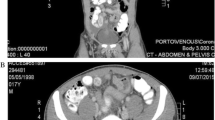
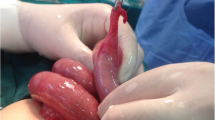
Abstract
Background
Perforation of Meckel Diverticulum (MD) is a rare cause of pneumoperitoneum in neonates. We hereby report six cases of perforation of MD in neonates, with addition of 53 cases from systematic review of the literature. A systematic review was performed using Mesh terms “Neonate, Meckel Diverticulum, Perforation, Pneumoperitoneum.” All reports of perforated MD in the English literature were identified. Details of our 6 cases were analyzed in similar fashion.
Results
A total of 3027 manuscripts were screened and 59 cases including 6 of our own were identified. The vast majority (78%) were female. Fifty patients (84.7%) presented in the newborn period. Half of the cases (52.5%) had associated anomalies and 13 neonates (22%) required oxygen supplementation including CPAP or ventilatory support before surgery. In 73% of the cases, a resection of gut was undertaken. Histopathological assessment in 44 cases (74.6%) revealed no ectopic gastric mucosa. Three cases demised prior to treatment. The outcome in the vast majority was excellent with 84.7% surviving and discharged well.
Conclusion
Perforated MD is an unusual cause of a pneumoperitoneum in the newborns. Diagnosis is established at laparotomy and it rare to find ectopic mucosa histopathologically. The overall outcome is excellent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pneumoperitoneum is a serious condition in neonates requiring immediate surgical intervention. The most common causes in this age group are necrotizing enterocolitis and intestinal atresia including a host of idiopathic pathologies. A rare cause is a perforated Meckel diverticulum (MD), of which, only a limited number of cases have been reported to date [1,2,3].
Authors encountered few cases of perforated MD and it intrigued us to look into the literature. We had many unanswered questions, which we intended to answer. These include
-
1.
As commonly said that MD is two times more common in males than females, does this rule also apply in neonates having perforated MD.
-
2.
What may be the cause of perforation of MD.? Is it hypertrophied gastric mucosa?
-
3.
What is the outcome in terms of survival of these neonates?
-
4.
Do these neonates present late in neonatal life? If so, then some environmental factor may be involved and must be investigated.
-
5.
Is there any particular pattern of presentations of perforated MD which may help us diagnose these patients early?
-
6.
What may the risk factors for mortality in these patients?
In this systematic review, we intended to look for the presentation details and outcomes of the newborns with MD and tried to answer these questions. Here, we report six cases of perforated MD in neonates and their details are being summarized in Table 1.
Methodology
We conducted this systematic review with the aim to get all reports from the literature about MD perforation in neonates. We used PRISMA checklist to maintain the integrity and structure. It was performed using Mesh terms “Neonate, Meckel Diverticulum, Perforation, Pneumoperitoneum.” Three databases were accessed: PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane. No filter for the time, language, or region was applied during the literature search, and all data to date (May 2021) was retrieved. We included all reports/studies reporting perforated MD in neonates. Two authors (NL and MA), acting independently identified full-text reports which were then collated. Included were all reports of perforation of MD, irrespective of the outcome. Further, reference lists of all those full texts were seen to identify any missing reports, and if found, it was included. Also, we went through the literature review table of these manuscripts to find any missing reports. Neonate was defined as any child within 30 days of life at the time of presentation. The following information was extracted from the reports; author, journal, year of publication, gestational age in weeks, gender, age at the time of presentation, the weight of the child at the time of presentation, associated anomaly, treatment strategy, histopathology report, in particular whether ectopic tissue was found, pre-operative history of ventilation, and outcome. Details of our own cases were similarly recorded on an Excel spreadsheet and analyzed. Along with simple descriptive statistics, we also conducted logistic regression analysis to look for the odd’s ratio (OR) for mortality among these factors in order to identify the risk factors.
