for spaceflight and life on earth. Aging Cell. 2023;22(9):e13935.
Wu B, Wang Y, Wu X, Liu D, Xu D, Wang F. On-orbit sleep problems of astronauts and countermeasures. Mil Med Res. 2018;5(1):17.
Perhonen MA, Franco F, Lane LD, Buckey JC, Blomqvist CG, Zerwekh JE, et al. Cardiac atrophy after bed rest and spaceflight. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2001;91(2):645–53.
Negishi K, Borowski AG, Popović ZB, Greenberg NL, Martin DS, Bungo MW, et al. Effect of gravitational gradients on cardiac filling and performance. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017;30(12):1180–8.
Arbeille P, Provost R, Zuj K. Carotid and femoral artery intima-media thickness during 6 months of spaceflight. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2016;87(5):449–53.
West JB, Elliott AR, Guy HJ, Prisk GK. Pulmonary function in space. JAMA. 1997;277(24):1957–61.
Liu C, Zhong G, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Tan Y, Li Y, et al. Alteration of calcium signalling in cardiomyocyte induced by simulated microgravity and hypergravity. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3):e12783.
Walls S, Diop S, Birse R, Elmen L, Gan Z, Kalvakuri S, et al. Prolonged exposure to microgravity reduces cardiac contractility and initiates remodeling in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2020;33(10):108445.
da Silveira WA, Fazelinia H, Rosenthal SB, Laiakis EC, Kim MS, Meydan C, et al. Comprehensive multi-omics analysis reveals mitochondrial stress as a central biological hub for spaceflight impact. Cell. 2020;183(5):1185-201.e20.
Li J, Hou B, Tumova S, Muraki K, Bruns A, Ludlow MJ, et al. Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature. 2014;515(7526):279–82.
Xu J, Mathur J, Vessières E, Hammack S, Nonomura K, Favre J, et al. GPR68 senses flow and is essential for vascular physiology. Cell. 2018;173(3):762-75.e16.
Versari S, Longinotti G, Barenghi L, Maier JA, Bradamante S. The challenging environment on board the International Space Station affects endothelial cell function by triggering oxidative stress through thioredoxin interacting protein overexpression: the ESA-SPHINX experiment. FASEB J. 2013;27(11):4466–75.
Hughson RL, Robertson AD, Arbeille P, Shoemaker JK, Rush JW, Fraser KS, et al. Increased postflight carotid artery stiffness and inflight insulin resistance resulting from 6-mo spaceflight in male and female astronauts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;310(5):H628–38.
Vaziri ND, Ding Y, Sangha DS, Purdy RE. Upregulation of NOS by simulated microgravity, potential cause of orthostatic intolerance. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2000;89(1):338–44.
Verbanck S, Larsson H, Linnarsson D, Prisk GK, West JB, Paiva M. Pulmonary tissue volume, cardiac output, and diffusing capacity in sustained microgravity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1997;83(3):810–6.
Herault S, Fomina G, Alferova I, Kotovskaya A, Poliakov V, Arbeille P. Cardiac, arterial and venous adaptation to weightlessness during 6-month MIR spaceflights with and without thigh cuffs (bracelets). Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000;81(5):384–90.
Martin DS, South DA, Wood ML, Bungo MW, Meck JV. Comparison of echocardiographic changes after short- and long-duration spaceflight. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2002;73(6):532–6.
Arbeille P, Fomina G, Roumy J, Alferova I, Tobal N, Herault S. Adaptation of the left heart, cerebral and femoral arteries, and jugular and femoral veins during short- and long-term head-down tilt and spaceflights. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2001;86(2):157–68.
Summers RL, Martin DS, Meck JV, Coleman TG. Mechanism of spaceflight-induced changes in left ventricular mass. Am J Cardiol. 2005;95(9):1128–30.
Westby CM, Martin DS, Lee SM, Stenger MB, Platts SH. Left ventricular remodeling during and after 60 days of sedentary head-down bed rest. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016;120(8):956–64.
Norsk P, Asmar A, Damgaard M, Christensen NJ. Fluid shifts, vasodilatation and ambulatory blood pressure reduction during long duration spaceflight. J Physiol. 2015;593(3):573–84.
Iwasaki K, Levine BD, Zhang R, Zuckerman JH, Pawelczyk JA, Diedrich A, et al. Human cerebral autoregulation before, during and after spaceflight. J Physiol. 2007;579(Pt 3):799–810.
Marshall-Goebel K, Laurie SS, Alferova IV, Arbeille P, Auñón-Chancellor SM, Ebert DJ, et al. Assessment of jugular venous blood flow stasis and thrombosis during spaceflight. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(11):e1915011.
Fu Q, Shibata S, Hastings JL, Platts SH, Hamilton DM, Bungo MW, et al. Impact of prolonged spaceflight on orthostatic tolerance during ambulation and blood pressure profiles in astronauts. Circulation. 2019;140(9):729–38.
Arbeille P, Provost R, Zuj K. Carotid and femoral arterial wall distensibility during long-duration spaceflight. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2017;88(10):924–30.
Shibata S, Wakeham DJ, Thomas JD, Abdullah SM, Platts S, Bungo MW, et al. Cardiac effects of long-duration space flight. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;82(8):674–84.
Ling S, Li Y, Zhong G, Zheng Y, Xu Q, Zhao D, et al. Myocardial CKIP-1 overexpression protects from simulated microgravity-induced cardiac remodeling. Front Physiol. 2018;9:40.
