Abstract
Background
The growth-regulating factor-interacting factor (GIF) gene family plays a vital role in regulating plant growth and development, particularly in controlling leaf, seed, and root meristem homeostasis. However, the regulatory mechanism of heteromorphic leaves by GIF genes in Populus euphratica as an important adaptative trait of heteromorphic leaves in response to desert environment remains unknown.
Results
This study aimed to identify and characterize the GIF genes in P. euphratica and other five Salicaceae species to investigate their role in regulating heteromorphic leaf development. A total of 27 GIF genes were identified and characterized across six Salicaceae species (P. euphratica, Populus pruinose, Populus deltoides, Populus trichocarpa, Salix sinopurpurea, and Salix suchowensis) at the genome-wide level. Comparative genomic analysis among these species suggested that the expansion of GIFs may be derived from the specific Salicaceae whole-genome duplication event after their divergence from Arabidopsis thaliana. Furthermore, the expression data of PeGIFs in heteromorphic leaves, combined with functional information on GIF genes in Arabidopsis, indicated the role of PeGIFs in regulating the leaf development of P. euphratica, especially PeGIFs containing several cis-acting elements associated with plant growth and development. By heterologous expression of the PeGIF3 gene in wild-type plants (Col-0) and atgif1 mutant of A. thaliana, a significant difference in leaf expansion along the medial-lateral axis, and an increased number of leaf cells, were observed between the overexpressed plants and the wild type.
Conclusion
PeGIF3 enhances leaf cell proliferation, thereby resulting in the expansion of the central-lateral region of the leaf. The findings not only provide global insights into the evolutionary features of Salicaceae GIFs but also reveal the regulatory mechanism of PeGIF3 in heteromorphic leaves of P. euphratica.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Salicaceae species are commonly chosen as exemplary forest trees in various research studies owing to their ease of vitro regeneration, rapid vegetative reproduction, and significant ecological and economic importance across the Northern Hemisphere [1,2,3,4]. In particular, Populus euphratica characterized by its extraordinary tolerance to drought and salinity, serves as a pivotal species in desert oases and stands out as an exceptional relic plant thriving in extremely arid environments [5, 6]. P. euphratica exhibits a distinct pattern of leaf heteroblasty, with adult trees displaying a sequential production of linear (Li, leaf index ≥ 4), lanceolate (La, 2 ≤ leaf index < 4), ovate (Ov, 1 ≤ leaf index < 2), and broad ovate (Bo, leaf index < 1) leaves as they ascend from the lower canopies to the upper canopies, accompanied by a gradual increase in leaf width and area [7]. Previous research indicated that broad Ov and Bo leaves in P. euphratica exhibit greater resilience to drought than narrow Li and La leaves, as evidenced by their thicker palisade tissue and enhanced photosynthetic activity [8]. In addition, a significant and positive association was observed between leaf area and the content of proline [9]. So, the presence of heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica suggests its capacity to adjust to the dry desert environment. Hence, identifying and characterizing the genes involving in the heteromorphic leaf development of P. euphratica are crucial for revealing the functional divergence and adaptive evolution of heteromorphic leaves.
Growth-regulating factors-Interacting Factors (GIFs) represent a class of transcriptional co-activators that collaborate with growth-regulating factors (GRFs). Typically, GIFs can interact with GRFs, forming a plant-specific transcriptional complex [10]. The GIF gene family was initially discovered in Arabidopsis thaliana in 2004 [11]. GIF genes have been intricately linked with plant growth and development [12, 13]. In a recent study, it was revealed that GIFs play a vital role in maintaining the precise expression patterns of key developmental factors [14]. GIF transcriptional coregulators assume the responsibility of regulating the quiescent center organization and the meristem size in A. thaliana [15]. GIF2 and GIF3 are two additional proteins instrumental in cell proliferation and the development of lateral organs [16]. Gif2 and gif3 mutations have been associated with the production of smaller lateral organs than the wild-type plant species in A. thaliana [17, 18]. The single gif mutant lines in A. thaliana presented a phenotype akin to the control, whereas the gif triple mutant gif1/gif2/gif3 exhibited an aberrant pistil [18].
Beyond their roles in model plants, GIFs exert considerable influence in rice [19, 20], maize [21], tomato [22], and tea [23]. Although GIFs have been investigated in certain plant species, further exploration of this gene family is warranted in Salicaceae. Recent advancements in the genomics of Salicaceae species offer an opportunity to characterize the GIF gene family. In the presents research, a genome-wide analysis of the GIF gene family was conducted. The structures, conserved motifs, cis-elements, and expression patterns of this family were characterized, a comparative genomics analysis was performed across six different Salicaceae species. The role of PeGIF3 in the heteromorphic leaf development in P. euphratica was further revealed through heterologous expression in A. thaliana. The results could offer crucial and precious data for forthcoming investigations concerning the functional characterization of the GIF gene family in Salicaceae species.