Results
A total of 3027 manuscripts were screened and 62 cases were identified. Nine cases were excluded as the manuscripts were published in languages other than English [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60]. A total of 59 cases, including our own six cases, were finally included in the study (Table 1). The details of all the cases are summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
Twenty-three patients (39%) were born prematurely, and the majority of patients (79.7%) were male. Fifty patients (84.7%) presented in the newborn period. Almost half of the cases (52.5%) reported other congenital anomalies. These anomalies included Omphalocele, anorectal malformation, Hirschsprung’s disease, meconium ileus, and many more (Table 1). Mothers of 11 neonates had some complications during gestation, including, bronchial asthma, UTI, Diabetes, PIH, HELLP syndrome, and abruptio placenta. Thirteen neonates (22%) required oxygen supplementation including CPAP or ventilatory support before surgery. Preoperative imaging rarely gives a clue as to the cause of the pneumoperitoneum. Only one case was suspected preoperatively and the rest diagnosed at laparotomy. In 73% of the cases, surgeons opted to resect the involved segment and restore the continuity of the gut. Histopathological assessment in 44 cases (74.6%) revealed no ectopic gastric mucosa. Three cases were diagnosed on autopsy as patients died before any treatment. The outcome in the vast majority was excellent with 84.7% of cases discharged well. Composite data are summarized in Table 2. Logistic regression showed that none of the factors were significantly associated with the mortality among these patients (Table 3).
Discussion
MD is a remnant of the omphalomesenteric duct, which normally regresses during the 5th–7th week of gestation. Its typically a 3–6-cm-long outpouching on the antimesenteric border, 50–75 cm from the ileo-caecal junction and usually contains all four intestine layers. In 30 to 50% of patients, it contains ectopic tissues which maybe gastric, pancreatic, colonic, duodenal, or endometrial. Despite being the most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract, symptomatic manifestation in the neonatal period is rare. Complications may occur in up to 4% of cases, and in the symptomatic, intestinal perforation is seen fewer than 10% of cases [1]. Diverticular length and base diameter are well-known predisposing factors to complications with long, narrow-based diverticula thought to predispose to obstruction on the basis of intussusception and inflammation [3, 5, 7]. Common manifestations of neonatal MD include perforation, intussusception, segmental ileal dilatation, and ileal volvulus [8, 28, 61]. Bertozzi and colleagues [15] identified bowel obstruction (58.3%) and pneumoperitoneum (33.3%) as the most common clinical manifestations. Umbilical catheterization is a rare cause of iatrogenic perforation [61].
Typically, MD is synonymous with the rule of 2; seen in 2% of the population, twice as frequent in the male sex with two percent being symptomatic [15]. Our collective review of perforated cases found a significant male predominance with a ratio of 51 to 8. This trend is interesting and has not previously been identified and further study to explain this phenomenon is required.
The timing of presentation is also of interest as 84.7% of patients in this review presented within the first week of life. Some presented immediately after birth suggesting a peri or very early post-natal onset of pathology [23, 26, 45]. There is no evidence to suggest that the perforations occur antenatally and it would be rare for this to be detected as expectant mothers are not routinely subjected to ultrasound screening in the last days of pregnancy. Gilbert et al., reported a neonate who died before any intervention and suspected the perforation to be antenatal [49].
The etiology of perforated MD is elusive, and many theories have been put forth. In older children and adults, ulceration induced perforation secondary to gastric ectopic tissue within a MD is well recognized. Only 6.8% (n = 4) of cases in this study had documented gastric tissue within the MD suggesting that other factors are responsible [27]. Tekant et al. proposed H. Pylori infection as a possibility [34]. Some have postulated, but without much support, that this may be secondary to the separation of vitelline remnants from the abdominal wall [6]. Oyachi et al. proposed a knotting of a long MD around itself, leading to weakness in the intestine walls ultimately leading to perforation [27]. We however did not see evidence of this in our cases as the perforations were discreet and at the tip of the MD with no proximal obstruction.