Ogneva IV, Maximova MV, Larina IM. Structure of cortical cytoskeleton in fibers of mouse muscle cells after being exposed to a 30-day space flight on board the BION-M1 biosatellite. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014;116(10):1315–23.
Goldstein MA, Edwards RJ, Schroeter JP. Cardiac morphology after conditions of microgravity during COSMOS 2044. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1992;73(2 Suppl):94S-100S.
Philpott DE, Popova IA, Kato K, Stevenson J, Miquel J, Sapp W. Morphological and biochemical examination of Cosmos 1887 rat heart tissue: Part I–ultrastructure. FASEB J. 1990;4(1):73–8.
Wang Z, Wang XC, Chen YF, Wang CL, Chen L, Jiang MY, et al. Loss and recovery of myocardial mitochondria in mice under different tail suspension time: apoptosis and mitochondrial fission, fusion and autophagy. Exp Physiol. 2023;108(9):1189–202.
Wnorowski A, Sharma A, Chen H, Wu H, Shao NY, Sayed N, et al. Effects of spaceflight on human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte structure and function. Stem Cell Reports. 2019;13(6):960–9.
Zhong G, Zhao D, Li J, Liu Z, Pan J, Yuan X, et al. WWP1 deficiency alleviates cardiac remodeling induced by simulated microgravity. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:739944.
Han X, Qu L, Yu M, Ye L, Shi L, Ye G, et al. Thiamine-modified metabolic reprogramming of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte under space microgravity. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):86.
Guarnieri S, Morabito C, Bevere M, Lanuti P, Mariggiò MA. A protective strategy to counteract the oxidative stress induced by simulated microgravity on H9C2 cardiomyocytes. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:9951113.
Camberos V, Baio J, Mandujano A, Martinez AF, Bailey L, Hasaniya N, et al. The impact of spaceflight and microgravity on the human Islet-1+ cardiovascular progenitor cell transcriptome. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3577.
Liang L, Yuan W, Qu L, Li H, Zhang L, Fan GC, et al. Administration of losartan preserves cardiomyocyte size and prevents myocardial dysfunction in tail-suspended mice by inhibiting p47(phox) phosphorylation, NADPH oxidase activation and MuRF1 expression. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):279.
Liang L, Li H, Cao T, Qu L, Zhang L, Fan GC, et al. Calpain activation mediates microgravity-induced myocardial abnormalities in mice via p38 and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(49):16840–51.
Kang H, Fan Y, Sun A, Jia X, Deng X. Simulated microgravity exposure modulates the phenotype of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;66(1):121–30.
Janmaleki M, Pachenari M, Seyedpour SM, Shahghadami R, Sanati-Nezhad A. Impact of simulated microgravity on cytoskeleton and viscoelastic properties of endothelial cell. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32418.
Yan R, Liu H, Lv F, Deng Y, Li Y. Rac1/Wave2/Arp3 pathway mediates rat blood-brain barrier dysfunction under simulated microgravity based on proteomics strategy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5165.
Zhang R, Jiang M, Zhang J, Qiu Y, Li D, Li S, et al. Regulation of the cerebrovascular smooth muscle cell phenotype by mitochondrial oxidative injury and endoplasmic reticulum stress in simulated microgravity rats via the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(8):165799.
Liu ZF, Wang HM, Jiang M, Wang L, Lin LJ, Zhao YZ, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress enhances vasoconstriction by altering calcium homeostasis in cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells under simulated microgravity. Biomed Environ Sci. 2021;34(3):203–12.
Zhao H, Shi Y, Qiu C, Zhao J, Gong Y, Nie C, et al. Effects of simulated microgravity on ultrastructure and apoptosis of choroidal vascular endothelial cells. Front Physiol. 2020;11:577325.
Locatelli L, Cazzaniga A, De Palma C, Castiglioni S, Maier JAM. Mitophagy contributes to endothelial adaptation to simulated microgravity. FASEB J. 2020;34(1):1833–45.
Li C, Pan Y, Tan Y, Wang Y, Sun X. PINK1-dependent mitophagy reduced endothelial hyperpermeability and cell migration capacity under simulated microgravity. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:896014.
Hoffler GW, Wolthuis RA, Johnson RL. Apollo space crew cardiovascular evaluations. Aerosp Med. 1974;45(8):807–23.
Nicogossian A, Hoffler GW, Johnson RL, Gowen RJ. Determination of cardiac size following space missions of different durations: the second manned Skylab mission. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1976;47(4):362–5.
Buderer MC, Rummel JA, Michel EL, Mauldin DG, Sawin CF. Exercise cardiac output following Skylab missions: the second manned Skylab mission. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1976;47(4):365–72.
Norsk P. Adaptation of the cardiovascular system to weightlessness: surprises, paradoxes and implications for deep space missions. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020;228(3):e13434.
Quiñones MA. Assessment of diastolic function. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2005;47(5):340–55.
Previtali M, Chieffo E, Ferrario M, Klersy C. Is mitral E/E’ ratio a reliable predictor of left ventricular diastolic pressures in patients without heart failure? Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;13(7):588–95.
Carrick-Ranson G, Hastings JL, Bhella PS, Shibata S, Levine BD. The effect of exercise training on left ventricular relaxation and diastolic suction at rest and during orthostatic stress after bed rest. Exp Physiol. 2013;98(2):501–13.
