Abstract
Background
Osteoporosis is a major health concern for postmenopausal women, and the effect of simvastatin (Sim) on bone metabolism is controversial. This study aimed to investigate the effect of simvastatin on the bone microstructure and bone mechanical properties in ovariectomized (OVX) mice.
Methods
24 female C57BL/6J mice (8-week-old) were randomly allocated into three groups including the OVX + Sim group, the OVX group and the control group. At 8 weeks after operation, the L4 vertebral bones were dissected completely for micro-Computed Tomography (micro-CT) scanning and micro-finite element analysis (µFEA). The differences between three groups were compared using ANOVA with a LSD correction, and the relationship between bone microstructure and mechanical properties was analyzed using linear regression.
Results
Bone volume fraction, trabecular number, connectivity density and trabecular tissue mineral density in the OVX + Sim group were significantly higher than those in the OVX group (P < 0.05). For the mechanical properties detected via µFEA, the OVX + Sim group had lower total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress compared to the OVX group (P < 0.05). In the three groups, the mechanical parameters were significantly correlated with bone volume fraction and trabecular bone mineral density.
Conclusions
The findings suggested that simvastatin had a potential role in the treatment of osteoporosis. The results of this study could guide future research on simvastatin and support the development of simvastatin-based treatments to improve bone health.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Osteoporosis is a common health issue for the postmenopausal women, and its prevalence is increasing with the aging of the population [1]. Osteoporosis is characterized by decreased bone mineral density and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue that increases the risk of bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture [2]. Hormonal changes, especially the reduction of estrogen after menopause, play a key role in the development of osteoporosis. Estrogen deficiency in osteoporotic patients has been associated with decreased bone formation, increased bone resorption, and a reduction in bone mineral density [3]. In the past few decades, menopausal hormone therapy has been used not only to prevent the bone loss and the degeneration of bone microstructure, but also to reduce the incidence of osteoporotic fractures [4]. However, the discovery that it is related to the increased risk of cardiovascular events and breast cancer and other adverse health consequences has limited its use [5]. Although a study showed that bisphophonates lead to a decreased risk of cardiovascular events [6], there are also some literature suggesting that it has adverse effects, including gastrointestinal reactions [7] and an increased risk of cardiovascular events [8]. There is still controversy over the effects of bisphophonates on cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it is important to search a potential new treatment option for osteoporosis.
As an organic compound, Simvastatin (Sim) is classified as a statin drug. Sim is a specific inhibitor of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) that is commonly used to reduce cholesterol levels and treat atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases [8,9,10,12]. In addition, it has been shown to affect bone turnover by inhibiting osteoclast activity through decreasing osteoclast formation, differentiation, proliferation, and function, and stimulating bone formation through reducing osteoblast apoptosis [13]. Studies have suggested that simvastatin may have a potential role in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis [14, 15]. The majority of related studies showed that simvastatin could increase bone mineral density, reduce bone resorption, and stimulate bone formation [15,16,18], while other studies detected a negative association between simvastatin and bone mineral density (BMD) and bone repair [19, 20]. The role of simvastatin in these animal model studies remains controversial.
In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of simvastatin on the bone microstructure and bone mechanical properties in ovariectomized mice by micro-Computed Tomography (micro-CT) scanning combined with micro-finite element analysis (µFEA).
Methods
Animals and experimental treatment
A total of 24 female C57BL/6J mice (8-week-old) were randomly allocated into three groups with 8 mice per group. Eight mice received bilateral ovariectomy (OVX), which was the OVX+Sim group. After 4 weeks of postoperative adaption [21], then simvastatin (Sigma S6196-5MG) dissolved in physiological saline was administered to mice by oral gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg per day [22] for 4 weeks. Eight mice (OVX group) underwent bilateral ovariectomy. The other eight mice (control group) were only performed back incision without ovariectomy. Then the mice in the OVX group and the control group received an equivalent amount of physiological saline as placebo for 4 weeks at 12 weeks of age. The living environment and rearing conditions (22–24℃ and 55–60% humidity in a room maintained on a 12/12-h light/dark cycle) of all mice were the same. The mice received ad libitum access to standard chow pellets and water throughout the experimental period.
At 16-week-old, mice in each group were euthanized by over anesthesia (Pentobarbital Sodium, 150 mg/kg) to extract the L4 vertebral bone completely. Then we stored them in 70% ethanol solution respectively. The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of our institution and was performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines for the use of laboratory animals.
