Abstract
Due to the construction problem of the original concrete mixing pile, the inclined settlement of a building occurred. After analysis and calculation, the uneven pile distribution in the north and south region is adopted to reduce the subsidence and correct the deviation. According to the comparison between the calculated results and the measured data of the project, the two are basically consistent, which indicates that the method of uneven pile distribution can successfully adjust the distribution of the reaction force of the base and achieve the effect of subsidence reduction and deviation correction.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Adopting new pile foundation reinforcement scheme for existing buildings foundation reinforcement and correction is more common reinforcement scheme, and each part of the existing buildings foundation quality accident is often accompanied by foundation uneven settlement, and the problem of excess tilt, therefore, in the process of strengthening full tilt, with uneven sheet pile can reduce the deformation, optimization of basal counterforce distribution difference.
2 Project Overview
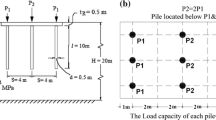
The main buildings of this project are shear wall structure, raft foundation, foundation buried depth of about 2.5–3.5 m. Among them, Building B has 15 floors above ground and 1 floor underground, and the basement is connected to the underground garage. The surface layer of the site is plain fill soil, and the underlying layer is Quaternary and Tertiary Marine sedimentary soil. From top to bottom, it is divided into 5 geotechnical engineering layers. The measured buried depth of stable water level is about 3 m. The typical geological profile is shown in Fig. 1, and the physical and mechanical parameters of the soil layer are shown in Table 1.
The basement soil of Building B is layer ② which is Medium sand with a bearing capacity characteristic value of 120 kPa. The superstructure design requires that the bearing capacity after foundation treatment is 300 kPa and 250 kPa, respectively. The bearing capacity and deformation of natural foundation can not meet the requirements of superstructure. The original foundation treatment scheme uses cement soil mixing pile composite foundation.
The design parameters of composite foundation of raw soil–cement mixing pile in Building B are as follows: The characteristic value of bearing capacity of single pile is 300kN, the characteristic value of bearing capacity of composite foundation is 250 kPa, the pile length is 15−18 m, the pile end falls in the fourth layer gravel sand layer, the pile spacing is 1 m and 1.2 m, the pile diameter is 500 mm, the strength grade of cement body of the pile is not less than 5.1 MPa, the thickness of mattress is 250 mm.
Since the construction of the main structure in July 2012, up to October 2013 before the foundation reinforcement, the settlement of the two buildings has been too large, with the settlement of building A reaching 30 cm and the settlement of Building B approaching 20 cm, and the inclination reaching 4.76‰. The settlement and differential settlement have no convergence trend. Therefore, it can be judged that there are defects in the construction quality of soil–cement mixing pile of this project, which has not reached the expected purpose of design.
3 Calculation Method and Results
When the existing building is reinforced and the new piles under the base pass through the soft soil layer and enter the distributed friction piles of relatively good soil layer, the settlement of the middle point of the reduced-sink composite pile foundation can be calculated according to the following formula [1, 2].
s- settlement amount at the center of pile foundation;
ss– midpoint settlement caused by additional pressure of foundation soil at the bottom of cap (Fig. 2.);
ssp– settlement caused by pile-soil interaction;
po– the hypothetical average additional pressure of natural foundation calculated by the combination of quasi-permanent values of load effects (kPa);
Esic– The compression modulus of the soil under the bottom of the cap shall be the modulus of the soil loaded after unloading;
m– The number of soil layers in the depth range of foundation settlement calculation; The calculated depth of settlement can be determined by stress ratio or deformation ratio.
qsu、Es– the average thickness-weighted ultimate friction and average compression modulus of the pile side within the range of the pile;
d– Pile diameter, when it is a square pile, d = 1.27b(b is the length of the section side of the square pile);
sa/d– equivalent distance to diameter ratio;
zi,zi-1– the distance between the bottom of the cap and the bottom surface of the i and i-1 layers;
αi,αi-1– the average additional stress coefficient of corner points from the bottom of cap to the bottom of the i and i-1 soil layers; Rectangle aspect ratio a/b and depth aspect ratio zi/b = 2zi/Bc were calculated according to equivalent cap area, which were determined by Appendix D of Technical Code for Building Pile Foundation (JGJ 94–2008). The equivalent width of the cap: Bc = B \(\sqrt{{A}_{C}}\)/L,B、L is the width and length of the outer edge plane of the building foundation;
F– Total additional load (kN) acting on the bottom of the bearing platform under the combination of quasi-permanent value of load effect;
ηp– Influence coefficient of foundation pile penetration deformation; According to the soil quality of the bearing layer of pile end, the sand is 1.0, the silt is 1.15, and the viscous soil is 1.30.