A tenable hypothesis is diverticulitis within the pouch resulting in erosion of the wall with resultant perforation. In this review, although no ectopic mucosa was found (n = 44), inflammation was noted supporting the inflammatory hypothesis as a reasonable cause for the perforation. Although presentation is within the first week of life it is likely that the trigger for the inflammatory process occurs in the perinatal period with gradually progression. Notwithstanding this, a single case has been reported where abdominal distension with ventilatory support was required at birth and later surgery confirming a perforated MD [13].
Perforation of the appendix proximal to distal Hirschsprung’s disease is well documented. Skelly reported a case where the child had skip segment Hirschsprung’s disease, and a perforated MD [17].
The standard presentation for perforated MD is a clinically acute abdomen with X ray confirmation of free intra-abdominal air. Rarely, unusual manifestations such as a scrotal pneumatocele secondary a perforated MD are seen [39]. It is exceptional for a specific diagnosis to be made preoperatively and a definite diagnosis of MD is usually established on laparotomy. However, Ojha et al. reported a case of a neonate where a pre-operative abdominal X-ray showed a massively dilated gut loop with outpouching which raised the possibility of a perforated MD [31].
With respect to management, most surgeons, 72.9% (n = 43), opted for resection along with end-to-end anastomosis. However, in some cases, 10.2% (n = 6), due to the patient’s poor clinical status, surgeons opted for an ileostomy. More recently, laparoscopy has been utilized in the management of these cases [1]. In instances where patients are too unwell to be shifted to the operating room, exploration is performed in the NICU setting [14]. With adequate perioperative support, the outcome for these patients is excellent.
Perforated MD is a rare entity where the diagnosis is only made at exploration. The management involves a resection of the MD with primary or delayed anastomosis and the outcome is excellent. Ectopic gastric mucosa is not a frequent finding on histopathology and the pathogenesis of perforation is more likely to be related to an inflammatory process within the diverticulum.
In summary we found following answers:
-
1.
Question: As commonly said that MD is two times more common in males than females, does this rule also apply in neonates having perforated MD?
Answer: No, this rule does not apply in this cohort of patients. Male preponderance is much more (6.3:1)
-
2.
Question: What may be the cause of perforation of MD. Is it gastric mucosa?
Answer: Gastric mucosa is found in only 8.5% of cases. So, the cause remains largely unknown.
-
3.
Question: What is the outcome in terms of survival of these neonates?
Answer: Generally, these neonates have a good survival as other surgical conditions of this age group.
-
4.
Question: Do these neonates present late in neonatal life? If so, then some environmental factor may be involved and must be investigated.
Answer: Most of these patients present in early neonatal age, so we don’t presume the involvement of some environmental agents; however, the possibility can’t be ruled out.
-
5.
Question: Is there any particular pattern of presentations of perforated MD which may help us diagnose these patients early?
Answer: No, we did not find any particular pattern and generally it was non-specific presentation with intestinal obstruction.
-
6.
What may the risk factors for mortality in these patients?
Answer: We did not find any factor being significantly associated with the mortality.
Availability of data and materials
Available for review (if needed)
Abbreviations
- MD:
-
Meckel’s diverticulum
References
Masuko T, Tanaka Y, Kawashima H, Amano H. Diagnostic laparoscopy for neonatal perforated Meckel's diverticulum. J Minim Access Surg. 2016;12(1):71–2. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-9941.158150.
McKelvie M, Soares-Oliveira M, Wang-Koh Y, Trayers C, Aslam A. Beware the innocent presentation of a spontaneous perforated Meckel Diverticulum: A rare case and review of the literature. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2019;35(12):881–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/pec.0000000000001993.
Wang YJ, Wang T, Xia SL, Zhang YC, Chen WB, Li B. Perforation of Meckel`s diverticulum in a very low birth weight neonate with severe pneumoperitoneum and review of literature. Turk J Pediatr. 2019;61(3):460–5. https://doi.org/10.24953/turkjped.2019.03.025.
