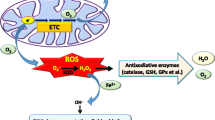
Abstract
Background
In tumor treatment, protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been extensively utilized. However, the efficacy of TKI is significantly compromised by drug resistance. Consequently, finding an effective solution to overcome TKI resistance becomes crucial. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a group of highly active molecules that play important roles in targeted cancer therapy including TKI targeted therapy. In this review, we concentrate on the ROS-associated mechanisms of TKI lethality in tumors and strategies for regulating ROS to reverse TKI resistance in cancer.
Main body
Elevated ROS levels often manifest during TKI therapy in cancers, potentially causing organelle damage and cell death, which are critical to the success of TKIs in eradicating cancer cells. However, it is noteworthy that cancer cells might initiate resistance pathways to shield themselves from ROS-induced damage, leading to TKI resistance. Addressing this challenge involves blocking these resistance pathways, for instance, the NRF2-KEAP1 axis and protective autophagy, to promote ROS accumulation in cells, thereby resensitizing drug-resistant cancer cells to TKIs. Additional effective approaches inducing ROS generation within drug-resistant cells and providing exogenous ROS stimulation.
Conclusion
ROS play pivotal roles in the eradication of tumor cells by TKI. Harnessing the accumulation of ROS to overcome TKI resistance is an effective and widely applicable approach.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Protein tyrosine kinases are protein kinases that phosphorylate tyrosine residues on downstream proteins in signal transduction, playing a crucial role in cellular life activities [1]. Protein tyrosine kinases are categorized into receptor tyrosine kinases and nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, both of which are implicated in tumor-related activities such as growth, proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis [2, 3]. Among receptor tyrosine kinases are the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR); and in the nonreceptor tyrosine kinases group are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), ABL kinase, and Src kinase. Numerous targeted inhibitors for these kinases have been developed and are widely used in clinical cancer therapies with good therapeutic effects. Nonetheless, the development of drug resistance limits the efficacy of TKIs. Resistance to TKIs often results from different gene mutations in the targets or the activation of alternative pathways, and these complex mechanisms make it difficult to develop widely effective means to overcome resistance [4, 5]. Consequently, it is necessary to summarize the commonalities of TKI resistance in cancer.
ROS are a group of highly active molecules containing oxygen, such as singlet oxygen (1O2), superoxide (O2•-), hydroxyl radical (OH•) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Endogenous ROS arise from various sources such as mitochondrial metabolism, peroxisomes, and the function of transmembrane NADPH oxidases (NOXs) [6]. ROS play multiple roles in tumor cells. Low ROS levels generally support tumor initiation, progression, and survival, whereas elevated ROS levels tend to cause oxidative harm on DNA, proteins, and lipids, often resulting in cell death [7, 8]. The induction of high ROS levels in cancer cells, aimed at triggering regulated cell death, represents one of the main effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy [9]. Similarly, in targeted cancer therapies, ROS-mediated tumor cell death is also universal and closely linked to the development of drug resistance, such as ROS and EGFR [10, 11]. Consequently, as an important factor in tumor treatment response, summarizing the mechanisms of ROS in the TKI treatment process and drug resistance may be a breakthrough in overcoming widespread TKI resistance See Table 1.
The ROS-mediated mechanisms of cancer cell killing by different TKIs
ROS play many important roles in cells. Accumulating ROS can induce a cascade of cellular events, especially mitochondrial damage and apoptosis [12]. This phenomenon also frequently occurs during TKI treatment. In this section, we aim to illustrate the tumor cell killing effects of different types of TKIs through ROS-related mechanisms (Fig. 1).
Treatment with TKIs leads to the accumulation of ROS in cancer cells through various mechanisms. High levels of ROS induce apoptosis through the activation of various pathways, including JNK and P38MAPK, endoplasmic reticulum stress, DNA damage, and repression of antiapoptotic proteins XIAP and FLIP. Additionally, the increase of ROS induces ferroptosis in cancer cells. Furthermore, ROS activates ATM and cause DNA damage, leading to cellular senescence and death
ErbB inhibitors
Commercial ErbB inhibitors mainly target two targets: ErbB1 (EGFR) and ErbB2 (HER2).
Gefitinib, as the first marketed EGFR-TKI, has achieved good clinical efficacy against EGFR 19 exon deletion (19Del) and L858R mutation in exon 21 (L858R). Under gefitinib treatment, lung cancer cells show a rise in ROS levels over time, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction [13]. In glioma, gefitinib promotes ROS production via NOX2 and NOX4, triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress and activating the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/c-Jun N-terminal kinase/Noxa (Ask1/JNK/Noxa) pathway, which results in caspase-dependent apoptosis [14]. Erlotinib, another selective EGFR-TKI, increase the ROS levels in lung cancer cells, promoting JNK phosphorylation that activates c-Jun and caspase-3 to lead to apoptosis [15]. In head and neck cancer (HNSCC), erlotinib elevates NOX4 expression and hydrogen peroxide production, which not only cause cytotoxicity but also protective autophagy [16, 17]. For serine/threonine kinase 11-deficient non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, erlotinib suppresses growth and induces apoptosis through the activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and suppression of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling, due to increased ROS and associated mitochondrial damage [18]. Furthermore, the third-generation EGFR-TKI, Osimertinib, has been shown to elevate the ROS levels in NSCLC cells, leading to mitochondrial impairment and cellular apoptosis [19].
Herceptin (trastuzumab) is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting the extracellular domain of HER2 [20]. In lung cancer cells, herceptin is known to promote ROS production, which activates caspase 3/7 and leads to apoptosis [21]. However, in breast cancer, it inhibits survivin via the HER2/β-catenin/T-cell factor 4-survivin pathway, resulting in apoptosis [22]. HER2 is able to inhibit protein kinase B (PKB or AKT)- and protein kinase C α-dependent pathways [23] or promote GPX1 expression to initiate ROS clearance [24], but the blockade of HER2 by herceptin leads to intracellular accumulation of ROS and cell death, which is an important reason for cardiac toxicity during herceptin treatment.