Ψ– The experience coefficient of settlement calculation is 1.0 if there is no local experience.
Building B has 14 floors above ground and 1 floor underground. The settlement amount at the maximum point (north side of the building) is 299.96 mm, at the minimum point (south side of the building) is 240.88 mm, and the maximum differential settlement amount from south to north is 59.08 mm. Therefore, uneven pile distribution is adopted to reduce subsidence and correct deviation in the north and south areas of the project. The steel pipe pile is φ299 mm/φ245 mm directly, the pile length is about 18 m, and the pile end falls on the gravel sand layer in layer 4. The bearing capacity of φ245 mm single pile is 250 kN, and that of φ299 mm single pile is 300 kN. The pile replacement ratio on the north side of the foundation is about 62%, and the pile replacement ratio on the south side is about 35% (Fig. 3.).
According to the results, the reaction force of the base on the south side of the foundation is about 50 kPa−200 kPa, and the reaction force of the base on the north side of the foundation is about 50 kPa−110 kPa, and the stress concentration state appears at the base side (Fig. 4, Fig. 5).
Through the adjustment of uneven pile distribution, the settlement gradually decreases from south to north. The new settlement in the south of the foundation is about 36 mm, and the north is about 21 mm, the settlement difference in the central axis is 15 mm. The foundation tilts to the south, and the foundation tilts back about 0.0013L. It shows that the variable stiffness leveling design of uneven pile can adjust the uneven settlement of foundation (Fig. 6, Fig. 7).
4 Comparative Analysis of Engineering Measurement and Design [3]
After the settlement of the building stabilized, the average measured soil stress between piles on the north side of the foundation of Building B was 45 kPa, on the south side was 85 kPa, and the average stress on the top of the mixing pile was 149 kPa. According to the results, the base reaction on the north side of the foundation was 80 kPa, and on the south side was 105 kPa (Fig. 8, Fig. 9).
In November 2013, the north pile was connected with the foundation and sealed. By May 2017, the measured post-construction deformation was 32 mm−46 mm. Excluding the settlement generated according to the original settlement rate, the construction disturbance settlement was about 15 mm, and the new settlement was about 17 mm−31 mm.
5 Conclusion
After the uneven pile distribution method was adopted in this project, the average measured soil stress between piles on the north side of the foundation was 45 kPa, on the south side was 85 kPa, and the average stress on the top of the stirred pile was 149 kPa. The pile replacement ratio of the north side of the foundation (the side with large settlement) is 62%, the calculated base reaction value of the north side of the foundation is 80 kPa, the pile replacement ratio of the south side of the foundation (the side with small settlement) is 35%, the calculated base reaction value of the south side of the foundation is 105 kPa. The new settlement in the south of the foundation is about 36 mm, in the north is about 21 mm, and the foundation receding is about 0.0013L. The results show that the distribution of basal reaction can be adjusted successfully by the method of uneven pile distribution, and the effect of subsidence reduction and deviation correction can be achieved.
References
China Academy of Building Research (2011) Code for design of building foundation (GB50007–2011) (Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press) p 28
China Academy of Building Research (2008) Technical code for building pile foundations (JGJ94–2008) (Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press) p 57
China Academy of Building Research (2012) Technical code for improvement of soil and foundation of existing buildings (JGJ123–2012) (Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press) p 37
Acknowledgements
This article was supported by the Science and Technology Program of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (2016-K5-055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, S. et al. (2023). Application of Ununiform Arrangement Piling in Reinforcement and Correction of Existing Structures. In: Feng, G. (eds) Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Civil Engineering. ICCE 2022. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 327. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2532-2_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2532-2_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2531-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2532-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)