Bindi E, Cruccetti A, Ilari M, Mariscoli F, Carnielli VP, Simonini A, et al. Meckel's diverticulum perforation in a newborn positive to Sars-Cov-2. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2020;62:101641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsc.2020.101641.
Charki MT, Abdellaoui H, Andaloussi S, Oukhouya MA, Mahmoudi A, El Madi A, et al. Congenital fistulisation of Meckel's diverticulum in omphalocele sac: case report. Pan Afr Med J. 2019;32:20. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2019.32.20.15010.
Orelaru FO, Reddy NS, Brahmamdam P. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2018;37:37–40.
Le N, Alemayehu H, Singh V, Hendrickson RJ. Pneumoperitoneum in a micro–preemie due to perforated Meckel’s diverticulum. J Neonatal Surg. 2018;7(1):16. https://doi.org/10.21699/jns.v7i1.670.
Louati H, Zouari M, Jallouli M, Dhaou MB, Zitouni H, Mhiri R. Perforated Meckel's Diverticulum causing intussusception in a neonate. J Neonatal Surg. 2017;6(3):73. https://doi.org/10.21699/jns.v6i3.568.
Jin H, Han J-W, Oh C, Kim H-Y, Jung S-E. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in omphalocele. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2017;17:28–30.
Ayari F, Achour R, Boussetta A, Cheour M, Bensmail T. Neonatal perforation of Meckel diverticulum: About two cases. Health Care Curr Rev. 2017;5(183):2.
Frooghi M, Bahador A, Golchini A, Haghighat M, Ataollahi M, Javaherizadeh H. Perforated Meckel's Diverticulum in a 3-day-old Neonate; A Case Report. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2016;8(4):323–6. https://doi.org/10.15171/mejdd.2016.43.
Alvares BR, Yumioka AS, Dos Santos GG. Uncommon presentation of perforated Meckel's diverticulum in preterm newborn. Radiol Bras. 2015;48(4):265–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-3984.2014.0134.
Borgi A, Bouziri A, Boujelbene N, Sghairoun N, Belhadj S, Benjeballah N. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a very preterm baby revealed at birth. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2014;33(2):119–22. https://doi.org/10.3109/15513815.2013.850133.
Smolkin T, Hayari L, Zohar Y, Steinberg R, Makhoul IR. Meckel diverticulum in a premature infant: too tiny but still perforates. J Pediatr. 2013;162(5):1075.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.11.029.
Bertozzi M, Melissa B, Radicioni M, Magrini E, Appignani A. Symptomatic Meckel's diverticulum in newborn: two interesting additional cases and review of literature. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29(9):1002–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182a315e5.
Crankson S, Kadhi A, Al Tawil K, Ahmed IA. Meckel’s diverticulum: a rare cause of intestinal perforation in a preterm newborn. Ann Pediatr Surg. 2013;9(4):147–9.
Skelly B, Ervine E, Bisharat M, Gannon C, Dick A. Small bowel skip segment Hirschprung’s disease presenting with perforated Meckel’s diverticulum. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012;28(6):645–8.
Qasim M, Shaukat M. Spontaneous perforation of Meckel's Diverticulum in a neonate. J Neonatal Surg. 2012;1(1):11.
Lee DS. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a 1-day-old neonate. Am Surg. 2012;78(1):E26–7.
Khan A, de Waal K. Pneumoperitoneum in a Micropremie: Not always NEC. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:295657. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/295657.
Kampfen S, Hacker F, Schulzke S, Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a female neonate. In: Wkly SM, editor. Joint annual meeting of the foederatio Paedo medicorum helveticorum Swiss Society of Paediatrics Swiss Society of Paediatric Surgery Swiss Society for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychotherapy; August 13, 2011. SWITZERLAND: EMH SWISS MEDICAL PUBLISHERS LTD FARNSBURGERSTR 8, CH-4132 MUTTENZ; 2011. p. 33S-S.
Anay K, Ramesh N, Peter R, Varadarajan K. Spontaneous perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in an extremely premature baby. J Neonatal-Perinatal Med. 2011;4(3):273–5.