Afatinib, lapatinib and neratinib are all pan-ErbB inhibitors, that can block both the EGFR and HRE2 pathways [25,26,27]. Afatinib acts on EGFR and activates the P38MAPK signaling pathway to inhibit xCT, causing ROS increase, lipid peroxidation, and cell ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells [28]. Likewise, afatinib promotes accumulation of intracellular ROS, followed by apoptosis in lung cancer cells [29]. In hepatoma cells, lapatinib treatment results in mitochondrial toxicity, evidenced by raised levels of mitochondrial O2- and cytoplasmic H2O2 [30]. Similarly, neratinib induces ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells, which is characterized by increased ROS and malondialdehyde content, enhanced Fe2+ activity, and downregulated GPX4 and ferritin heavy chain 1 expression [31].
ALK inhibitors
Crizotinib is a highly potent and selective ALK/c-MET dual inhibitor [32]. Crizotinib treatment leads to the accumulation of intracellular ROS, causing further mitochondrial depolarization and activating the ROS-dependent apoptotic pathway, thereby killing cervical cancer cells [33]. In another study involving human alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells, crizotinib displayed the potential to induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner through ROS accumulation, as indicated by caspase 3 activation and PARP proteolytic cleavage downregulation [34].
VEGFR inhibitors
Axitinib is a second-generation VEGFR inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2012 for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) [35, 36]. Axitinib significantly inhibits the activity of RCC by promoting the release of ROS and inducing cancer cell apoptosis [37]. Moreover, the accumulation of ROS induced by axitinib causes a DNA damage response and oxidative stress-dependent activation of the ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase, triggering cellular senescence [38, 39]. Pazopanib is a new multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, and the platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) [40]. Pazopanib induces small cell lung cancer cell apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) process via upregulation of ROS levels [41]. Regorafenib is also a broad-spectrum tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting VEGFR1-3, TEK receptor tyrosine kinase (TIE-2), etc. Regorafenib increases ROS generation by promoting NOX5 expression and activates ROS-mediated ER stress, c-Jun and P38MAPK signaling pathways [42]. In addition, regorafenib treatment promotes Bim-mediated ROS accumulation and cancer cell apoptosis via blocking AKT-mediated FOXO3a nuclear export [43].
BCR-ABL inhibitors
Imatinib is the first tyrosine kinase inhibitor to be marketed and used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) by targeting the oncogenic protein BCR-ABL. In CML, the BCR-ABL gene induces the production of ROS, cause DNA damage and regulate the DNA repair process, which leads to genomic instability, increased gene mutations, and tumor progression [44]. For leukemia with BCR-ABL mutations, imatinib directly inhibits the BCR-ABL protein to reduce ROS-related processes. However, imatinib also has an opposing impact on ROS. It increases ROS and induces ER stress by inhibiting PDGFR phosphorylation, which activates JNK phosphorylation, leading to mitochondrial-related cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells [45]. Imatinib elevates intracellular peroxide levels and activates JNK and p38 protein phosphorylation, enhancing caspase 3/9 enzyme activity and disrupting mitochondrial membrane potential, which drives ROS-dependent apoptosis in melanoma B16F0 cells [46]. Nilotinib, a second-generation TKI targeting imatinib-resistance CML patients, increases the activity of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) by phosphorylating the Ser473 site of AKT, resulting in NOX4 upregulated, ROS accumulation and cell apoptosis [47]. In addition, it is interesting to note that H2O2 downregulates the levels of the antiapoptotic proteins FLICE-like inhibitory protein (FLIP) and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) in imatinib-resistant K562 cells, which tends to promote CML cell apoptosis [48]. These findings illustrate the dual nature of ROS in both promoting tumor growth and contributing to tumor cell death.
FGFR inhibitors
Lenvatinib is an oral multitarget receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is approved for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and metastatic renal cell carcinoma [49, 50]. Lenvatinib inhibits the expression of xCT and GPX4 by inhibiting FGFR4, leading to the accumulation of lipid ROS and ultimately ferroptosis in HCC [51]. Another study found that lenvatinib prevents nuclear translocation of β-catenin to inhibit the expression of GPX2, thereby increasing the levels of ROS in HCC cells and furthering cancer cell apoptosis [52]. Erdafitinib, a novel FGFR inhibitor, disturbed lysosome functions by altering the matrix pH value, which resulted in blocked autolysosome degradation and autophagy. Blocked autophagy elevated intracellular ROS levels, causing DNA damage accumulation and apoptosis, which account for the cytotoxicity of erdafitinib in FGFR3- altered bladder cancer [53].
Contrary view
In most studies, TKIs cause tumor cell death by causing intracellular ROS accumulation, but there are still some studies that suggest that ROS plays a role in promoting tumor progression. For instance, treating patients with wide-type EGFR lung cancer with cisplatin revealed that TKIs produced neither a synergistic nor an enhancing effect on platinum-based chemotherapy, with some evidence pointing to a possible antagonistic effect [54]. Subsequent research indicated that gefitinib suppressed the EGFR-ERK/AKT signaling pathway, which activated FOXO3a and lowered ROS levels, thereby obstructing the caspase-independent cell death prompted by cisplatin [55]. Pedunculoside, a triterpene saponin extracted from Ilex rotunda Thunb, downregulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related protein expression through the MAPK and NRF2 pathways, decreases ROS production, and counteracts NSCLC metastasis [56]. Moreover, ROS have been reported to induce tumor growth by upregulating DNMT1 expression and downregulating miR-199a and miR-125b expression, thereby promoting the expression of ErbB2 and ErbB3 [57]. The promotion of tumor progression by ROS is more evident in BCR-ABL positive cells. As mentioned above, ROS induced by BCR-ABL causes chronic oxidative DNA damage and stimulates homologous recombination repair, leading to a high gene mutation rate, which is also one of the important reasons for the emergence of imatinib resistance in leukemia [58, 59].
In conclusion, TKIs elevate ROS levels within tumor cells through various mechanisms, as detailed in Table 2, leading to apoptosis, ferroptosis, and increased cytotoxicity. However, in certain instances, the production of ROS can also mediate genomic instability, metastasis, and the inhibition of apoptosis in cancer cells. Therefore, understanding the specific role of ROS requires considering many factors, such as the type, level, location, and persistence of ROS, as well as the origin, environment, and stage of the tumor [6].