Results
Identification and characterization of GIFs in six Salicaceae species
A total of four, four, six, four, four, and five GIF genes were identified in P. euphratica, Populus pruinose, Populus deltoides, Populus trichocarpa, Salix sinopurpurea, and Salix suchowensis, respectively. Then, in accordance to the location on chromosomes, the GIF members within the Salicaceae species were assigned names as follows: PeGIF1-4, PpGIF1-4, PdGIF1-6, PtGIF1-4, SPUGIF1-4, and SSUGIF1-5. Almost all of the GIF genes were located on single chromosome in the six Salicaceae species (Fig. 1). Subsequently, the characteristics of GIF genes and their encoded proteins were comprehensively analyzed (Table 1). The analysis of protein sequences revealed that the GIF proteins have the potential to encode amino acids ranging from 79 to 223, with a molecular weight varying between 8930.16 and 23495.28 kDa. Additionally, their isoelectric point was observed to fall within the range of 4.71–5.93.
Analysis of phylogenetic and conserved motifs in multi-species of GIFs
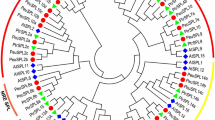
The evolutionary relationships and potential functions of 30 GIFs from six Salicaceae and one Brassicaceae species were investigated by constructing a phylogenetic tree. The analysis confirmed the classification of GIF genes into three subfamilies, denoted as group I-III. Specifically, group I encompassed 13 genes (two ATGIFs, two PeGIFs, two PpGIFs, two PdGIFs, two PtGIFs, two SPUGIFs, and SSUGIF3), group II comprised 12 genes (ATGIF1, PeGIF3, PpGIF2, two PtGIFs, two PdGIFs, two SPUGIFs, and three SSUGIFs), group III contained five genes (two PdGIFs, PpGIF4, PeGIF2, and SSUGIF1) uniquely belonged to Salicaceae (Fig. 2A). The unique GIFs from group III indicated they occurred after that divergence between Arabidopsis and Salicaceae. Then, MEME software was employed to predict the conserved motifs in these GIF genes. Five motifs were identified, with motif 1 representing the conserved SSXT (SNH) domain located in the N-terminal region, common among most GIF genes. Notably, motif 3 and motif 4 were present in most genes, whereas motif 2 exclusively appeared in group I and II genes. Motif 5 was primarily found in group II members, suggesting its uniqueness to this group. Motifs 2 and 5 at C-terminus were presented in the GIF members of Salicaceae species only, possibly indicating their unique roles. Therefore, besides the expanded gene number of GIFs in Salicaceae, the variations of GIF domain numbers may also contribute to the novelty of GIFs in Salicaceae.
Analysis of conserved motifs and phylogenetic relationships among GIF genes across seven species. (A) Neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree between P. euphratica and other six species followed by conserved motifs. The three groups were marked with different colors on tree branches. (B) The 30 GIF genes in seven species have 5 conserved motifs
Collinearity analysis of multi-species GIFs
A collinear analysis of GIFs between P. euphratica and other six species (A. thaliana, P. pruinose, P. deltoides, P. trichocarpa, S. sinopurpurea and S. suchowensis) was conducted to further investigate the evolutionary processes of PeGIFs in Populus. The number of GIF collinear fragments between P. euphratica and the other species were as follows: eight pairs with P. pruinose and S. suchowensis, twelve pairs with P. deltoides and P. trichocarpa, and five pairs with S. sinopurpurea, respectively (Fig. 3). This result revealed that the collinearity of GIFs within the poplar species was more conservative than that between P. euphratica and A. thaliana (five collinear fragments). These results suggested that the GIF gene family is relatively conserved without dramatic expansion nor loss in Salicaceae. Notably, 50 pairs of PeGIF genes exhibited collinear relationships between P. euphratica and the other five Salicaceae species, indicating that these GIF-included collinear fragments likely predated the ancestral divergence. The retention of GIF-included collinear fragments possibly resulted from the whole genome duplication that occurred in Salicaceae [24].