Nakazawa N, Shimotakahara A, Okazaki T, Lane GJ, Yamataka A. Antenatal perforation of meckel's diverticulum presenting as meconium peritonitis: Case report and literature review. J Japanese Soc Pediatr Surg. 2009;45(6):942–5. https://doi.org/10.11164/jjsps.45.6_942.
Alkan M, Guler G, Yildirim F, Doran F, Zorludemir U, Olcay I. Perforation of an inflamed Meckel's diverticulum in a newborn: report of a case. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2009;20(3):235–6. https://doi.org/10.4318/tjg.2009.0017.
Aguayo P, Fraser JD, St Peter SD, Ostlie DJ. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a micropremature infant and review of the literature. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009;25(6):539–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-009-2378-y.
Mavridis G, Livaditi E, Vassiliadou E, Christopoulos-Geroulanos G. Intrauterine fistulation of perforated Meckel's diverticulum to the surface of the sac of an intact exomphalos minor. Minerva Pediatr. 2008;60(2):253–4.
Oyachi N, Takano K, Hasuda N, Arai H, Koshizuka K, Matsumoto M. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum manifesting as aseptic peritonitis in a neonate: report of a case. Surg Today. 2007;37(10):881–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-007-3519-3.
Sy ED, Shan YS, Yang YR, Tsai HM, Lin CH. Hirschsprung’s disease, a rare precipitating factor in neonatal perforated Meckel’s diverticulum. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41(7):1319–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2006.03.041.
Chang YT, Lin JY, Huang YS. Spontaneous perforation of Meckel's diverticulum without peritonitis in a newborn: report of a case. Surg Today. 2006;36(12):1114–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-006-3317-3.
Lim JY, Jang SH, Cho JM, Ko GH, Park ES, Seo JH, et al. A case of Meckel's diverticulum presented with acute abdomen in a newborn. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;8(2):222.
Ojha S, Menon P, Rao KL. Meckel's diverticulum with segmental dilatation of the ileum: radiographic diagnosis in a neonate. Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34(8):649–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1165-0.
Zahraa J, Abu-Ekteish F, Al Bassam AR, Nosir AA. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate mimicking necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2003;19(6):418–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pec.0000101585.65509.02.
Okazaki S, Higuchi A, Yamamoto H, Haruhiko M, Kondo Y, Matsuda M, et al., editors. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate delivered to a mother with hyperthyroidism. Int Congr Ser; 2003: Elsevier.
Tekant GT, Yeşildağ E, Emir H, Yeker Y, Dervişoğlu S, Celayir S, et al. Association of Meckel's diverticulum perforation and Helicobacter pylori infection in a neonate. Pediatr Cerrahi Derg. 2001;15:39–40.
Kumar P, Ojha P, Singh UK. Spontaneous perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate. Indian Pediatr. 1998;35(9):906–8.
Gandy J, Byrne P, Lees G. Neonatal Meckel's diverticular inflammation with perforation. J Pediatr Surg. 1997;32(5):750–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3468(97)90024-5.
Yeh JT, Lai HS, Duh YC. Perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate. J Formos Med Assoc. 1996;95(8):644–5.
Ford EG, Woolley MM. Tracheoesophageal fistula associated with perforatead Meckel's diverticulum. J Pediatr Surg. 1992;27(9):1223–4.
Coppes M, Roukema J, Bax N. Scrotal pneumatocele: a rare phenomenon. J Pediatr Surg. 1991;26(12):1428–9.
Khope S, Rao PL. Intra-uterine perforation of Meckel's diverticulum with undescended testis (a case report). J Postgrad Med. 1988;34(2):114–6b.
Wright JE, Bhagwandeen SB. Antenatal perforation of Meckel's diverticulum presenting as an inflamed hydrocele. J Pediatr Surg. 1986;21(11):989–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3468(86)80119-1.
Dalens B, Tanguy A, Vanneuville G, Haberer JP. Spontaneous perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1981;12(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(81)90062-9.