Promoting ROS accumulation to overcome TKI resistance
When the concentration of ROS increases beyond the physiological concentration, they may damage cells. To protect themselves from ROS damage, cells initiate appropriate countermeasures to cope with ROS elevation and maintain cellular oxidative stress homeostasis [60]. Under TKI stress, cancer cells trigger anti-ROS pathways to cope with the accumulation of ROS, and the activation of these antioxidant pathways contribute to the development of drug resistance in cancer cells. Therefore, blocking these antioxidant pathways in cancer cells is an effective strategy to overcome TKI resistance. Additionally, activating other intracellular ROS generation pathways or providing exogenous ROS stimulation is also a choice for synergistic TKIs to exert killing effects (Fig. 2). Here we summarize some mechanisms for overcoming TKI resistance by promoting intracellular ROS accumulation.
Schematic representation showing strategies to promote ROS accumulation and overcome TKI resistance. (A) In normal cancer cells, TKI treatment leads to the accumulation of intracellular ROS and results in cell death. (B) In TKI-resistant cancer cells, ROS induce the activation of intracellular resistance pathways. These activated pathways feedback to inhibit the accumulation of ROS, leading to a decrease in ROS levels, thereby allowing cells to become resistant to oxidative damage and survive. (C) By blocking resistance pathways with corresponding inhibitors, the accumulation of ROS induced by TKIs can be restored, making cancer cells re-sensitized to TKIs. (D) Promoting endogenous ROS generation or providing exogenous ROS stimuli can re-induce the accumulation of ROS in cancer cells, making them re-sensitized to TKIs
Blocking intracellular resistance pathways to overcome TKI resistance
Autophagy
Autophagy is a catabolic degradation process of cells under internal or external stress and has been proposed as a cell death mechanism, called programmed cell death type II [61, 62]. Autophagy is the process of transferring cytoplasmic macromolecules, aggregated proteins, damaged organelles or pathogens to lysosomes, which are then digested and decomposed into nucleotides, amino acids, fatty acids, sugars and ATP, and finally recycling [63,64,65]. The role of autophagy in cancer is complex, including tumor occurrence, development, and maintenance of malignancy [63]. Oxidative stress is a major trigger of autophagy, with ROS participating in signal transduction in autophagic cells [66]. Autophagy plays different roles in TKI treatment, including toxic autophagy-mediated cell death and protective autophagy-mediated TKI resistance.
Autophagy has been frequently observed in tumor treatment with TKIs, such as afatinib for head and neck cancer [67], osimertinib for lung cancer [68], lenvatinib for liver cancer [69], and erlotinib for head and neck cancer [17]. Autophagy-dependent cell death is usually accompanied by an increase in autophagy markers and the accumulation of autophagosomes [70]. Lapatinib, in combination with the BCL-2 family inhibitor obatoclax (GX15-070), kills resistant breast cancer cells through mTOR inhibition and P38MAPK activation, resulting in ROS production, ER stress signal activation, and stimulation of toxic autophagy [71, 72]. When lenvatinib is administered alongside the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor entinostat, it activates ATM and the elongation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) via ROS. This activation increases Beclin1 and autophagy-related 5 expression, resulting in the enhanced formation of toxic autophagosomes and reduced expression of protective mitochondrial proteins in hepatoma cells [69]. Similarly, crizotinib markedly elevates ROS levels to promote autophagy activation and pyroptosis, mediating hepatotoxicity during the therapy process [73]. In addition, autophagy caused by TKIs can also induce ferroptosis of killer cells. For example, neratinib increases ROS and Fe2+ activities and downregulates GPX4, leading to ferroptosis of AML cells [31, 74].
Unlike toxic autophagy, ROS-induced protective autophagy mediates the insensitivity of cancer cells to TKIs. Afatinib inhibits mTOR through the ROS/DNA damage responses 1/tuberous sclerosis 1 (ROS/REDD1/TSC1) axis, stimulates protective autophagy in HNSCC cells, and diminishes their susceptibility to cell death [67]. In lung cancer cells, the accumulation of ROS caused by afatinib treatment led to the downregulation of AKT/mTOR signal transduction and produces protective autophagy; however, the combination of autophagy inhibitors enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of afatinib [29]. Vandetanib, a multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces protective autophagy and leads to chemical resistance by increasing the levels of ROS in NSCLC cells [75]. In HNSCC, erlotinib upregulated the expression of NOX4 and caused ROS production, which not only induces toxicity but also a degree of protective autophagy [17]. Therefore, the application of autophagy inhibitors has become an effective method of blocking protective autophagy and improving TKI responsiveness. The combination of autophagy inhibitors and TKIs can drive the differentiation of primitive cells and sensitize imatinib-resistant leukemia stem cells [76]. Additionally, pairing an autophagy inhibitor with erlotinib improves the efficacy of HNSCC therapies [17].
In summary, although the role of autophagy in TKI treatment is very complex, promoting ROS accumulation and causing toxic autophagy or using autophagy inhibitors to block ROS-induced protective autophagy effectively improves the sensitivity of cancer cells to TKIs. The specific application of autophagy in tumor cells may be related to factors such as cell type and tumor stage, and further exploration is needed.
NRF2-KEAP1 pathway
The transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2 (NRF2) is considered one of the main mediators of the cellular antioxidant response. The main function of NRF2 is activating the cellular antioxidant response by inducing the transcription of target genes [77,78,79]. Kelch ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) serves as a substrate adaptor protein for a cullin 3-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase that binds to NRF2 as a dimer, mediating the ubiquitination degradation of NRF2 [77, 80]. Osimertinib exposure leads to an upregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3), which competes with NRF2 for KEAP1 binding, diminishing NRF2 degradation, activating antioxidant pathways, and contributing to osimertinib resistance in lung cancer [19]. Lapatinib treatment activates the accumulation of the NRF2- KEAP1 pathway in hepatoma cells via ROS [30]. Similarly, activation of the NRF2- KEAP1 pathway is also observed in TKI treatments of lung cancer, breast cancer and kidney cancer, and is related to the emergence of drug resistance [37, 81, 82]. Berberine counteracts lapatinib resistance in breast cancer by reducing c-Myc levels and disrupting NRF2 stability [82]. Bexarotene, an NRF2 inhibitor, enhances the effectiveness of HER1 blockade when used with HER1 inhibitors such as lapatinib or erlotinib [83]. Silencing KEAP1 reverses the lethality of axitinib in RCC, while silencing NRF2 increases the sensitivity of RCC to axitinib [37]. The covalent JNK inhibitor JNK-IN-8 overcomes NRF2 activation caused by lapatinib treatment by inhibiting the JNK pathway, increasing ROS levels and promoting triple negative breast cancer cell apoptosis [84]. The downstream target gene of NRF2 was also found to be involved in TKI resistance; for instance, glutaredoxin was found to be upregulated in gefitinib-resistant cells [85], and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) was upregulated in osimertinib-resistant cells [86]. The antimalarial drug dihydroartemisinin (DHA) reduces the expression of HO-1 in osimertinib-resistant NSCLC cells, inhibiting cell proliferation and cooperating with osimertinib to improve ROS levels and reverse the resistance of NSCLC to osimertinib [86]. Additionally, siramesine and lapatinib in combination synergistically induce ferroptosis through HO-1 degradation, increased ROS, and lipid peroxidation [87].