Analysis of collinearity among GIFs involving P. euphratica and six additional species. (A) P. euphratica and A. thaliana, (B) P. euphratica and P. pruinose, (C) P. euphratica and P. deltoides, (D) P. euphratica and P. trichocarpa, (E) P. euphratica and S. sinopurpurea, (F) P. euphratica and S. suchowensis. The presence of gray lines in the background denotes collinear blocks within P. euphratica and other plant genomes, and the red lines emphasize collinear GIF pairs
Analysis of cis-regulatory elements of GIF Genes
The PlantCARE online website was used to predict cis-acting elements to analyze the possible factors influencing the expression patterns of GIF gene family members. The promoters of almost all GIFs contained various cis-acting elements associated with plant growth and development, phytohormone responses and stress responses (Fig. 4B). For instance, elements related to plant development, such as CAT-box, TGA-box, AAGAA-motif, GCN4-motif, as-1, Box4, G-box and so on (Fig. 4A). Meanwhile, stress-related elements are regulated by specific cis-acting motifs including antioxidant response element (ARE), GC-rich motif (GC-motif), TC-rich repeats (TCRRs), MYB binding site (MBS), low temperature-responsive (LTR) element, and wound-induced promoter motif (WUN-motif). The presence of MBS associated with drought stress response was observed in all GIFs, indicating their crucial role in mediating the response to drought-induced stress. Among the hormone-responsive elements, the prominent ones included abscisic acid (ABRE), auxin (TGA-element), gibberellin (TATC-box, P-box, and GARE-motif), MeJA (TGACG-motif and CGTCA-motif), and salicylic acid (TCA-element). The cis-acting elements related to MeJA were the most prevalent among hormone-responsive elements. The analysis suggested that GIF genes may participate in diverse growth and developmental processes possibly mediated by hormone signal transduction or environmental stimulus.
Cis-element analysis of GIF promoters in six Salicaceae species. (A) Numbers and gradient red colors serving as indicators of the abundance of cis-acting elements related to plant development present in each gene. (B) Color-coded histograms depicting the distribution of cis-acting elements in each gene, categorized into three distinct groups. (C) Pie charts depicting the distribution of distinct cis-acting elements within each category
Expression of PeGIFs in heteromorphic leaves from juvenile to adult
The expression levels on four types of heteromorphic leaves (Li, La, Ov, and Bo) at three different developmental stages (P1, P2, and P3) were assessed to investigate the transcriptional regulation of PeGIFs underlying the developmental and functional differentiation processes of heteromorphic leaves. The expression of PeuTF02G01597 (PeGIF1), and PeuTF14G00928 (PeGIF4) exhibited very similar in four leaf shapes and did not exhibit regular changes. By contrast, the expression of PeuTF13G00452 (PeGIF3) in leaves with different leaf shapes increased continuously during the same period, and it was specifically upregulated in Ov and Bo leaves at the early stage of leaf development (Fig. 5A). PeGIF3 showed regular changes in different leaf shapes and its expression level was significantly higher than that of PeuTF12G00083 (PeGIF2). PeGIF3, which is homologous to ATGIF1 in A. thaliana, which plays a crucial role in leaf development. Moreover, the expression of PeGIF3 significantly decreased during the later stages of leaf growth (P2 and P3), suggesting its potential involvement in promoting broad-leaf expansion during early morphogenesis. These results suggested that PeGIF3 plays a dynamic role in regulating the development of broad leaves (Ov and Bo) in P. euphratica, qRT-PCR analysis was further adopted to confirm the expression levels of PeGIFs in heteromorphic leaves at P1 (Fig. 5B∼5 C). All the PeGIFs evaluated by qRT-PCR showed a similar expression pattern from RNA-seq results. Collectively, PeGIF3 also encompasses multiple growth-related elements (AAGAA-motif and as-1), particularly auxin-related elements (TGA-box). These results indicated that up-regulation of PeGIF3 may regulate the occurrence of broad heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica.
PeGIF genes expression patterns in heteromorphic leaves. (A) Expression patterns of PeGIFs across three stages (P1, P2, and P3) in four heteromorphic leaves (Li, La, Ov, and Bo). (B) qRT-PCR data on the expression patterns of PeGIF3 for heteromorphic leaves in P1 stage. (C) qRT-PCR data on the expression patterns of other PeGIFs for heteromorphic leaves in P1 stage
Subcellular localization of PeGIF3
The GV3101 Agrobacterium strain carrying the 35 S:PeGIF3-YFP construct was introduced into tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) to investigate the subcellular distribution of the PeGIF3 protein in plant cells, and the subcellular localization of PeGIF3 was visualized using a confocal laser scanning microscope. The fluorescence signal of 35 S: PeGIF3-YFP coincides with the nuclear localization signal of NLS-mCherry (Fig. 6). The subcellular localization of PeGIF3 was observed to be predominant in the nucleus.