McManus JE, Rao HK, Cochran RA Jr, Elhassani SB. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in the newborn. J S C Med Assoc. 1980;76(6):273–5.
Lin HP, Ong TH, Prathap K. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in the newborn. J Singap Paediatr Soc. 1978;20(1):54–5.
de Oliveira J. Neonatal peritonitis due to intrauterine perforation of Meckel's diverticulum: L. Gubern Salisachs and S. Ferrer Pi. Arch. de Pediat.(Barcelona) 17: 293–316, May–June 1966. J Pediatr Surg. 1967;2(3):278–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3468(67)90046-2.
Mestel A, Trusler G, Humphreys R, Simpson J. Pneumoperitoneum in the newborn. Can Med Assoc J. 1966;95(5):201.
Rogers C. Pneumoperitoneum in the newborn. Surgery. 1964;56:842.
Abramson DJ. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum, peritonitis, and intestinal obstruction in the newborn with survival. Meckel's diverticulum in siblings. Am J Dis Child. 1960;10:277–81. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.1960.04020040279018.
Gilbert EF, Rainey JR Jr. Meconium peritonitis caused by a rupture of a Meckel's diverticulum in a newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1958;53(5):597–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(58)80150-x.
Rosza S. Intrauterine perforation of Meckel's diverticulum. Am J Roentgenol Radium Therapy, Nucl Med. 1953;69:944–7.
Hunter WC. Perforated gangrenous Meckel's Diverticulum in a new-Born infant: Report of a case. Am J Dis Child. 1928;35(3):438–42.
Lamesch A. Peritonitis due to perforation of a Meckel's diverticulum combined with volvulus due to malrotation in a 5-day-old newborn infant. Bull Soc Sci Med Grand Duche Luxemb. 1971;108(2):211–5.
Kim DW, Kim SS, Park JO, Lee DS. Spontaneous perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a neonate. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;7(1):119–24.
Lee SHY, Kwun K. A case of perforated Meckel's diverticulum in a 5-day-old neonate. J Korean Surg Soc. 1989;36:817–21.
Afanas'ev VP. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a newborn infant. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 1980;9:100–1.
Butenko VN. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a 2-day-old infant. Klin Khir. 1981;12:47.
Buzykin PF. Perforation of Meckel's diverticulum in a newborn. Vestn Khir Im I I Grek. 1979;122(2):78–9.
Shukowski V. Perforated peritonitis in newborn. Med Obozr Mosk. 1902;57:117.
Daum R, Hollmann G. Fetal perforation of Meckel's diverticulum as a cause of newborn infant ileus. Zentralbl Chir. 1967;92(3):107–9.
Garrido F, Sanchez A, Rubio F, Hernandez A, Quintero S, Bernal C, et al. Intestinal perforation as the first sign of Meckel's diverticulum in the neonatal period. Rev Esp Pediatr. 1997;53:561–4.
Costa S, De Carolis MP, Savarese I, Manzoni C, Lacerenza S, Romagnoli C. An unusual complication of umbilical catheterisation. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167(12):1467–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-008-0691-4.
Acknowledgements
Nil
Funding
Nil
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Naeem Liaqat, Anies Mahomed: conceptualization, methodology, software. Sajid Nayyar, Nadeem Akhtar, Sajjad Ali: data curation, Writing—original draft preparation. Naveed Haider, Nadeem Akhtar: visualization, investigation, writing manuscript, and proof-reading. Nadeem Akhtar: supervision. Naeem Liaqat, Anies Mahomed: software, validation. Naeem Liaqat, Anies Mahomed, Sajid Nayyar, Nadeem Akhtar: writing—reviewing and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Yes, obtained.
Consent for publication
We give consent.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liaqat, N., Mahomed, A., Nayyar, S.I. et al. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum in neonates: a report of six cases and systematic review of the literature. Ann Pediatr Surg 18, 18 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43159-021-00154-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43159-021-00154-z