Kumar A, Tahimic CGT, Almeida EAC, Globus RK. Spaceflight modulates the expression of key oxidative stress and cell cycle related genes in heart. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):9088.
Liu H, Xie Q, Xin BM, Liu JL, Liu Y, Li YZ, et al. Inhibition of autophagy recovers cardiac dysfunction and atrophy in response to tail-suspension. Life Sci. 2015;121:1–9.
Barańska W, Skopiński P, Kaplański A. Morphometrical evaluation of myocardium from rats flown on biosatellite Cosmos-1887. Mater Med Pol. 1990;22(4):255–7.
Morey-Holton ER, Globus RK. Hindlimb unloading rodent model: technical aspects. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002;92(4):1367–77.
Globus RK, Morey-Holton E. Hindlimb unloading: rodent analog for microgravity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016;120(10):1196–206.
Hargens AR, Vico L. Long-duration bed rest as an analog to microgravity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016;120(8):891–903.
Tomilovskaya E, Shigueva T, Sayenko D, Rukavishnikov I, Kozlovskaya I. Dry immersion as a ground-based model of microgravity physiological effects. Front Physiol. 2019;10:284.
Amirova L, Navasiolava N, Rukavishvikov I, Gauquelin-Koch G, Gharib C, Kozlovskaya I, et al. Cardiovascular system under simulated weightlessness: head-down bed rest vs. dry immersion. Front Physiol. 2020;11:395.
Nguyen HP, Tran PH, Kim KS, Yang SG. The effects of real and simulated microgravity on cellular mitochondrial function. NPJ Micrograv. 2021;7(1):44.
Petersen LG, Damgaard M, Petersen JC, Norsk P. Mechanisms of increase in cardiac output during acute weightlessness in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;111(2):407–11.
Lee SMC, Martin DS, Miller CA, Scott JM, Laurie SS, Macias BR, et al. Venous and arterial responses to partial gravity. Front Physiol. 2020;11:863.
Kohn F, Hauslage J, Hanke W. Membrane fluidity changes, a basic mechanism of interaction of gravity with cells? Micrograv Sci Technol. 2017;29(5):337–42.
Respress JL, Gershovich PM, Wang T, Reynolds JO, Skapura DG, Sutton JP, et al. Long-term simulated microgravity causes cardiac RyR2 phosphorylation and arrhythmias in mice. Int J Cardiol. 2014;176(3):994–1000.
Acharya A, Brungs S, Lichterfeld Y, Hescheler J, Hemmersbach R, Boeuf H, et al. Parabolic, flight-induced, acute hypergravity and microgravity effects on the beating rate of human cardiomyocytes. Cells. 2019;8(4):352.
Cui Y, Zhang SM, Zhang QY, Fan R, Li J, Guo HT, et al. Modulation of intracellular calcium transient in response to beta-adrenoceptor stimulation in the hearts of 4-wk-old rats during simulated weightlessness. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010;108(4):838–44.
Helmstadter KG, Ljubojevic-Holzer S, Wood BM, Taheri KD, Sedej S, Erickson JR, et al. CaMKII and PKA-dependent phosphorylation co-regulate nuclear localization of HDAC4 in adult cardiomyocytes. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021;116(1):11.
Wang AH, Yang XJ. Histone deacetylase 4 possesses intrinsic nuclear import and export signals. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(17):5992–6005.
Zhong G, Li Y, Li H, Sun W, Cao D, Li J, et al. Simulated microgravity and recovery-induced remodeling of the left and right ventricle. Front Physiol. 2016;7:274.
Snyder LB, Lai Y, Doviak H, Freeburg LA, Laney VK, Moore A, et al. Ubiquitin ligase Wwp1 gene deletion attenuates diastolic dysfunction in pressure-overload hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021;321(5):H976–84.
Zhao Y, Zhong G, Du R, Zhao D, Li J, Li Y, et al. Ckip-1 3’-UTR attenuates simulated microgravity-induced cardiac atrophy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:796902.
Zhao D, Zhong G, Li J, Pan J, Zhao Y, Song H, et al. Targeting E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 prevents cardiac hypertrophy through destabilizing DVL2 via inhibition of K27-linked ubiquitination. Circulation. 2021;144(9):694–711.
Ling S, Sun Q, Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang P, Wang X, et al. CKIP-1 inhibits cardiac hypertrophy by regulating class II histone deacetylase phosphorylation through recruiting PP2A. Circulation. 2012;126(25):3028–40.
Veliz AL, Mamoun L, Hughes L, Vega R, Holmes B, Monteon A, et al. Transcriptomic effects on the mouse heart following 30 days on the International Space Station. Biomolecules. 2023;13(2):371.
Connor MK, Hood DA. Effect of microgravity on the expression of mitochondrial enzymes in rat cardiac and skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1998;84(2):593–8.
Acharya A, Nemade H, Papadopoulos S, Hescheler J, Neumaier F, Schneider T, et al. Microgravity-induced stress mechanisms in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. iScience. 2022;25(7):104577.
Garrett-Bakelman FE, Darshi M, Green SJ, Gur RC, Lin L, Macias BR, et al. The NASA Twins study: a multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight. Science. 2019;364(6436):eaau8650.
Greaves D, Guillon L, Besnard S, Navasiolava N, Arbeille P. 4 Day in dry immersion reproduces partially the aging effect on the arteries as observed during 6 month spaceflight or confinement. NPJ Micrograv. 2021;7(1):43.