The accumulation of ROS generated during TKI treatment induces activation of the intracellular NRF2-KEAP1 pathway. NRF2 regulates the expression of downstream target genes through transcriptional regulation to produce antioxidant effects that counteract ROS’s harmful impact on cells [88, 89], which is one of the mechanisms of TKI resistance (Fig. 3). Therefore, targeting the NRF2-KEAP1 pathway in drug-resistant cancer cells has emerged as a viable strategy to overcome TKI resistance.
Activated antioxidant pathways in TKI resistant cancer cells. (A) There are two primary pathways for GSH production: de novo synthesis and GSSG reduction. In TKI resistant cancer cells, AKR1B1 promotes cysteine transport, SHMT2 enhances glycine production, and both cysteine and glycine serve as substrates for stimulating de novo synthesis of GSH. In addition, Sirtuin5, TRXR1 and PPP contributes to the reduction pathway of GSH by increasing NADPH levels. (B) JNK1, JNK2 and c-Myc upregulate NRF2. SOCS3 upregulates NRF2 by inhibiting the NRF2-KEAP1 combination. Upregulated NRF2 then exerts antioxidant effects through downstream molecules like HO-1. (C) Antioxidant enzymes increase in TKI resistant cells and subsequently suppress intracellular ROS. The boxes display the corresponding TKIs
Glutathione metabolism
Glutathione (GSH) is the most abundant antioxidant in the body. It interacts with ROS to form disulfide-oxidized (GSSG) forms under the catalysis of GPXs, thereby clearing excess ROS in cells and shielding them from oxidative stress [90]. There are two main ways to generate GSH: first one is the two-step ATP-dependent enzymatic reaction catalyzed by glutamate cysteine ligase and GSH synthetase with cysteine and glutamic acid as substrates; second, GSSG is reduced to GSH with the assistance of GSH reductase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) [91, 92]. Changes in substrates, cofactors, and enzymes during the synthesis of GSH impact intracellular GSH levels and modify cellular resilience to ROS (Fig. 3). Studies have shown that glutathione metabolism is involved in TKI resistance. Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1 (AKR1B1) is upregulated in gefitinib-, erlotinib-, and osimertinib-resistant lung cancer cells and accelerates the de novo synthesis of glutathione by promoting the cystine transporter solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) expression, thereby reducing treatment-induced stress, such as ROS accumulation, ultimately leading to resistance [93]. The activated metabolism of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) generates NADPH, increases the intracellular GSH/GSSG ratio and protects cells from ROS-induced damage, contributing to erlotinib resistance in pancreatic cancer [94] and imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors [95]. Sirtuin5 increases the stability of isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) at the succinylation site K413, resulting in greater NADPH production, which augments the antioxidant defenses of renal cancer cells and their resistance to sunitinib [96]. Likewise, serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2) activated in lapatinib-resistant breast cancer promotes the synthesis of glycine and increases the synthesis of GSH [97]. In addition, certain drugs can overcome TKI resistance by inhibiting the generation of GSH. For instance, shikonin inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 (TRXR1), thereby inhibiting the reduction of GSSG to GSH, causing apoptosis of gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells [98]. Greensporone A produces ROS through depletion of GSH levels, and enhances the activity of imatinib in leukemia cells [99]. Therefore, inhibiting glutathione metabolism in TKI-resistant cells is a good method to induce intracellular ROS accumulation and restore TKI sensitivity.
Antioxidant enzymes
Antioxidant enzymes are enzymes that have the ability to convert peroxides into less toxic products, helping cells avoid damage from peroxides, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidases (GPX) and peroxiredoxin (PRDX) [100, 101]. In erlotinib-resistant lung cancer cells, the upregulated expression of SOD2 and GPX4 induced by aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 (ALDH1A1) reduces the ROS-RCS levels caused by erlotinib and endows TKI resistance [102]. PRDX2 is overexpressed and highly demethylated in gefitinib-resistant A549 cells, causing a decrease in ROS and participating in JNK phosphorylation and the apoptosis signaling pathway, thus playing an important role in cancer cell survival [103]. In HCC, the rise of transcription factor E26 transformation-specific-1 (Ets-1) leads to the expression of GPX2, causing mitochondrial damage and a significant reduction in mitochondrial ROS production, resulting in sorafenib resistance [104]. GPX and catalase activity seem elevated in imatinib-resistant CML cells compared to sensitive ones [105]. Increasing antioxidant enzymes in drug-resistant cells participates in the occurrence of TKI resistance by reducing ROS damage (Fig. 3), so inhibiting antioxidant enzyme activity in drug-resistant cells may be a potential method to overcome TKI resistance.