Function of PeGIF3 involving leaf phenotypes
Fully expanded first rosette leaf was derived from the 10-day-old wild-type plants, atgif1 mutant plants, and transgenic wild-type plants overexpressing the PeGIF3 gene, and the complementation of PeGIF3 in atgif1 mutant plants were analyzed to elucidate the cellular underpinnings of transgenic plant phenotypes. Twenty specimens of each line were selected for sampling. The atgif1 mutant exhibited a more pronounced leaf width and leaf area defect. On the contrary, leaf width and leaf area were significantly higher in the overexpressed transgenic plants than in the wild-type plants (Fig. 7A). However, no significant differences were found in leaf length (Table 2). The phenotypes of transgenic atgif1 plants expressing the PeGIF3 gene were comparable to those of the wild type. Subsequently, we conducted analysis of leaf anatomy and observed significant variations in cell number among plants with different backgrounds (Fig. 7B). However, no statistically significant differences were detected in terms of cell area. The findings suggest that PeGIF3 promotes leaf cell proliferation, leading to the expansion of the central-lateral region of the leaf, potentially enhancing leaf area.
Discussion
The heteromorphic leaves in P. euphratica exhibit functional divergence at physiological and cytological levels. GIF proteins, recognized as key players in leaf development, positively regulate leaf size. Previous investigations predominantly focused on the involvement of GIF genes in plant growth and development, including their role in maintaining the homeostasis of leaf, seed, and root meristems in A. thaliana [14, 18, 25]. GIF genes have also been associated with modulating tissue and organ size in rice [19, 26, 27]. In maize, they have been implicated in regulating shoot architecture and meristem determinacy [21]. However, their presence and characteristics in Salicaceae remain unexplored. Recent releases of high-quality genomes for Salicaceae species, including P. euphratica, P. pruinose, P. deltoides, P. trichocarpa, S. sinopurpurea, and S. suchowensis, have opened new avenues for studying the GIF family in Salicaceae. In the present study, a total of 27 members belonging to the GIF family were identified within six Salicaceae species. Four genes were identified in each of the following species: P. euphratica, P. pruinosa, P. deltoides, and S. sinopurpurea. Five genes were identified in P. deltoides and S.suchowensis, allowing for an exploration of their structures and phylogenetic relationships within these species. The 27 GIF members were classified into three subfamilies on the basis of domain analysis and phylogenetic tree to confirm the evolutionary relationships between GIFs. The presence of highly conserved domains in the GIF protein within the same group suggested a potential similarity in function. The ATGIF1 transcription coactivator gene was previously characterized as a positive regulator of cell proliferation in lateral organs, such as leaves and flowers, of A. thaliana [16]. In the present study, members located in the same subfamily as ATGIF1 were hypothesized to function in regulating plant growth.
The presence of the highly-conserved SSXT motif was detected in all members comprising the GIF gene family. The findings are in line with those of prior research [11]. The N-terminal region of GIF proteins shares similarity with the SNH domain discovered in SYNOVIAL TRANSLOCATION (SYT) in humans, which interacts with BRAHMA (BRM) and BRAHMA RELATED GENE1 (BRG1), two ATPases involved in SWITCH/SUCROSE NONFERMENTING (SWI/SNF) chromatin remodeling processes in human cells. Based on sequence similarity, GIF transcriptional coactivators may act together by reciprocally binding to SWI/SNF chromatin remodelers [28]. Motifs 2 and 5 at C-terminus were presented in the GIF members of Salicaceae species only, implying that these members may have undergone functional divergence or acquired novel functions throughout the course of plant evolution.
The promoter analysis unveiled a significant number of plant growth and development elements (CAT-box, TGA-box, AAGAA-motif, GCN4-motif, as-1, Box4, and G-box ), phytohormone-responsive elements (ABRE, CGTCA, and TGACG), and stress-responsive elements (ARE, MYB, and MYC) in the promoter regions of the GIF genes. Among these elements, all genes have Box4 elements, which are part of the conserved DNA module involved in light response. In addition, G-box were important for early senescence of rice flag leaves [29]. Notably, auxin-related elements (TGA-box) were present in most members of each species, suggesting a role for GIF genes in regulating Populus growth and development. Other elements related to growth and development in some GIF genes were found, including the CAT-box related to meristem expression and the GCN4-motif related to endosperm expression. These GIF gene members have been linked to plant development, a finding consistent with that of previous research in A. thaliana [30].
The analysis of gene expression patterns in heteromorphic leaves led to the identification of differentially regulated genes specific to P. euphratica. The expression of PeGIF3 significantly increased and exhibited a notable disparity between the heteromorphic leaves at P1, which is consistent with the qRT-PCR results. Therefore, PeGIF3 may be closely regulated in increasing the size of broad leaves early during leaf morphogenesis in P. euphratica. The examination of transgenic plants showed a significant difference in the number of leaf cells between the overexpressed plants and the wild type. The subsequent observation revealed that PeGIF3 was predominantly observed in the nucleus, consistent with the conserved motifs analysis of GIFs in multi-species in this study. Therefore, PeGIF3 may enhance leaf cell proliferation, thereby resulting in the expansion of the leaf central-lateral region.