Su YT, Cheng YP, Zhang X, Xie XP, Chang YM, Bao JX. Acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide mediates structural remodeling of cerebral artery and small mesenteric artery in simulated weightless rats. Life Sci. 2020;243: 117253.
Willeit P, Tschiderer L, Allara E, Reuber K, Seekircher L, Gao L, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness progression as surrogate marker for cardiovascular risk: meta-analysis of 119 clinical trials involving 100 667 patients. Circulation. 2020;142(7):621–42.
Dijk JM, Algra A, van der Graaf Y, Grobbee DE, Bots ML. Carotid stiffness and the risk of new vascular events in patients with manifest cardiovascular disease. The SMART study. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(12):1213–20.
Li TZ, Yuan M, Chen ZH, Guo YH, Kang CY, Wang JY, et al. Effect of simulated microgravity and its associated mechanism on pulmonary circulation in rats. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013;26(2):118–27.
Mocumbi A, Humbert M, Saxena A, Jing ZC, Sliwa K, Thienemann F, et al. Pulmonary hypertension. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024;10(1):1.
Deanfield JE, Halcox JP, Rabelink TJ. Endothelial function and dysfunction: testing and clinical relevance. Circulation. 2007;115(10):1285–95.
Buravkova LB, Rudimov EG, Andreeva ER, Grigoriev AI. The ICAM-1 expression level determines the susceptibility of human endothelial cells to simulated microgravity. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(3):2875–85.
Zonneveld R, Martinelli R, Shapiro NI, Kuijpers TW, Plötz FB, Carman CV. Soluble adhesion molecules as markers for sepsis and the potential pathophysiological discrepancy in neonates, children and adults. Crit Care. 2014;18(2):204.
Giannotta M, Trani M, Dejana E. VE-cadherin and endothelial adherens junctions: active guardians of vascular integrity. Dev Cell. 2013;26(5):441–54.
Liu H, Wang ZC, Yue Y, Yu JW, Cai Y, Bai YG, et al. Simulated microgravity induces an inflammatory response in the common carotid artery of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;92(8):661–8.
Jiang M, Wang H, Liu Z, Lin L, Wang L, Xie M, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent activation of iNOS/NO-NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to endothelial inflammation and apoptosis associated with microgravity. FASEB J. 2020;34(8):10835–49.
Ma J, Kahwaji CI, Ni Z, Vaziri ND, Purdy RE. Effects of simulated microgravity on arterial nitric oxide synthase and nitrate and nitrite content. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2003;94(1):83–92.
Sangha DS, Vaziri ND, Ding Y, Purdy RE. Vascular hyporesponsiveness in simulated microgravity: role of nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2000;88(2):507–17.
White AR, Ryoo S, Bugaj L, Attarzadeh DO, Thiyagarajan S, Chen K, et al. Early changes in vasoreactivity after simulated microgravity are due to an upregulation of the endothelium-dependent nitric oxide/cGMP pathway. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;110(2):395–404.
Zhang R, Bai YG, Lin LJ, Bao JX, Zhang YY, Tang H, et al. Blockade of AT1 receptor partially restores vasoreactivity, NOS expression, and superoxide levels in cerebral and carotid arteries of hindlimb unweighting rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;106(1):251–8.
Sun L, Wang DS, Ren W, Xiang QL. Changes in vasoreactivity of rat pulmonary artery after 7 d tail-suspension. Space Med Med Eng (Beijing). 2001;14(1):1–5.
Nyhan D, Kim S, Dunbar S, Li D, Shoukas A, Berkowitz DE. Impaired pulmonary artery contractile responses in a rat model of microgravity: role of nitric oxide. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002;92(1):33–40.
Zhang R, Ran HH, Cai LL, Zhu L, Sun JF, Peng L, et al. Simulated microgravity-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in rat cerebral arteries. FASEB J. 2014;28(6):2715–24.
Zhang R, Ran HH, Peng L, Xu F, Sun JF, Zhang LN, et al. Mitochondrial regulation of NADPH oxidase in hindlimb unweighting rat cerebral arteries. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95916.
Cho HJ, Cho HJ, Kim HS. Osteopontin: a multifunctional protein at the crossroads of inflammation, atherosclerosis, and vascular calcification. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2009;11(3):206–13.
Suganuma E, Babaev VR, Motojima M, Zuo Y, Ayabe N, Fogo AB, et al. Angiotensin inhibition decreases progression of advanced atherosclerosis and stabilizes established atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(8):2311–9.
Dillmann WH. Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2019;124(8):1160–2.
Kadosaka T, Watanabe M, Natsui H, Koizumi T, Nakao M, Koya T, et al. Empagliflozin attenuates arrhythmogenesis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by normalizing intracellular Ca2+ handling in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023;324(3):H341–54.
Okabe K, Matsushima S, Ikeda S, Ikeda M, Ishikita A, Tadokoro T, et al. DPP (dipeptidyl peptidase)-4 Inhibitor attenuates Ang II (angiotensin II)-induced cardiac hypertrophy via GLP (glucagon-like peptide)-1-dependent suppression of Nox (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase) 4-HDAC (histone deacetylase) 4 pathway. Hypertension. 2020;75(4):991–1001.
Khajehlandi M, Bolboli L, Siahkuhian M, Rami M, Tabandeh M, Khoramipour K, et al. Endurance training regulates expression of some angiogenesis-related genes in cardiac tissue of experimentally induced diabetic rats. Biomolecules. 2021;11(4):498.