Increasing ROS production to overcome TKI resistance
NADPH oxidases are important enzymes mediating the production of hydrogen peroxide and peroxides within the body [106]. The levels of cellular ROS are affected by their expression and activity. In previous explanations, it has been shown that the NOX family plays a role in the TKI-induced cell killing process [14, 16, 42, 47]. Additionally, activated NOX family enzymes lead to the death of drug-resistant cells. Combining erlotinib with ampelopsin induces caspase-dependent apoptosis through the NOX2-ROS-Bim pathway, overcoming resistance to erlotinib in NSCLC cells [107]. 6-Shogaol stimulates ROS production via NOX4 in ovarian cancer, leading to ER stress, eIF2α phosphorylation, and upregulation of activating transcription factor 4 and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), which induces apoptosis and overcomes gefitinib resistance [108]. In EGFRT790M TKI-resistant NSCLC cells, sanguinarine activates NOX3, leading to the accumulation of ROS, resulting in NADPH depletion, causing methionine reductase A (MsrA) to destroy its protein reduction protection against methionine 790 of EGFR, causing EGFR peroxidation and degradation, and inducing cancer cell apoptosis [109]. Therefore, activating the NOX family to increase ROS production in drug-resistant cells is also a choice to overcome TKI resistance.
Providing exogenous ROS stimulation to overcome TKI resistance
In addition to influencing the production and clearance of endogenous ROS, the use of exogenous ROS heightens the sensitivity of cancer cells to TKIs. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) serves as a notable method for such intervention. PDT works by accumulating photosensitizers in tumor cells that release energy when exposed to specific wavelengths of light, leading to the production of ROS and subsequent cytotoxicity [110, 111]. This process resembles how TKIs promote cell death through ROS induction. Hence, combining TKIs with PDT effectively enhances ROS accumulation in tumors, strengthens cytotoxic effects, and improves tumor cell sensitivity to TKIs. This approach has shown promise in various cancers including lung [112, 113], prostate [114], renal cell [115], colorectal adenocarcinoma [116], and liver cancer [117]. Moreover, PDT has been found to complement axitinib in tumor suppression by damaging tumor blood vessels [118], and to augment the immune response when used with dasatinib [119].
Other methods
Besides the primary anti-ROS or pro-ROS production pathways that target TKI resistance, this section will also mention some potential resistance mechanisms related to intracellular ROS. Although the relationship between these mechanisms and ROS is not very clear, it is evident they play a part in the ROS-related TKI resistance process, like when combining HDAC inhibitors with TKIs.
Histone acetylase causes cancer progression by acetylating histones and inhibiting gene expression, while histone acetylation inhibitors (HDACis) inhibit tumor progression by blocking HDAC, regulating cell cycle arrest, chemical sensitization, apoptosis, and upregulation of tumor suppressors [120, 121]. Treating tumors with HDACis stimulates the generation of ROS, triggers the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis, and is linked to cell death [122, 123]. For instance, the HDACi vorinostat enhances the therapeutic effect of gefitinib or erlotinib, resulting in strong synergistic anti-proliferation and pro-apoptotic effects, overcoming EGFR-TKI resistance. This synergy is associated with the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and increased DNA damage [124, 125]. Overexpression of HO-1 activates HDACs, which diminishes ROS levels and causes imatinib resistance in CML cells [126]. Combining HDACis with imatinib in resistant leukemia cells greatly increases mitochondrial damage and cell death, potentially because it prevents the acetylated heat shock protein 90 from binding to BCR-ABL, aiding in the proteasomal degradation of BCR-ABL protein [127, 128]. Additionally, when HDACis are used alongside other drugs, they contribute to the destruction of imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL positive cells, as seen in combinations with polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors [129], the dual BCR-ABL/Aurora kinase inhibitor KW-2449 [130], and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib [131]. Although the mechanism of ROS production mediated by HDACis is unclear, the potential of HDACis combined with TKI in overcoming drug resistance cannot be denied, and is worthy of further mechanistic exploration.
Combination therapy can effectively overcome TKI resistance [132], and therefore, identifying suitable treatment pairings is a viable strategy to overcome TKI resistance. Similar to the drug combinations of HDACis with TKIs, there are other therapeutic pairings which enhance ROS accumulation in cancer cells, thereby increasing the efficacy of TKIs. In Table 3, we have listed several such therapeutic combinations.
Some studies have found other TKI resistance mechanisms associated with ROS. Treatment of breast cancer cells with the lysosome-disrupting agent siramesine alongside lapatinib elevates FeCl3 levels, diminishes the iron transport protein ferroportin 1, raises cytosolic ROS, and induces ferroptosis [135]. In osimertinib-induced drug-resistant persistent cells, miR-21-5p is upregulated, and adenylosuccinate lyase, an essential enzyme in the de novo purine biosynthesis pathway, is inhibited. The inhibition of ADSL prevents the generation of acadesine, leading to low ROS levels in drug-resistant persistent cells [140]. The overexpression of NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex 4-like 2 (NDUFA4L2) promotes mitochondrial relocalization of HER2 and inhibits the production of ROS, thus making HER2-positive breast cancer cells more resistant to herceptin treatment [141]. Elevated ROS activity in lenvatinib-resistant cells is involved in inducing EGFR activation, leading to drug resistance in HCC cells [142]. In erdafitinib-resistant bladder cancer cells, high levels of prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha 2 (P4HA2) stabilize hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), which activates downstream target genes and lowers ROS levels in bladder cancer [53]. In contrast, sustained activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 causes an increase in ROS accumulation and chronic oxidative damage to DNA, leading to the accumulation of mutations and participating in the resistance of CML to imatinib [143]. These complex and diverse mechanisms suggest that ROS play important and variable roles in TKI resistance, requiring further study based on more specific tumor types and TKI types.
In addition to these studies on specific mechanisms, certain studies have found that the combination of some compounds and TKIs may eradicate drug-resistant cancer cells through causing ROS accumulation-related effects such as ES stress, mitochondrial damage, and apoptosis (Table 4). By combining these natural extracts or drugs that have been clinically applied with TKIs, better safety can be achieved while enhancing TKI efficacy, which is beneficial for clinical conversion.
Beyond the scope of the first three generations of TKI drugs discussed in this paper, the emerging fourth-generation TKI drugs also warrant attention. These fourth-generation TKIs are primarily designed to overcome mutations that have arisen in the targets of first three generations of TKI therapies [154]. Notable examples include drugs developed to target the third-generation EGFR-TKI C797S mutation, such as BLU-945 and EAI045 [155, 156]. Additionally, compounds such as TPX-0131 and NVL-655 are being designed to address dual-mutation positive ALK subtypes that previous ALK-TKIs have been unable to effectively target [157]. Nonetheless, these drugs are currently in the clinical research phase, and their anti-tumor efficacy awaits further validation through additional clinical data. Furthermore, the role of ROS in the tumoricidal mechanisms induced by these novel TKIs and its potential impact on drug sensitivity require further investigation upon the market availability of these drugs and subsequent in-depth studies.