Micro-CT scanning
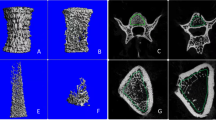
All trabecular bone of the L4 vertebral bones were examined with a micro-CT (NEMO micro-CT, model NMC-100) from PINGSENG Healthcare (Kunshan) Inc. All samples were placed in the sample holder vertically along the long axis. The scanning settings used were as follows: source voltage of 90 kV; current of 50 µA; scanning time of 10 min; voxel size of 0.015 × 0.015 × 0.015 mm; number of projections of 4000. After scanning, we used Avatar v1.6.5 (PINGSENG Healthcare lnc.) software to perform 3D reconstruction. The volume of interest (VOI) was seen in Fig. 1. We used segmentation algorithms such as thrshold segmentation, region growing, morphological operations and Boolean operations, and a threshold of 700 was used to extract the mineralized bone from soft tissue and marrow phase. The bone volume fraction (BV/TV)(%), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th)(mm), trabecular number (Tb.N)(1/mm), trabecular separation (Tb.Sp)(mm), structure model index (SMI), connectivity density (Conn.D)(1/mm3), trabecular tissue mineral density (Tb.TMD) (g/cm3) were evaluated based on the micro-CT scan results. All the measurements were performed by a junior physician under the supervision of a senior physician.
Micro-finite element analysis
Ansys17 (ANSYS Inc., USA) was used for micro-finite element analysis to simulate the axial compression tests for each trabecular bone in the longitudinal directions. Trabecular bone tissues were modelled as an isotropic linear elastic material with a Young’s modulus of 15 GPa and a Poisson’s ratio of 0.3 [23, 24]. For each bone segment model, uniaxial compression tests were performed for the µFEA analysis. This allowed us to determine total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress values, which represented the mechanical properties. Equivalent strain and equivalent stress respectively indicate the degree of deformation and tension inside the object. Equivalent elastic strain represents the overall deformation or elongation experienced by a material due to an applied load, considering both linear and nonlinear behavior. The equivalent elastic strain combines all the individual strain components (such as axial, shear, and volumetric strains) into a single value that represents the overall deformation. It is typically calculated using the Hooke’s law relationship between stress and strain for linear elastic materials. For nonlinear materials, more complex constitutive models are used. Equivalent stress is a scalar value that represents the intensity of stress at a point in a material, considering both normal and shear stresses. In complex stress states (such as multiaxial loading), different stress components (such as tensile, compressive, and shear stresses) act simultaneously. Equivalent stress simplifies this by combining all stress components into a single value. It is calculated as the square root of the sum of the squares of the deviatoric stresses.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyzes were performed by SPSS software, version 27.0. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to test the normality of the quantitative data. The results showed that all quantitative data approximately conformed to the normal distribution. Quantitative data are presented as the means ± standard deviation (SD). The Levene test was used for variance homogeneity analysis. Bone trabecular microstructural parameters among each group were compared by ANOVA with an LSD correction to account for intergroup differences between the three groups. Linear regression was used to analyze the relationship of trabecular bone microstructural parameters and micro-finite element parameters. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Micro-CT scanning
There were significant intra-group differences between three groups in BV/TV, Tb.Th, Tb.N, Tb.Sp and Tb.TMD (P < 0.05) (Table 1; Fig. 2A and E). In contrast, SMI of vertebral bone did not show significant intra-group differences between three groups (P > 0.05) (Table 1). Specifically, the OVX + Sim group displayed a significant increase of BV/TV, Tb.N, Conn.D and Tb.TMD when compared to the OVX group (P < 0.05) (Table 1). Although there was no remarkable difference, the OVX + Sim group had more Tb.Th and less Tb.Sp when compared to the OVX group (P > 0.05) (Table 1). Interestingly, Tb.N and Conn.D in the OVX + Sim group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 1). And there was no remarkable difference of SMI in the OVX + Sim and control group (P > 0.05) (Table 1). Moreover, when compared to the control group, the OVX group showed a significant reduction in BV/TV, Tb.Th, Tb.N and Tb.TMD, while an increase in Tb.Sp (P < 0.05) (Table 1). Furthermore, three-dimensional reconstruction showed that the trabecular of the OVX+Sim group appeared to be denser than that of the control group and the OVX group (Fig. 3A and C).