Zuo GF, Ren XM, Ge Q, Luo J, Ye P, Wang F, et al. Activation of the PP2A catalytic subunit by ivabradine attenuates the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;130:170–83.
Lu X, Yang B, Qi R, Xie Q, Li T, Yang J, et al. Targeting WWP1 ameliorates cardiac ischemic injury by suppressing KLF15-ubiquitination mediated myocardial inflammation. Theranostics. 2023;13(1):417–37.
Matsubara J, Sugiyama S, Sugamura K, Nakamura T, Fujiwara Y, Akiyama E, et al. A dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, des-fluoro-sitagliptin, improves endothelial function and reduces atherosclerotic lesion formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(3):265–76.
Lim S, Lee GY, Park HS, Lee DH, Tae Jung O, Kyoung Min K, et al. Attenuation of carotid neointimal formation after direct delivery of a recombinant adenovirus expressing glucagon-like peptide-1 in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113(2):183–94.
Siragusa M, Oliveira Justo AF, Malacarne PF, Strano A, Buch A, Withers B, et al. VE-PTP inhibition elicits eNOS phosphorylation to blunt endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in diabetes. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(6):1546–56.
Rossman MJ, Santos-Parker JR, Steward CAC, Bispham NZ, Cuevas LM, Rosenberg HL, et al. Chronic supplementation with a mitochondrial antioxidant (MitoQ) improves vascular function in healthy older adults. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):1056–63.
Lehmann LH, Jebessa ZH, Kreusser MM, Horsch A, He T, Kronlage M, et al. A proteolytic fragment of histone deacetylase 4 protects the heart from failure by regulating the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway. Nat Med. 2018;24(1):62–72.
Jiang H, Jia D, Zhang B, Yang W, Dong Z, Sun X, et al. Exercise improves cardiac function and glucose metabolism in mice with experimental myocardial infarction through inhibiting HDAC4 and upregulating GLUT1 expression. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020;115(3):28.
El Assar M, Álvarez-Bustos A, Sosa P, Angulo J, Rodríguez-Mañas L. Effect of physical activity/exercise on oxidative stress and inflammation in muscle and vascular aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8713.
Morishima T, Tsuchiya Y, Iemitsu M, Ochi E. High-intensity resistance exercise with low repetitions maintains endothelial function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;315(3):H681–6.
Qiu S, Cai X, Yin H, Sun Z, Zügel M, Steinacker JM, et al. Exercise training and endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):64.
da Cunha ND, Schoenfeld BJ, Prestes J. Potential implications of blood flow restriction exercise on vascular health: a brief review. Sports Med. 2020;50(1):73–81.
Shay JW, Cucinotta FA, Sulzman FM, Coleman CN, Minna JD. From mice and men to earth and space: joint NASA-NCI workshop on lung cancer risk resulting from space and terrestrial radiation. Cancer Res. 2011;71(22):6926–9.
Seawright JW, Sridharan V, Landes RD, Cao M, Singh P, Koturbash I, et al. Effects of low-dose oxygen ions and protons on cardiac function and structure in male C57BL/6J mice. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2019;20:72–84.
Nemec-Bakk AS, Sridharan V, Landes RD, Singh P, Cao M, Dominic P, et al. Effects of low-dose oxygen ions on cardiac function and structure in female C57BL/6J mice. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2022;32:105–12.
Brojakowska A, Jackson CJ, Bisserier M, Khlgatian MK, Grano C, Blattnig SR, et al. Lifetime evaluation of left ventricular structure and function in male C57BL/6J mice after gamma and space-type radiation exposure. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5451.
Yan X, Sasi SP, Gee H, Lee J, Yang Y, Mehrzad R, et al. Cardiovascular risks associated with low dose ionizing particle radiation. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e110269.
Kobayashi S, Susa T, Tanaka T, Wada Y, Okuda S, Doi M, et al. Urinary 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine reflects symptomatic status and severity of systolic dysfunction in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2011;13(1):29–36.
van der Pol A, van Gilst WH, Voors AA, van der Meer P. Treating oxidative stress in heart failure: past, present and future. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21(4):425–35.
Shiloh Y, Ziv Y. The ATM protein kinase: regulating the cellular response to genotoxic stress, and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(4):197–210.
Halade GV, Lee DH. Inflammation and resolution signaling in cardiac repair and heart failure. EBioMedicine. 2022;79:103992.
Gadeberg HC, Bryant SM, James AF, Orchard CH. Altered Na/Ca exchange distribution in ventricular myocytes from failing hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;310(2):H262–8.
Ragone I, Barallobre-Barreiro J, Takov K, Theofilatos K, Yin X, Schmidt LE, et al. SERCA2a protein levels are unaltered in human heart failure. Circulation. 2023;148(7):613–6.
Bushdid PB, Osinska H, Waclaw RR, Molkentin JD, Yutzey KE. NFATc3 and NFATc4 are required for cardiac development and mitochondrial function. Circ Res. 2003;92(12):1305–13.
Yang TT, Xiong Q, Enslen H, Davis RJ, Chow CW. Phosphorylation of NFATc4 by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(11):3892–904.
Koturbash I, Miousse IR, Sridharan V, Nzabarushimana E, Skinner CM, Melnyk SB, et al. Radiation-induced changes in DNA methylation of repetitive elements in the mouse heart. Mutat Res. 2016;787:43–53.