Conclusion and future perspectives
TKIs are pivotal in modern cancer therapy, as they elevate intracellular ROS, which damages DNA, proteins, and organelles, ultimately causing cancer cell death. This phenomenon is commonly observed during TKI action against cancer cells. Cancer cells often respond to oxidative stress by activating antioxidant pathways for self-protection, and these pathways can lead to TKI resistance. By inhibiting these pathways, the response of drug-resistant cancer cells to TKIs may improve. Additionally, stimulating ROS generation within drug-resistant cells or providing exogenous ROS stimulation is also an effective means to overcome TKI resistance. Although it is evident that ROS plays a vital role in TKI resistance, the specific mechanisms of ROS-related cell death or resistance are not fully understood due to ROS complexity and variations in tumor origin, microenvironment, and stage. Hence, precise and in-depth research is needed. In summary, promoting ROS accumulation to overcome TKI resistance is a universal and effective method, and deeper exploration of the mechanisms can provide opportunities to identify critical therapeutic targets.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AKR1B1:
-
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- ALDH1A1:
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1
- ALK:
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- AMPK:
-
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- Ask1:
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- ATM:
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- CML:
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia
- DHA:
-
Dihydroartemisinin
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- eIF2α:
-
Elongation initiation factor 2α
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- Ets-1:
-
E26 transformation–specific-1
- FGFR:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor
- FLIP:
-
FLICE-like inhibitory protein
- GPX:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSK3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
- GSSG:
-
Disulfide-oxidized
- GSTP1:
-
Glutathione S-transferase pi
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HDACi:
-
Histone acetylation inhibitor
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck cancer
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- IDH2:
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-Terminal kinase
- KEAP1:
-
Kelch ECH-associated protein 1
- MsrA:
-
Methionine reductase A
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NDUFA4L2:
-
NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex 4-like 2
- NOX:
-
NADPH oxidase
- NRF2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- O2 :
-
Superoxide
- OH• :
-
Hydroxyl radical
- P4HA2:
-
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha 2
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PDGFR:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor
- PDT:
-
Photodynamic therapy
- PPP:
-
Pentose phosphate pathway
- PRDX:
-
Peroxiredoxin
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- REDD1:
-
DNA damage responses 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SHMT2:
-
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2
- SLC7A11:
-
Solute carrier family 7 member 11
- SOCS3:
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TIE-2:
-
TEK receptor tyrosine kinase
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- TRXR1:
-
Thioredoxin reductase 1
- TXNRD1:
-
Thioredoxin reductase 1
- UBE1:
-
Ubiquitin-activating enzyme 1
- TSC1:
-
Tuberous sclerosis 1
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- XBP1:
-
X-box binding protein‐1
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- 1O2:
-
Singlet oxygen
References
Wang Z, Cole PA. Catalytic mechanisms and Regulation of protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 2014;548:1–21.
Jiao Q, Bi L, Ren Y, Song S, Wang Q, Wang Y. Shan. Advances in studies of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their acquired resistance. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):36.
Saraon P, Pathmanathan S, Snider J, Lyakisheva A, Wong V, Stagljar I. Receptor tyrosine kinases and cancer: oncogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Oncogene. 2021;40(24):4079–93.
Passaro A, Jänne PA, Mok T, Peters S. Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat Cancer. 2021;2(4):377–91.
Lin JJ, Riely GJ, Shaw AT, Targeting ALK. Precision Medicine takes on Drug Resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(2):137–55.
Cheung EC, Vousden KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(5):280–97.
Aboelella NS, Brandle C, Kim T, Ding ZC, Zhou G. Oxidative stress in the Tumor Microenvironment and its relevance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2021;13(5):986.
Mijatović S, Savić-Radojević A, Plješa-Ercegovac M, Simić T, Nicoletti F, Maksimović-Ivanić D. The double-faced role of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in solid tumors. Antioxidants. 2020;9(5):374.
Chen Y, Li Y, Huang L, Du Y, Gan F, Li Y et al. Antioxidative Stress: Inhibiting Reactive Oxygen Species Production as a Cause of Radioresistance and Chemoresistance. Tong Q, editor. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1–16.
Teppo HR, Soini Y, Karihtala P. Reactive oxygen species-mediated mechanisms of action of targeted Cancer Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:1485283.
Weng MS, Chang JH, Hung WY, Yang YC, Chien MH. The interplay of reactive oxygen species and the epidermal growth factor receptor in tumor progression and drug resistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):61.
Dixon SJ, Stockwell BR. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(1):9–17.
Okon IS, Coughlan KA, Zhang M, Wang Q, Zou MH. Gefitinib-mediated reactive oxygen specie (ROS) instigates mitochondrial dysfunction and drug resistance in Lung Cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(14):9101–10.
Chang CY, Pan PH, Wu CC, Liao SL, Chen WY, Kuan YH, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to Gefitinib-Induced apoptosis in Glioma. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):3934.
Shan F, Shao Z, Jiang S, Cheng Z. Erlotinib induces the human non–small-cell lung cancer cells apoptosis via activating ROS ‐dependent JNK pathways. Cancer Med. 2016;5(11):3166–75.
Orcutt KP, Parsons AD, Sibenaller ZA, Scarbrough PM, Zhu Y, Sobhakumari A, et al. Erlotinib-mediated inhibition of EGFR Signaling induces metabolic oxidative stress through NOX4. Cancer Res. 2011;71(11):3932–40.
Sobhakumari A, Schickling BM, Love-Homan L, Raeburn A, Fletcher EVM, Case AJ, et al. NOX4 mediates cytoprotective autophagy induced by the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib in head and neck cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;272(3):736–45.
Whang YM, Park SI, Trenary IA, Egnatchik RA, Fessel JP, Kaufman JM, et al. LKB1 deficiency enhances sensitivity to energetic stress induced by erlotinib treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. Oncogene. 2016;35(7):856–66.