Comparison of micro-CT parameters and mechanical properties of L4 vertebral bone for three groups of mice. A. BV/TV: bone volume fraction, B. Tb.Th: trabecular thickness, C. Tb.N: trabecular number, D. Tb.Sp: trabecular separation, E. Tb.TMD: trabecular tissue mineral density, F. total deformation, G. equivalent elastic strain, H. equivalent stress. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001
Micro-finite element analysis
For the mechanical properties detected via µFEA, the OVX + Sim group had lower total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress than did the OVX group (P < 0.05) (Table 1; Fig. 2F and H). The OVX + Sim group had higher total deformation than did the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 1; Fig. 2F and H). Moreover, the OVX group had higher total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress than did the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 1; Fig. 2F and H).
Correlation between trabecular bone parameters and bone strength
For all the samples (Table 2), total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress were negatively correlated with BV/TV (r=-0.837, -0.724 and − 0.876, P < 0.05, respectively), Tb.Th (r=-0.749, -0.450 and − 0.605, P < 0.05, respectively), Tb.TMD (r=-0.844, -0.617 and − 0.765, P < 0.05, respectively). Equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress were negatively correlated with Tb.N (r=-0.635 and − 0.726, P < 0.05, respectively). Furthermore, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress were positively correlated with Tb.Sp (r = 0.607 and 0.678, P < 0.05, respectively).
The relationship varied when divided into different groups (Table 3). In the OVX + Sim group, total deformation and equivalent stress were negatively correlated with BV/TV (r=-0.864 and − 0.925, P < 0.05, respectively), Tb.N (r=-0.839 and − 0.901, P < 0.05, respectively). Total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress were also negatively correlated with Tb.TMD (r=-0.809, -0.714 and − 0.884, P < 0.05, respectively). In the control group and OVX group, equivalent stress was negatively correlated with BV/TV (r=-0.793 and − 0.802, P < 0.05, respectively).
Figure 4 shows the results from the linear regression, assessing the associations of trabecular bone microstructural parameters with micro-finite element variables. Equivalent stress was negatively correlated with BV/TV (R2 = 0.767, P < 0.05). Total deformation was negatively correlated with BV/TV and Tb.TMD (R2 = 0.701, P < 0.05 and R2 = 0.711, P < 0.05, respectively).
Discussion
Herein, we attempted to investigate the effect of simvastatin on the bone microstructure and mechanical properties in ovariectomized mice by micro-CT combined with micro-finite element analysis. Previous clinical studies have suggested that simvastatin may have a potential beneficial effect on bone metabolism, primarily by reducing bone resorption rather than stimulating bone formation [23,24,27]. It prevents estrogen deficiency-induced decrease in bone density [27]. However, data on the effects and mechanisms of simvastatin on bone structure have been limited to specific criteria, and accurate validation of its efficacy is needed [26,27,28,31]. In the present study, we aimed to determine the therapeutic potential of simvastatin in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis. This study selected clinically commonly used cholesterol-lowering drug simvastatin, using an ovariectomized mouse model to observe the effects of the drug on osteoporosis. We demonstrated that simvastatin can serve as a method for treating OVX-induced bone loss.
Estrogen plays an essential role in the process of bone remodeling [30,31,34]. Estrogen deficiency increases bone loss and osteoclast formation by increasing various cytokines and growth factors, and reduces the absorption and availability of intestinal calcium. The OVX animal model has been widely utilized in the study of postmenopausal osteoporosis caused by estrogen deficiency [35]. Our research found that ovariectomy could lead to a decrease in BV/TV, Tb.Th, Tb.N, Tb.TMD and an increase in Tb.Sp, total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress, which was in accordance with previous studies conducted on OVX mice [18, 36, 37]. Although there was no significant difference in Conn.D, we can also find that Conn.D decreased after ovariectomy. Previous studies reported that OVX mice not only lead to the decrease of bone mineral density, but also impaired the spatial structure of bone trabeculae and mechanical properties [36,37,40].