Conclusion
In this study, 27 GIF genes were identified in six Salicaceae species, and their structures, phylogenetic relationships, conserved motifs and collinearity across Salicaceae species were characterized, with Arabidopsis as an outgroup. The detailed cis-element analysis showed that the Salicaceae GIFs are involved in multiple developmental processes and regulated by diverse factors such as phytohormones signals and environmental stimulus. Only PeGIF3 showed a gradual upregulation along with the development of heteromorphic leaves of Li, La, Ov, and Bo, and it was specifically upregulated in Ov and Bo leaves at the early stage of leaf development. The essential involvement of PeGIF3 in P. euphratica leaf development was elucidated using RNA-Seq data and qRT-PCR. Further overexpression of PeGIF3 in the atgif1 mutant and wild type of Arabidopsis results in enhanced leaf expansion along the medial-lateral region and increased cell population. The findings provide a foundation for further functional investigations into GIF genes in Salicaceae species and promote the study on leaf morphological variation among these species.
Methods
Identification and characterization of GIF homologs in salicaceae
The PeGIFs were identified on the basis of P. euphratica genome data [31]. The hidden Markov model (HMM) profiles for the GIF domain SSXT (PF05030) were acquired from the Pfam protein family database (http://pfam.xfam.org). HMMER (version 3.0, http://hmmer.org/) was employed to conduct a search for potential GIF genes in the six Salicaceae species. The superfluous candidate genes were excluded, and the remaining genes underwent additional validation using SMART (http://smart.emblheidelberg.de/). The protein physicochemical properties of GIF proteins, such as the amino acid count, molecular weight, and theoretical isoelectric point, were determined using the ProtParam tool (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/). The GIFs from five other Salicaceae species were identified on the basis of the genome data of Populus pruinose (National Center for Biotechnology Information, with BioProject accession number PRJNA863418), P. deltoides (WV94_445) [32], P. trichocarpa (V3.1) [4], S. sinopurpurea [33], and S. suchowensis [34]. The chromosomal location of GIFs was obtained from the genome annotation files, and the chromosome physical location of the GIF genes was displayed using MapChart software (version 2.32).
Analysis of phylogenetic relationship consensus sequence in multi-species GIFs
A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the amino acid sequences that encode GIF genes from P. euphratica and various other species. The SMART website was utilized to extract the domain coordinates from the GIF protein sequence of P. euphratica and other various species. The sequences of the GIF domain were extracted using its coordinates and merged into a new sequence matrix. Then, the merged protein sequences were aligned by ClustalW. After the amino acid sequences were aligned, gap trimming was performed using the multiple alignment trimming tools of TBtools software [35], with a site coverage cutoff parameter set at 0.95. Subsequently, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA v7 software employing the neighbor-joining (NJ) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) was shown next to the branches. The Dayhoff matrix-based method was used to calculate evolutionary distances, which were expressed as the number of amino acid substitutions per site. Ambiguous positions were excluded for each pair of sequences using the pairwise deletion option. TBtools and iTOL online website (https://itol.embl.de/) were used to visualize the phylogenetic tree.
Additionally, we used the MEME tool (http://meme-suite.org/) to classify and analyze the conserved motifs of each GIF protein sequence. We set the maximum motif number was 5 and other parameters are default settings.
Collinearity analysis of multi-species GIFs
The BLASTP alignment was used to identify orthologous pairs between P. euphratica and six other species (P. pruinose, P. trichocarpa, P. deltoides, S. sinopurpurea, S. suchowensis, and A. thaliana). Then, the collinear blocks between P. euphratica and each other species of P. deltoide, P. trichocarpa, A. thaliana, S. sinopurpurea and S. sinopurpurea were identified using MCscan software and visualized using JCVI (https://zenodo.org/record/31631/).
Promoter analysis ofGIFpromoters.
The upstream 2000 bp (bp) sequences apart from the transcription start sites of these PeGIFs genes were identified as potential promoters using TBtools. Subsequently, the cis-elements within each promoter were identified using PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/).
RNA-seq for heteromorphic leaves
A total of 12 samples for four leaf shapes in cultivated forests, including Li, La, Ov, and Bo leaves, were collected across the development of leaf age. These samples were collected at various stages of leaf development. Leaf age was categorized into three periods based on field sampling and observation. The P1 was defined as the first day when the leaf blades started unfolding. This was followed by P2 occurring on the 15th day when there was an increase in leaf area. Finally, P3 occurred on the 30th day when leaves reached maturity. Each type of heteromorphic leaves with different leaf ages was replicated three times for sampling. The napkin was used to delicately clean the leaves, which were then rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at an ultra-low temperature of -80℃ in a refrigerator for RNA-seq analysis (the dataset has been made available to the public for access [7] and preservation through the National Genomics Data Center (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/), under project number PRJCA005959.