Meng Y, Lin W, Wang N, Wei X, Huang Q, Liao Y. Bazedoxifene-induced ROS promote mitochondrial dysfunction and enhance osimertinib sensitivity by inhibiting the p-STAT3/SOCS3 and KEAP1/NRF2 pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;196:65–80.
Goldenberg MM. Trastuzumab, a recombinant DNA-Derived humanized monoclonal antibody, a Novel Agent for the treatment of metastatic breast Cancer. Clin Ther. 1999;21(2):309–18.
Dogan I, Cumaoglu A, Aricioglu A, Ekmekci A. Inhibition of ErbB2 by Herceptin reduces viability and survival, induces apoptosis and oxidative stress in Calu-3 cell line. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;347(1–2):41–51.
Zhu H, Zhang G, Wang Y, Xu N, He S, Zhang W, et al. Inhibition of ErbB2 by Herceptin reduces survivin expression via the ErbB2-β-catenin/TCF4-survivin pathway in ErbB2-overexpressed breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(5):1156–62.
Gordon LI, Burke MA, Singh ATK, Prachand S, Lieberman ED, Sun L, et al. Blockade of the erbB2 receptor induces Cardiomyocyte Death through mitochondrial and reactive Oxygen species-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(4):2080–7.
Belmonte F, Das S, Sysa-Shah P, Sivakumaran V, Stanley B, Guo X, et al. ErbB2 overexpression upregulates antioxidant enzymes, reduces basal levels of reactive oxygen species, and protects against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Am J Physiol-Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(8):H1271–80.
Marquez-Medina D, Popat S. Afatinib: a second-generation EGF receptor and ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2015;11(18):2525–40.
Ocaña A, Amir E. Irreversible pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitors and breast cancer: current status and future directions. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35(8):685–91.
Burstein HJ, Sun Y, Dirix LY, Jiang Z, Paridaens R, Tan AR, et al. Neratinib, an irreversible ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with Advanced ErbB2-Positive breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(8):1301–7.
Wei G, Wang Y, Yang P, Peng S, Duan S, Hu X, et al. Enhancing vulnerability of Afatinib using Erastin via xCT-mediated ROS/P38MAPK signaling feedback loop in gastric cancer cells. Gene. 2023;873:147468.
Hu X, Shi S, Wang H, Yu X, Wang Q, Jiang S, et al. Blocking autophagy improves the anti-tumor activity of afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma with activating EGFR mutations in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4559.
Roos NJ, Aliu D, Bouitbir J, Krähenbühl S. Lapatinib activates the Kelch-Like ECH-Associated protein 1-Nuclear factor erythroid 2-Related factor 2 pathway in HepG2 cells. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:944.
Ma H, Liu Y, Miao Z, Cheng S, Zhu Y, Wu Y, et al. Neratinib inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells by activating autophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Drug Dev Res. 2022;83(7):1641–53.
Cui JJ, Tran-Dubé M, Shen H, Nambu M, Kung PP, Pairish M, et al. Structure based Drug Design of Crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent and selective dual inhibitor of mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor (c-MET) kinase and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J Med Chem. 2011;54(18):6342–63.
Varma DA, Tiwari M. Crizotinib-induced anti‐cancer activity in human cervical carcinoma cells via ROS ‐dependent mitochondrial depolarization and induction of apoptotic pathway. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021;47(11):3923–30.
Megiorni F, McDowell HP, Camero S, Mannarino O, Ceccarelli S, Paiano M, et al. Crizotinib-induced antitumour activity in human alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells is not solely dependent on ALK and MET inhibition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34(1):112.
Loo V. First-line systemic therapy for metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: critical Appraisal of Emerging options. Target Oncol. 2019;14(6):639–45.
Atkins MB, Plimack ER, Puzanov I, Fishman MN, McDermott DF, Cho DC, et al. Axitinib in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced renal cell cancer: a non-randomised, open-label, dose-finding, and dose-expansion phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(3):405–15.
Huang H, Wu Y, Fu W, Wang X, Zhou L, Xu X, et al. Downregulation of Keap1 contributes to poor prognosis and axitinib resistance of renal cell carcinoma via upregulation of Nrf2 expression. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(5):2044–54.
Morelli MB, Amantini C, Santoni M, Soriani A, Nabissi M, Cardinali C, et al. Axitinib induces DNA damage response leading to senescence, mitotic catastrophe, and increased NK cell recognition in human renal carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(34):36245–59.
Mongiardi MP, Radice G, Piras M, Stagni V, Pacioni S, Re A, et al. Axitinib exposure triggers endothelial cells senescence through ROS accumulation and ATM activation. Oncogene. 2019;38(27):5413–24.
Van Der Graaf WT, Blay JY, Chawla SP, Kim DW, Bui-Nguyen B, Casali PG, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2012;379(9829):1879–86.
Li Y, Chen C, Liu H, Li C, Zhang Z, Wang C. Pazopanib restricts small cell lung cancer proliferation via reactive oxygen SPECIES-MEDIATED endoplasmic reticulum stress. Thorac Cancer. 2022;13(17):2421–8.
Sui H, Xiao S, Jiang S, Wu S, Lin H, Cheng L, et al. Regorafenib induces NOX5-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and potentiates the anti-tumor activity of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2023;39:100897.
Sun B, Chen H, Wang X, Chen T. Regorafenib induces Bim-mediated intrinsic apoptosis by blocking AKT-mediated FOXO3a nuclear export. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):37.
Antoszewska-Smith J, Pawlowska E, Blasiak J. Reactive oxygen species in BCR-ABL1-expressing cells-relevance to chronic myeloid leukemia. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(1):1–10.
Kim JL, Lee D, Jeong S, Kim BR, Na YJ, Park SH, et al. Imatinib-induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells is mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1616–26.
Chang SP. Imatinib mesylate induction of ROS-dependent apoptosis in melanoma B16F0 cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2011;62(3):183–91.
Yang Q, Wen L, Meng Z, Chen Y. Blockage of endoplasmic reticulum stress attenuates nilotinib-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibition of the Akt-GSK3β-Nox4 signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;822:85–94.
Paul T. H2O2 mediated FLIP and XIAP down-regulation involves increased ITCH expression and ERK-Akt crosstalk in imatinib resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cell line K562. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:265–76.