We observed that simvastatin treatment inhibited OVX-induced bone loss in mice. Wu et al. [41] studied the microstructure and mechanical properties of the axial bone in mice by comparing the changes in microstructure and mechanical properties of L4 vertebrae between ketogenic diet and OVX mice. And they found that OVX can damage the microstructure of the lumbar vertebrae in mice and lead to loss of cancellous bone. The most common osteoporotic fracture in the elderly population is vertebral compression fracture. Therefore, we selected the L4 vertebral body for observation. Cheon et al. [18] used two doses of statin, low dose (1 mg/kg) and high dose (10 mg/kg), respectively. In their experiment, the low-dose group did not effectively treat osteoporosis (many parameters were not significantly different from the control group). Meanwhile, we found in the study by Leutner et al. [20] that excessive doses (50 mg/kg) of simvastatin will promote the development of osteoporosis. In other words, excessive doses of simvastatin were harmful to bones. Therefore, a dose of 10 mg/kg of simvastatin was ultimately chosen for this study. Based on our analysis of 3D micro-CT images of the vertebra, simvastatin (10 mg/kg) significantly improved BV/TV, Tb.N, Conn.D and Tb.TMD. The results showed that simvastatin treatment not only increased bone density, but also improved the spatial structure of bone trabecular. Bone quality encompasses the microscopic structure of bone trabeculae, the macroscopic geometric structure of bone and the material properties of constituent bone tissues [42]. This study was consistent with those of previous studies [22, 37]. Recently, a cross-sectional analysis focused on the effects of statins on BMD in elderly males [43]. Consistent with our results, the oral treatment with therapeutic doses of statins was associated with a significant increase of BMD at L1-L4 in elderly men compared with the control group. A recent study [20] found that high doses of statin can damage bone quantity. As the mice were fed for a year in their experiments, the interference of age factors may be one reason for the discrepancy in the results [44].
While examining the mechanical properties of the trabeculae bone, we found that the total deformation, equivalent elastic strain and equivalent stress were reduced in the OVX + Sim group when compared with the OVX group, showing that simvastatin might improve mechanical properties and enhance bone strength caused by OVX. However, the total deformation in the OVX + Sim group was higher than that of the control group, indicating that simvastatin cannot completely reverse bone mechanical properties to normal levels. Through micro-CT scanning and biomechanical evaluations, Yang et al. [45] found that treatment with simvastatin was effective in enhancing bone strength and promoting bone defect repair. This difference may be due to the limited sample size in our study and we only studied the vertebral bones.
To discover the relationship between the microstructure and the mechanical properties of the vertebral trabeculae bone, we conducted a linear regression. We presented the correlations between microstructure and biomechanical properties both as all three groups separate and combined to explore group-specific effects while considering overall trends. Among these indicators, we found that BV/TV and Tb.TMD were negatively correlated with the mechanical properties. These findings indicated that the change of BV/TV in the vertebrae was crucial in the bone mechanical properties. Lamya Karim et al. found that the bone with high BV/TV had greater post-yield strain and stronger resistance to fractures than the bone with low BV/TV [46]. This showed that BV/TV is a prominent indicator reflecting bone mechanical properties and is positively associated with mechanical properties.
There are some limitations in this study. Firstly, the sample size of our study was small. Secondly, owing to only vertebrae bone being selected for analysis, it is difficult to determine whether this effect will vary according to the selected bone sites. Finally, this study only conducted two different analyses (micro-CT and µFEA). In future research, it is necessary to further explore the mechanism of action of simvastatin in the treatment of osteoporosis.
In conclusion, the present study using micro-CT combined with µFEA demonstrates that simvastatin treatment had a positive effect on the bone microstructure and mechanical properties of ovariectomized mice. Although the OVX-induced estrogen-deficient osteoporosis model may fail to comprehensively simulate clinical pathological conditions, the results of our study provided new insights into the potential clinical application of simvastatin for the treatment of osteoporosis.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Sim:
-
Simvastatin
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density
- µFEA:
-
Micro-finite element analysis
- micro-CT:
-
Micro-Computed Tomography
- OVX:
-
Ovariectomy
- VOI:
-
Volume of interest
- BV/TV:
-
Bone volume fraction
- Tb.Th:
-
Trabecular thickness
- Tb.N:
-
Trabecular number
- Tb.Sp:
-
Trabecular separation
- SMI:
-
Structure model index
- Conn.D:
-
Connectivity density
- Tb.TMD:
-
Trabecular tissue mineral density
References
Arceo-Mendoza RM, Camacho PM. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: latest guidelines. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2021;50(2):167–78.
Noh J-Y, Yang Y, Jung H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(20):7623.
Rozenberg S, Bruyère O, Bergmann P, Cavalier E, Gielen E, Goemaere S, et al. How to manage osteoporosis before the age of 50. Maturitas. 2020;138:14–25.
Gosset A, Pouillès JM, Trémollieres F. Menopausal hormone therapy for the management of osteoporosis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;35(6):101551.
Rozenberg S, Al-Daghri N, Aubertin-Leheudre M, Brandi ML, Cano A, Collins P, et al. Is there a role for menopausal hormone therapy in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis? Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(12):2271–86.
Kranenburg G, Bartstra J W, Weijmans M, de Jong P A, Mali W P, Verhaar H J, et al. Bisphosphonates for cardiovascular risk reduction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 2016;252: 106–15.