Analysis of transcriptomes using short reads from illumina sequencing
As part of the study, we conducted whole transcriptome sequencing using mRNA-Seq on an Illumina Hiseq X-Ten platform, following the protocol recommended by the vendor. To assess the relative abundance of the annotated genes from P. euphratica, we employed HISAT2 (version 2.0.4) [36] to align the clean reads against our reference genome. The gene expression was quantified with FPKM using StringTie [37].
Validation of PeGIFs using quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
The heteromorphic foliage was collected from different canopies and stored in an ultra-low temperature refrigerator at -80℃ after being rapidly frozen with liquid nitrogen. The procedure followed the methodology described in a previous publication [38]. Actin gene was used as the endogenous control. Each reaction was performed in biological triplicates, and CT values obtained through qRT-PCR were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method to calculate relative fold change values.
Plant growth conditions, treatments, and sampling
All A. thaliana mutants and transgenic plants that were used in this study were from the Columbia (Col-0) ecotype. The Arabidopsis seeds were sown on moist soil, stratified at 4℃ for 3 days, and then transferred to a growth room with a temperature of 21℃ and a photoperiod of 16 h light/8 hours darkness. Atgif1 (SALK_208834C) seeds were obtained from the AraShare (https://www.arashare.cn/index/).
The leaves of P. euphratica were collected from the forest located at the eastern entrance of Tarim University.
Cloning, construction of transgenic plants
The laboratory has preserved Escherichia coli (DH5α), Agrobacterium tumefaciens (GV3101), overexpressed vector (pGreenII 0179). The RNA was extracted from P. euphratica Bo leaves using Trizol (Invitrogen, Co.,Ltd), followed by cDNA synthesis using the M5 Sprint qPCR RT kit with gDNA remover (Mei5 Biotechnology, Co.,Ltd). The full-length coding regions of PeGIF3 genes lacking a stop codon were amplified from cDNA, or plasmid using Phanta Max Super-Fidelity DNA polymerase (Vazyme, Co.,Ltd) to ensure high fidelity. Subsequently introduced into a yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) vector to generate a construct using the T4 DNA Ligase (Sangon Biotech, Co.,Ltd). The PeGIF3::YFP fusion was inserted into the pGreenII 0179 vector, which contained a CaMV 35 S promoter and a NOS terminator cassette. The floral dip method was utilized for the transformation of Arabidopsis plants [39, 40]. The overexpression of PeGIF3 was established with a wild-type background. The single-insertion homozygous T3 lines of the PeGIF3 complement were carefully chosen and established in the atgif1 mutant background. Three lines were selected for analysis in each transgenic plants with different backgrounds.
Subcellular localization of PeGIF3 gene
Transform the constructed 35 S:PeGIF3-YFP vector into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101. Reconstitute the strain harboring the target plasmid (NLS-mcherry) in LB medium supplemented with appropriate antibiotics for overnight cultivation. Inoculate the bacterial solution obtained in the second step into fresh LB medium, simultaneously adding acetosyringone, and agitate until the bacteria reach an optical density (OD600) of 1.0-1.2. The supernatant should be discarded by centrifugation, and the bacteria should be resuspended in infection fluid (0.01 M MES (pH = 5.6), 0.01 M MgCl2·6H2O and 50 µM acetosyringone) until the OD value reaches approximately 1.0. Allow it to remain undisturbed for a duration of 3 h in a lightless environment. The target bacterial was combined with the NLS-mcherry in equal proportions, and tobacco were inoculated using a syringe. The treated plants were kept in darkness for 12 h and subsequently incubated under normal conditions for 36 h. The underlying epidermis of tobaccowas revealed in a dark environment and examined using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Nikon eclipse Ti2). The microscope was excited by a 488 nm laser and emitted signals were detected within the range of 500–550 nm.
Measurement of leaf phenotypes and cellular morphology
The leaf cross-section chosen for anatomical analysis was carefully selected to encompass the widest point of the primary vein and subsequently fixed using FAA solution. The paraffin section method was employed to convert these into permanent film [41]. The samples were subsequently examined and imaged using a scanning electron microscope (OPLENIC CORP). Cells present in the pericycle to the leaf margin were enumerated. The statistical analyses were conducted using Graphpad Prism 9 software. The least significant difference test was employed to determine statistically significant differences between means at a significance level of p < 0.05.
Leaf morphology and cell area were analyzed with an image analyzer (ImageJ Launcher-1.4.3.67).