Miousse IR, Skinner CM, Sridharan V, Seawright JW, Singh P, Landes RD, et al. Changes in one-carbon metabolism and DNA methylation in the hearts of mice exposed to space environment-relevant doses of oxygen ions (16O). Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2019;22:8–15.
Seawright JW, Samman Y, Sridharan V, Mao XW, Cao M, Singh P, et al. Effects of low-dose rate γ-irradiation combined with simulated microgravity on markers of oxidative stress, DNA methylation potential, and remodeling in the mouse heart. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0180594.
Napoli C, Benincasa G, Donatelli F, Ambrosio G. Precision medicine in distinct heart failure phenotypes: focus on clinical epigenetics. Am Heart J. 2020;224:113–28.
Yu T, Parks BW, Yu S, Srivastava R, Gupta K, Wu X, et al. Iron-ion radiation accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Radiat Res. 2011;175(6):766–73.
Belzile-Dugas E, Eisenberg MJ. Radiation-induced cardiovascular disease: review of an underrecognized pathology. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(18): e021686.
Helm A, Lee R, Durante M, Ritter S. The influence of C-ions and X-rays on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Front Oncol. 2016;6:5.
Yang VV, Stearner SP, Ainsworth EJ. Late ultrastructural changes in the mouse coronary arteries and aorta after fission neutron or 60Co gamma irradiation. Radiat Res. 1978;74(3):436–56.
Farah C, Michel LYM, Balligand JL. Nitric oxide signalling in cardiovascular health and disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(5):292–316.
Soucy KG, Lim HK, Kim JH, Oh Y, Attarzadeh DO, Sevinc B, et al. HZE 5⁶Fe-ion irradiation induces endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta: role of xanthine oxidase. Radiat Res. 2011;176(4):474–85.
Dong X, Tong F, Qian C, Zhang R, Dong J, Wu G, et al. NEMO modulates radiation-induced endothelial senescence of human umbilical veins through NF-κB signal pathway. Radiat Res. 2015;183(1):82–93.
Hendry JH, Akahoshi M, Wang LS, Lipshultz SE, Stewart FA, Trott KR. Radiation-induced cardiovascular injury. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2008;47(2):189–93.
Hamada N, Kawano KI, Yusoff FM, Furukawa K, Nakashima A, Maeda M, et al. Ionizing irradiation induces vascular damage in the aorta of wild-type mice. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(10):3030.
Baselet B, Rombouts C, Benotmane AM, Baatout S, Aerts A. Cardiovascular diseases related to ionizing radiation: the risk of low-dose exposure (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(6):1623–41.
Wu Z, Chen T, Qian Y, Luo G, Liao F, He X, et al. High-dose ionizing radiation accelerates atherosclerotic plaque progression by regulating P38/NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy/ferroptosis of endothelial cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023;117(1):223–36.
Yubero-Serrano EM, Fernandez-Gandara C, Garcia-Rios A, Rangel-Zuñiga OA, Gutierrez-Mariscal FM, Torres-Peña JD, et al. Mediterranean diet and endothelial function in patients with coronary heart disease: an analysis of the CORDIOPREV randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2020;17(9):e1003282.
Riccardi G, Giosuè A, Calabrese I, Vaccaro O. Dietary recommendations for prevention of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(5):1188–204.
García-Prieto CF, Fernández-Alfonso MS. Caloric restriction as a strategy to improve vascular dysfunction in metabolic disorders. Nutrients. 2016;8(6):370.
Elagizi A, Lavie CJ, O’Keefe E, Marshall K, O’Keefe JH, Milani RV. An update on omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular health. Nutrients. 2021;13(1):204.
Frei B, Birlouez-Aragon I, Lykkesfeldt J. Authors’ perspective: what is the optimum intake of vitamin C in humans? Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(9):815–29.
Violi F, Nocella C, Loffredo L, Carnevale R, Pignatelli P. Interventional study with vitamin E in cardiovascular disease and meta-analysis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;178:26–41.
Clements WT, Lee SR, Bloomer RJ. Nitrate ingestion: a review of the health and physical performance effects. Nutrients. 2014;6(11):5224–64.
Tierney AC, Rumble CE, Billings LM, George ES. Effect of dietary and supplemental lycopene on cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Nutr. 2020;11(6):1453–88.
Lapatto HAK, Kuusela M, Heikkinen A, Muniandy M, van der Kolk BW, Gopalakrishnan S, et al. Nicotinamide riboside improves muscle mitochondrial biogenesis, satellite cell differentiation, and gut microbiota in a twin study. Sci Adv. 2023;9(2):eadd5163.
Bredemeier M, Lopes LM, Eisenreich MA, Hickmann S, Bongiorno GK, d’Avila R, et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors for prevention of cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018;18(1):24.
Schmalen I, Reischl S, Wallach T, Klemz R, Grudziecki A, Prabu JR, et al. Interaction of circadian clock proteins CRY1 and PER2 is modulated by zinc binding and disulfide bond formation. Cell. 2014;157(5):1203–15.
Song S, Tien CL, Cui H, Basil P, Zhu N, Gong Y, et al. Myocardial Rev-erb-mediated diurnal metabolic rhythm and obesity paradox. Circulation. 2022;145(6):448–64.
Guo JH, Qu WM, Chen SG, Chen XP, Lv K, Huang ZL, et al. Keeping the right time in space: importance of circadian clock and sleep for physiology and performance of astronauts. Mil Med Res. 2014;1:23.