Tella SH, Gallagher JC. Prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;142:155–70.
Pittman CB, Davis LA, Zeringue AL, Caplan L, Wehmeier KR, Scherrer JF et al. Myocardial infarction risk among patients with fractures receiving bisphosphonates. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014; 89(1): 43–51.
Xu XC, Chen H, Zhang X, Zhai ZJ, Liu XQ, Qin A, et al. Simvastatin prevents alveolar bone loss in an experimental rat model of periodontitis after ovariectomy. J Transl Med. 2014;12:284.
Leutner M, Matzhold C, Bellach L, Deischinger C, Harreiter J, Thurner S, et al. Diagnosis of osteoporosis in statin-treated patients is dose-dependent. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(12):1706–11.
Xiong M, Xue Y, Zhu W, Deng A, Tan Z, Zhou G, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of statins for osteoporosis: a study protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12(5):e054158.
Khayatan D, Razavi SM, Arab ZN, Khanahmadi M, Momtaz S, Butler AE et al. Regulatory effects of statins on SIRT1 and other Sirtuins in Cardiovascular diseases. Life (Basel). 2022;12(5):760.
Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A, Maffulli N. Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9(1):18.
Shahrezaee M, Oryan A, Bastami F, Hosseinpour S, Shahrezaee MH, Kamali A. Comparative impact of systemic delivery of atorvastatin, simvastatin, and lovastatin on bone mineral density of the ovariectomized rats. Endocrine. 2018;60(1):138–50.
Guo Y, Huo J, Wu D, Hao H, Ji X, Zhao E, et al. Simvastatin inhibits the adipogenesis of bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells through the downregulation of chemerin/CMKLR1 signaling. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(2):751–61.
Chamani S, Liberale L, Mobasheri L, Montecucco F, Al-Rasadi K, Jamialahmadi T, et al. The role of statins in the differentiation and function of bone cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51(7):e13534.
Feng C, Xiao L, Yu JC, Li DY, Tang TY, Liao W, et al. Simvastatin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in rat model of osteoporosis through BMP-2/Smads signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(1):434–43.
Cheon Y-H, Lee CH, Kim S, Park GD, Kwak SC, Cho HJ, et al. Pitavastatin prevents ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by regulating osteoclastic resorption and osteoblastic formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;139:111697.
Kim SY, Yoo DM, Min C, Kim JH, Kwon MJ, Kim JH et al. Association between osteoporosis and previous statin use: a nested case-control study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(22):11902.
Leutner M, Butylina M, Matzhold C, Klimek P, Cuhaj C, Bellach L, et al. Simvastatin therapy in higher dosages deteriorates bone quality: consistent evidence from population-wide patient data and interventional mouse studies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;158:114089.
Cheon Y-H, Lee C H, Kim S, Park G D, Kwak S C, Cho H J, et al. Pitavastatin prevents ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by regulating osteoclastic resorption and osteoblastic formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;139:111697.
Li H, Gou Y, Tian F, Lian Q, Hu Y, Zhang L. The combined anti-osteoporotic effects of simvastatin and exercise in ovariectomized mice fed a high-fat diet. Exp Gerontol. 2022;164:111794.
Liu XS, Walker MD, McMahon DJ, Udesky J, Liu G, Bilezikian JP, et al. Better skeletal microstructure confers greater mechanical advantages in Chinese-American women versus white women. J Bone Min Res. 2011;26(8):1783–92.
Wang J, Zhou B, Liu XS, Fields AJ, Sanyal A, Shi X, et al. Trabecular plates and rods determine elastic modulus and yield strength of human trabecular bone. Bone. 2015;72:71–80.
Hong W, Wei Z, Qiu Z, Li Z, Fu C, Ye Z, et al. Atorvastatin promotes bone formation in aged apoE(-/-) mice through the Sirt1-Runx2 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):303.
Monteiro LO, Macedo AP, Shimano RC, Shimano AC, Yanagihara GR, Ramos J, et al. Effect of treatment with simvastatin on bone microarchitecture of the femoral head in an osteoporosis animal model. Microsc Res Tech. 2016;79(8):684–90.
Qadir F, Alam SM, Zehra T, Mehmood A, Siddiqi AQ. Role of Pitavastatin in Prevention of Osteopenic Changes in Ovariectomized rats. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2016;26(1):41–5.
Lambers FM, Kuhn G, Schulte FA, Koch K, Müller R. Longitudinal assessment of in vivo bone dynamics in a mouse tail model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90(2):108–19.