Data availability
RNA-seq data for P. euphratica’s heteromorphic leaves used in this study have been submitted to the NGDC(National Genomics Data Center, https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/) under the BioProject accession number PRJCA005959.
References
Bradshaw H, Ceulemans R, Davis J, Stettler R. Emerging model systems in plant biology: poplar (Populus) as a model forest tree. J Plant Growth Regul. 2000;19(3):306–13.
Brunner AM, Busov VB, Strauss SH. Poplar genome sequence: functional genomics in an ecologically dominant plant species. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9(1):49–56.
Taylor G. Populus: Arabidopsis for forestry. Do we need a model tree? Ann Botany. 2002;90(6):681–9.
Tuskan GA, Difazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science. 2006;313(5793):1596–604.
Qiu Q, Ma T, Hu Q, Liu B, Wu Y, Zhou H, Wang Q, Wang J, Liu J. Genome-scale transcriptome analysis of the desert poplar, Populus Euphratica. Tree Physiol. 2011;31(4):452–61.
Song Z, Ni X, Yao J, Wang F. Progress in studying heteromorphic leaves in Populus Euphratica: leaf morphology, anatomical structure, development regulation and their ecological adaptation to arid environments. Plant Signal Behav. 2021;16(4):1870842.
Wu Z, Jiang Z, Li Z, Jiao P, Zhai J, Liu S, Han X, Zhang S, Sun J, Gai Z. Multi-omics analysis reveals spatiotemporal regulation and function of heteromorphic leaves in Populus. Plant Physiol. 2023;192(1):188–204.
Liu Y, Li X, Chen G, Li M, Liu M, Liu D. Epidermal micromorphology and mesophyll structure of Populus Euphratica heteromorphic leaves at different development stages. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(9):e0137701.
Hao J, Yue N, Zheng C. Analysis of changes in anatomical characteristics and physiologic features of heteromorphic leaves in a desert tree, Populus Euphratica. Acta Physiol Plant. 2017;39:1–11.
Kim JH, Tsukaya H. Regulation of plant growth and development by the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR duo. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(20):6093–107.
Kim JH, Kende H. A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(36):13374–9.
Horiguchi G, Kim GT, Tsukaya H. The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal: Cell Mol Biology. 2005;43(1):68–78.
Vercruyssen L, Verkest A, Gonzalez N, Heyndrickx KS, Eeckhout D, Han SK, Jégu T, Archacki R, Van Leene J, Andriankaja M, et al. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 binds to SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes to regulate transcription during Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Cell. 2014;26(1):210–29.
Ercoli MF, Ferela A, Debernardi JM, Perrone AP, Rodriguez RE, Palatnik JF. GIF Transcriptional Coregulators Control Root Meristem Homeostasis. Plant Cell. 2018;30(2):347–59.
Li J, Pan W, Zhang S, Ma G, Li A, Zhang H, Liu L. A rapid and highly efficient sorghum transformation strategy using GRF4-GIF1/ternary vector system. Plant J 2023.
Lee BH, Ko JH, Lee S, Lee Y, Pak JH, Kim JH. The Arabidopsis GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR gene family performs an overlapping function in determining organ size as well as multiple developmental properties. Plant Physiol. 2009;151(2):655–68.
Liu Y, Guo P, Wang J, Xu ZY. Growth-regulating factors: conserved and divergent roles in plant growth and development and potential value for crop improvement. Plant J. 2023;113(6):1122–45.
Liang G, He H, Li Y, Wang F, Yu D. Molecular mechanism of microRNA396 mediating pistil development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014;164(1):249–58.
Duan P, Ni S, Wang J, Zhang B, Xu R, Wang Y, Chen H, Zhu X, Li Y. Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat Plants. 2015;2:15203.
Qin L, Chen H, Wu Q, Wang X. Identification and exploration of the GRF and GIF families in maize and foxtail millet. Physiol Mol Biology Plants. 2022;28(9):1717–35.
Zhang D, Sun W, Singh R, Zheng Y, Cao Z, Li M, Lunde C, Hake S, Zhang Z. GRF-interacting factor1 regulates shoot Architecture and Meristem Determinacy in Maize. Plant Cell. 2018;30(2):360–74.
Ai G, Zhang D, Huang R, Zhang S, Li W, Ahiakpa JK, Zhang J. Genome-wide identification and molecular characterization of the growth-regulating factors-interacting factor Gene Family in Tomato. Genes 2020, 11(12).
Wu ZJ, Wang WL, Zhuang J. Developmental processes and responses to hormonal stimuli in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) leaves are controlled by GRF and GIF gene families. Funct Integr Genom. 2017;17(5):503–12.