Barger LK, Flynn-Evans EE, Kubey A, Walsh L, Ronda JM, Wang W, et al. Prevalence of sleep deficiency and use of hypnotic drugs in astronauts before, during, and after spaceflight: an observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(9):904–12.
Monk TH, Kennedy KS, Rose LR, Linenger JM. Decreased human circadian pacemaker influence after 100 days in space: a case study. Psychosom Med. 2001;63(6):881–5.
Zhang H, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Tang C, Sun B, et al. Alterations in the activity and sleep of Drosophila melanogaster under simulated microgravity. NPJ Microgravity. 2021;7(1):27.
Fujita SI, Rutter L, Ong Q, Muratani M. Integrated RNA-seq analysis indicates asynchrony in clock genes between tissues under spaceflight. Life (Basel). 2020;10(9):196.
Archer SN, Möller-Levet C, Bonmatí-Carrión M, Laing EE, Dijk DJ. Extensive dynamic changes in the human transcriptome and its circadian organization during prolonged bed rest. iScience. 2024;27(3):109331.
Bonmatí-Carrión M, Santhi N, Atzori G, Mendis J, Kaduk S, Dijk DJ, et al. Effect of 60 days of head down tilt bed rest on amplitude and phase of rhythms in physiology and sleep in men. NPJ Microgravity. 2024;10(1):42.
Liu Z, Wan Y, Zhang L, Tian Y, Lv K, Li Y, et al. Alterations in the heart rate and activity rhythms of three orbital astronauts on a space mission. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2015;4:62–6.
Karemaker JM, Berecki-Gisolf J. 24-h blood pressure in space: the dark side of being an astronaut. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009;169(Suppl 1):S55–8.
Shiraishi M, Kamo T, Kamegai M, Baevsky RM, Funtova II, Chernikova A, et al. Periodic structures and diurnal variation in blood pressure and heart rate in relation to microgravity on space station MIR. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004;58(Suppl 1):S31–4.
El Jamal N, Lordan R, Teegarden SL, Grosser T, FitzGerald G. The circadian biology of heart failure. Circ Res. 2023;132(2):223–37.
Li E, Li X, Huang J, Xu C, Liang Q, Ren K, et al. BMAL1 regulates mitochondrial fission and mitophagy through mitochondrial protein BNIP3 and is critical in the development of dilated cardiomyopathy. Protein Cell. 2020;11(9):661–79.
Ingle KA, Kain V, Goel M, Prabhu SD, Young ME, Halade GV. Cardiomyocyte-specific Bmal1 deletion in mice triggers diastolic dysfunction, extracellular matrix response, and impaired resolution of inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(11):H1827–36.
Alibhai FJ, LaMarre J, Reitz CJ, Tsimakouridze EV, Kroetsch JT, Bolz SS, et al. Disrupting the key circadian regulator CLOCK leads to age-dependent cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017;105:24–37.
Reitz CJ, Alibhai FJ, de Lima-Seolin BG, Nemec-Bakk A, Khaper N, Martino TA. Circadian mutant mice with obesity and metabolic syndrome are resilient to cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;319(5):H1097–111.
Costello HM, Sharma RK, McKee AR, Gumz ML. Circadian disruption and the molecular clock in atherosclerosis and hypertension. Can J Cardiol. 2023;39(12):1757–71.
Schilperoort M, van den Berg R, Bosmans LA, van Os BW, Dollé MET, Smits NAM, et al. Disruption of circadian rhythm by alternating light-dark cycles aggravates atherosclerosis development in APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice. J Pineal Res. 2020;68(1):e12614.
Yang G, Chen L, Grant GR, Paschos G, Song WL, Musiek ES, et al. Timing of expression of the core clock gene Bmal1 influences its effects on aging and survival. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(324):324ra16.
Anea CB, Cheng B, Sharma S, Kumar S, Caldwell RW, Yao L, et al. Increased superoxide and endothelial NO synthase uncoupling in blood vessels of Bmal1-knockout mice. Circ Res. 2012;111(9):1157–65.
Lin C, Xu L, Tang X, Li X, Lu C, Cheng Q, et al. Clock gene Bmal1 disruption in vascular smooth muscle cells worsens carotid atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022;42(5):565–79.
Chen L, Zhang B, Yang L, Bai YG, Song JB, Ge YL, et al. BMAL1 disrupted intrinsic diurnal oscillation in rat cerebrovascular contractility of simulated microgravity rats by altering circadian regulation of miR-103/CaV1.2 signal pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):3947.
Pan X, Jiang XC, Hussain MM. Impaired cholesterol metabolism and enhanced atherosclerosis in clock mutant mice. Circulation. 2013;128(16):1758–69.
Wang CY, Wen MS, Wang HW, Hsieh IC, Li Y, Liu PY, et al. Increased vascular senescence and impaired endothelial progenitor cell function mediated by mutation of circadian gene Per2. Circulation. 2008;118(21):2166–73.
Viswambharan H, Carvas JM, Antic V, Marecic A, Jud C, Zaugg CE, et al. Mutation of the circadian clock gene Per2 alters vascular endothelial function. Circulation. 2007;115(16):2188–95.
Yang L, Chu Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhao X, He W, et al. Overexpression of CRY1 protects against the development of atherosclerosis via the TLR/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;28(1):525–30.
Sutton EL. Insomnia. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(3):Itc33–48.
Riemann D, Nissen C, Palagini L, Otte A, Perlis ML, Spiegelhalder K. The neurobiology, investigation, and treatment of chronic insomnia. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(5):547–58.