Oliviero S, Roberts M, Owen R, Reilly GC, Bellantuono I, Dall’Ara E. Non-invasive prediction of the mouse tibia mechanical properties from microCT images: comparison between different finite element models. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021;20(3):941–55.
Dai L, Xu M, Wu H, Xue L, Yuan D, Wang Y, et al. The functional mechanism of simvastatin in experimental osteoporosis. J Bone Min Metab. 2016;34(1):23–32.
Anagnostis P, Florentin M, Livadas S, Lambrinoudaki I, Goulis DG. Bone health in patients with Dyslipidemias: an underestimated aspect. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1639.
Khosla S, Oursler MJ, Monroe DG. Estrogen and the skeleton. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012;23(11):576–81.
Cheng CH, Chen LR, Chen KH. Osteoporosis due to hormone imbalance: an overview of the effects of Estrogen Deficiency and glucocorticoid overuse on bone turnover. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1376.
McNamara LM. Osteocytes and estrogen deficiency. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(6):592–603.
Yousefzadeh N, Kashfi K, Jeddi S, Ghasemi A. Ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis: a practical guide. Excli j. 2020;19:89–107.
Guo X, Yu X, Yao Q, Qin J. Early effects of ovariectomy on bone microstructure, bone turnover markers and mechanical properties in rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):316.
Ibrahim N, Khamis MF, Mod Yunoh MF, Abdullah S, Mohamed N, Shuid AN. Targeted delivery of lovastatin and tocotrienol to fracture site promotes fracture healing in osteoporosis model: micro-computed tomography and biomechanical evaluation. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e115595.
Hsu PY, Tsai MT, Wang SP, Chen YJ, Wu J, Hsu JT. Cortical bone morphological and trabecular bone microarchitectural changes in the Mandible and femoral Neck of Ovariectomized rats. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(4):e0154367.
Li Z, Liu P, Yuan Y, Liang X, Lei J, Zhu X, et al. Loss of longitudinal superiority marks the microarchitecture deterioration of osteoporotic cancellous bones. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021;20(5):2013–30.
Lei T, Liang Z, Li F, Tang C, Xie K, Wang P, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) attenuate changes in vertebral bone mass, architecture and strength in ovariectomized mice. Bone. 2018;108:10–9.
Wu X, Ding J, Xu X, Wang X, Liu J, Jiang J, et al. Ketogenic diet compromises vertebral microstructure and biomechanical characteristics in mice. J Bone Min Metab. 2019;37(6):957–66.
Wang F, Zheng L, Theopold J, Schleifenbaum S, Heyde C-E, Osterhoff G. Methods for bone quality assessment in human bone tissue: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):174.
Abbasloo S, Aghaei Meybodi HR, Fahimfar N, Gharibzadeh S, Sanjari M, Khalaji K, et al. The associations of statin intake and the trabecular bone score and bone mineral density status in elderly Iranian individuals: a cross-sectional analysis of the Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) program. Arch Osteoporos. 2021;16(1):144.
Yin H, Shi ZG, Yu YS, Hu J, Wang R, Luan ZP, et al. Protection against osteoporosis by statins is linked to a reduction of oxidative stress and restoration of nitric oxide formation in aged and ovariectomized rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;674(2–3):200–6.
Li Y, Zhang R, Ren M, Liu H, Yang M. Experimental study on the effects of simvastatin in reversing the femoral metaphyseal defects induced by sodium valproate in normal and ovariectomized rats. Heliyon. 2022;8(9):e10480.
Karim L, Vashishth D. Role of trabecular microarchitecture in the formation, accumulation, and morphology of microdamage in human cancellous bone. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(11):1739–44.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank PINGSENG Healthcare (Kunshan) Inc., which provided technical assistance for this research.
Funding
This study was supported by Academic Promotion Programme of Shandong First Medical University (No.2019QL017) and the Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Tai ‘an(2021NS251).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yb L: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Xq Y: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Xx D: Conceptualization, Investigation. Gh Z: Conceptualization, Investigation. Cq L: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. H Y: Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing. Tt Z: Conceptualization, Project administration. J Q: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Software, Writing - review & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong First Medical University and carried out in accordance with the guidelines for the use of laboratory animals of the National Institutes of Health. This study was reported in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Yuan, X., Dai, X. et al. The effects of simvastatin on the bone microstructure and mechanics of ovariectomized mice: a micro-CT and micro-finite element analysis study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 25, 748 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-024-07860-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-024-07860-w