Zhang ZS, Zeng QY, Liu YJ. Frequent ploidy changes in Salicaceae indicates widespread sharing of the salicoid whole genome duplication by the relatives of Populus L. and Salix L. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21(1):535.
Debernardi JM, Mecchia MA, Vercruyssen L, Smaczniak C, Kaufmann K, Inze D, Rodriguez RE, Palatnik JF. Post-transcriptional control of GRF transcription factors by microRNA miR396 and GIF co-activator affects leaf size and longevity. Plant Journal: Cell Mol Biology. 2014;79(3):413–26.
Yan S, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Guo P, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y. Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice. TAG Theoretical Appl Genet Theoretische und Angewandte Genetik. 2011;123(7):1173–81.
Li S, Gao F, Xie K, Zeng X, Cao Y, Zeng J, He Z, Ren Y, Li W, Deng Q, et al. The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol J. 2016;14(11):2134–46.
Xie Y, Skytting B, Nilsson G, Grimer RJ, Mangham CD, Fisher C, Shipley J, Bjerkehagen B, Myklebost O, Larsson O. The SYT-SSX1 fusion type of synovial sarcoma is associated with increased expression of cyclin A and D1. A link between t(X;18)(p11.2; q11.2) and the cell cycle machinery. Oncogene. 2002;21(37):5791–6.
Liu L, Xu W, Hu X, Liu H, Lin Y. W-box and G-box elements play important roles in early senescence of rice flag leaf. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20881.
Nelissen H, Eeckhout D, Demuynck K, Persiau G, Walton A, van Bel M, Vervoort M, Candaele J, De Block J, Aesaert S, et al. Dynamic changes in ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Complex Composition reveal a Growth Regulatory mechanism in the Maize Leaf. Plant Cell. 2015;27(6):1605–19.
Zhang Z, Chen Y, Zhang J, Ma X, Li Y, Li M, Wang D, Kang M, Wu H, Yang Y et al. Improved genome assembly provides new insights into genome evolution in a desert poplar (Populus Euphratica). Mol Ecol Resour 2020, 20(3).
Xue L, Wu H, Chen Y, Li X, Hou J, Lu J, Wei S, Dai X, Olson MS, Liu J. Evidences for a role of two Y-specific genes in sex determination in Populus deltoides. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5893.
Zhou R, Macaya-Sanz D, Carlson CH, Schmutz J, Jenkins JW, Kudrna D, Sharma A, Sandor L, Shu S, Barry K, et al. A willow sex chromosome reveals convergent evolution of complex palindromic repeats. Genome Biol. 2020;21(1):38.
Dai X, Hu Q, Cai Q, Feng K, Ye N, Tuskan GA, Milne R, Chen Y, Wan Z, Wang Z, et al. The willow genome and divergent evolution from poplar after the common genome duplication. Cell Res. 2014;24(10):1274–7.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194–202.
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc. 2016;11(9):1650–67.
Kovaka S, Zimin AV, Pertea GM, Razaghi R, Salzberg SL, Pertea M. Transcriptome assembly from long-read RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):1–13.
Liu C, Hao J, Qiu M, Pan J, He Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the MYB transcription factor in Japanese plum (Prunus salicina). Genomics. 2020;112(6):4875–86.
Zhang X, Henriques R, Lin SS, Niu QW, Chua NH. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(2):641–6.
Folkers U, Kirik V, Schöbinger U, Falk S, Krishnakumar S, Pollock MA, Oppenheimer DG, Day I, Reddy AS, Jürgens G, et al. The cell morphogenesis gene ANGUSTIFOLIA encodes a CtBP/BARS-like protein and is involved in the control of the microtubule cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 2002;21(6):1280–8.
Tsukaya H, Naito S, Rédei GP, Komeda Y. A new class of mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana, acaulis1, affecting the development of both inflorescences and leaves. Development. 1993;118(3):751–64.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32160355).
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32371838; the Biological Safety and Genetic Resources Management Project of the Science and Technology Development Center of the National Forestry and Grassland Administration, grant number KJZXSA202303 and Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Regional Innovation Guidance Program project, grant number 2021BB010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y., J.S. and C.Q., carried out the experiment, collected and organized data and wrote the manuscript. P.J. and Z.W. participated in designing the experiment and directed the study. Z.L. and Z.W., reviewed the manuscript. H.W, Y.Y. and Z.W., helped organize data. P.J., helped do the experiment. Z.L. and Z.W., corresponding author, raised the hypothesis underlying this work, designed the experiment, and helped organize the manuscript structure. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Sun, J., Qiu, C. et al. Comparative genomic analysis of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factors (GIFs) in six Salicaceae species and functional analysis of PeGIF3 reveals their regulatory role in Populus heteromorphic leaves. BMC Genomics 25, 317 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10221-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10221-5