Long V, Guertin MC, Dyrda K, Benrimoh D, Brouillette J. Descriptive study of anxiety and posttraumatic stress disorders in cardiovascular disease patients: from referral to cardiopsychiatric diagnoses. Psychother Psychosom. 2018;87(6):370–1.
Sato Y, Yoshihisa A, Hotsuki Y, Watanabe K, Kimishima Y, Kiko T, et al. Associations of benzodiazepine with adverse prognosis in heart failure patients with insomnia. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9(7):e013982.
Perlis ML, Posner D, Riemann D, Bastien CH, Teel J, Thase M. Insomnia Lancet. 2022;400(10357):1047–60.
Nowell PD, Mazumdar S, Buysse DJ, Dew MA, Reynolds CF 3rd, Kupfer DJ. Benzodiazepines and zolpidem for chronic insomnia: a meta-analysis of treatment efficacy. JAMA. 1997;278(24):2170–7.
Garde AH, Begtrup L, Bjorvatn B, Bonde JP, Hansen J, Hansen ÅM, et al. How to schedule night shift work in order to reduce health and safety risks. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2020;46(6):557–69.
Hannemann J, Laing A, Middleton B, Schwedhelm E, Marx N, Federici M, et al. Effect of oral melatonin treatment on insulin resistance and diurnal blood pressure variability in night shift workers. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Pharmacol Res. 2023;199:107011.
De Crescenzo F, D’Alò GL, Ostinelli EG, Ciabattini M, Di Franco V, Watanabe N, et al. Comparative effects of pharmacological interventions for the acute and long-term management of insomnia disorder in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2022;400(10347):170–84.
Krystal AD, Prather AA, Ashbrook LH. The assessment and management of insomnia: an update. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(3):337–52.
Solt LA, Wang Y, Banerjee S, Hughes T, Kojetin DJ, Lundasen T, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists. Nature. 2012;485(7396):62–8.
Banerjee S, Wang Y, Solt LA, Griffett K, Kazantzis M, Amador A, et al. Pharmacological targeting of the mammalian clock regulates sleep architecture and emotional behaviour. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5759.
Chung S, Lee EJ, Yun S, Choe HK, Park SB, Son HJ, et al. Impact of circadian nuclear receptor REV-ERBα on midbrain dopamine production and mood regulation. Cell. 2014;157(4):858–68.
Qian J, Vujovic N, Nguyen H, Rahman N, Heng SW, Amira S, et al. Daytime eating prevents mood vulnerability in night work. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(38): e2206348119.
Hirota T, Lee JW, St John PC, Sawa M, Iwaisako K, Noguchi T, et al. Identification of small molecule activators of cryptochrome. Science. 2012;337(6098):1094–7.
Sharma AX, Quittner-Strom EB, Lee Y, Johnson JA, Martin SA, Yu X, et al. Glucagon receptor antagonism improves glucose metabolism and cardiac function by promoting AMP-mediated protein kinase in diabetic mice. Cell Rep. 2018;22(7):1760–73.
Gill S, Le HD, Melkani GC, Panda S. Time-restricted feeding attenuates age-related cardiac decline in Drosophila. Science. 2015;347(6227):1265–9.
Manoogian ENC, Zadourian A, Lo HC, Gutierrez NR, Shoghi A, Rosander A, et al. Feasibility of time-restricted eating and impacts on cardiometabolic health in 24-h shift workers: the Healthy Heroes randomized control trial. Cell Metab. 2022;34(10):1442-56.e7.
Schilperoort M, Rensen PCN, Kooijman S. Time for novel strategies to mitigate cardiometabolic risk in shift workers. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020;31(12):952–64.
Singh BN, Yucel D, Garay BI, Tolkacheva EG, Kyba M, Perlingeiro RCR, et al. Proliferation and maturation: Janus and the Art of cardiac tissue engineering. Circ Res. 2023;132(4):519–40.
Hwang H, Rampoldi A, Forghani P, Li D, Fite J, Boland G, et al. Space microgravity increases expression of genes associated with proliferation and differentiation in human cardiac spheres. NPJ Microgravity. 2023;9(1):88.
Baio J, Martinez AF, Silva I, Hoehn CV, Countryman S, Bailey L, et al. Cardiovascular progenitor cells cultured aboard the International Space Station exhibit altered developmental and functional properties. NPJ Microgravity. 2018;4:13.
Rampoldi A, Forghani P, Li D, Hwang H, Armand LC, Fite J, et al. Space microgravity improves proliferation of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Reports. 2022;17(10):2272–85.
Camberos V, Baio J, Bailey L, Hasaniya N, Lopez LV, Kearns-Jonker M. Effects of spaceflight and simulated microgravity on YAP1 expression in cardiovascular progenitors: implications for cell-based repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2742.
Liu S, Tang L, Zhao X, Nguyen B, Heallen TR, Li M, et al. Yap promotes noncanonical Wnt signals from cardiomyocytes for heart regeneration. Circ Res. 2021;129(8):782–97.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (82125004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH, HJ, YFW, and JPS participated in the design and conception of the study. HH prepared the initial draft. HJ, YFW, and JPS reviewed and revised the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participants
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Jia, H., Wang, YF. et al. Cardiovascular adaptations and pathological changes induced by spaceflight: from cellular mechanisms to organ-level impacts. Military Med Res 11, 68 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-024-00570-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-024-00570-3