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F, et al. Lenvatinib versus Sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10126):1163–73.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Glen H, Michaelson MD, Molina A, Eisen T, et al. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(15):1473–82.
Iseda N, Itoh S, Toshida K, Tomiyama T, Morinaga A, Shimokawa M, et al. Ferroptosis is induced by lenvatinib through fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2022;113(7):2272–87.
Tan W, Zhang K, Chen X, Yang L, Zhu S, Wei Y, et al. GPX2 is a potential therapeutic target to induce cell apoptosis in lenvatinib against hepatocellular carcinoma. J Adv Res. 2023;44:173–83.
Li X, Li Y, Liu B, Chen L, Lyu F, Zhang P, et al. P4HA2 -mediated HIF ‐1α stabilization promotes erdafitinib‐resistance in FGFR3 ‐alteration bladder cancer. FASEB J. 2023;37(4):e22840.
Johnson DH. Targeted therapies in Combination with Chemotherapy in non–small cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(14):s4451–7.
Yamaguchi H, Hsu JL, Chen CT, Wang YN, Hsu MC, Chang SS, et al. Caspase-independent cell death is involved in the negative effect of EGF receptor inhibitors on cisplatin in non–small cell Lung Cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(4):845–54.
Fan Q, Liang X, Xu Z, Li S, Han S, Xiao Y, et al. Pedunculoside inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and overcomes Gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer through regulating MAPK and Nrf2 pathways. Phytomedicine. 2023;116:154884.
He J, Xu Q, Jing Y, Agani F, Qian X, Carpenter R, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate ERBB2 and ERBB3 expression via miR-199a/125b and DNA methylation. EMBO Rep. 2012;13(12):1116–22.
Nowicki MO, Falinski R, Koptyra M, Slupianek A, Stoklosa T, Gloc E et al. BCR/ABL oncogenic kinase promotes unfaithful repair of the reactive oxygen species -dependent DNA double-strand breaks. 2004;104(12).
Koptyra M, Falinski R, Nowicki MO, Stoklosa T, Majsterek I, Blasiak J et al. BCR/ABL kinase induces self-mutagenesis via reactive oxygen species to encode imatinib resistance. 2006;108(1).
Sies H, Belousov VV, Chandel NS, Davies MJ, Jones DP, Mann GE, et al. Defining roles of specific reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cell biology and physiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(7):499–515.
Edinger AL, Thompson CB. Death by design: apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16(6):663–9.
Mizushima N. The pleiotropic role of autophagy: from protein metabolism to bactericide. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12(S2):1535–41.
Li X, He S, Ma B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):12.
Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell. 2004;6(4):463–77.
Levine B. Cell biology: autophagy and cancer. 2007;446(7137):745–7.
Filomeni G, De Zio D, Cecconi F. Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(3):377–88.
Liu X, Suo H, Zhou S, Hou Z, Bu M, Liu X, et al. Afatinib induces pro-survival autophagy and increases sensitivity to apoptosis in stem-like HNSCC cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(8):728.
Tang ZH, Cao WX, Su MX, Chen X, Lu JJ. Osimertinib induces autophagy and apoptosis via reactive oxygen species generation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;321:18–26.
Roberts JL, Poklepovic A, Booth L, Dent P. The multi-kinase inhibitor lenvatinib interacts with the HDAC inhibitor entinostat to kill liver cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2020;70:109573.
Denton D, Kumar S. Autophagy-dependent cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(4):605–16.
Cruickshanks N, Tang Y, Booth L, Hamed H, Grant S, Dent P. Lapatinib and Obatoclax kill breast Cancer cells through reactive oxygen species-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Pharmacol. 2012;82(6):1217–29.
Tang Y, Hamed HA, Cruickshanks N, Fisher PB, Grant S, Dent P. Obatoclax and Lapatinib interact to induce toxic autophagy through NOXA. Mol Pharmacol. 2012;81(4):527–40.
Li M, Wang C, Yu Z, Lan Q, Xu S, Ye Z, et al. MGIG exerts therapeutic effects on crizotinib-induced hepatotoxicity by limiting ROS ‐mediated autophagy and pyroptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(16):4492–505.
Park E, Chung SW. ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(11):822.
Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Zou H, Cai N, Chen X, Xu L, et al. The multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib plays a bifunctional role in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):8629.
Xu X, Yin S, Ren Y, Hu C, Zhang A, Lin Y. Proteomics analysis reveals the correlation of programmed ROS-autophagy loop and dysregulated G1/S checkpoint with imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Proteomics. 2022;22(1–2):2100094.
Jaramillo MC, Zhang DD. The emerging role of the Nrf2–Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev. 2013;27(20):2179–91.
Lu MC, Ji JA, Jiang ZY, You QD. The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: an update: THE KEAP1-NRF2-ARE PATHWAY. Med Res Rev. 2016;36(5):924–63.
Menegon S, Columbano A, Giordano S. The dual roles of NRF2 in Cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2016;22(7):578–93.
De La Vega R, Chapman M, Zhang E. NRF2 and the hallmarks of Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2018;34(1):21–43.
Xie Y, Feng S, ling, He F, Yan PY, Yao XJ, Fan XX, et al. Down-regulating Nrf2 by tangeretin reverses multiple drug resistance to both chemotherapy and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2022;186:106514.
Zhang R, Qiao H, Chen S, Chen X, Dou K, Wei L, et al. Berberine reverses lapatinib resistance of HER2-positive breast cancer cells by increasing the level of ROS. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17(9):925–34.
Kankia IH, Khalil HS, Langdon SP, Moult PR, Bown JL, Deeni YY. NRF2 regulates HER1 signaling pathway to modulate the sensitivity of Ovarian Cancer cells to Lapatinib and Erlotinib. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:1–19.
Ebelt ND, Kaoud TS, Edupuganti R, Van Ravenstein S, Dalby KN, Van Den Berg CL. A c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor, JNK-IN-8, sensitizes triple negative breast cancer cells to lapatinib. Oncotarget. 2017;8(62):104894–912.
Wang L, Liu J, Liu J, Chen X, Chang M, Li J, et al. GLRX inhibition enhances the effects of geftinib in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells through FoxM1 signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145(4):861–72.
Cai X, Miao J, Sun R, Wang S, Molina-Vila MA, Chaib I, et al. Dihydroartemisinin overcomes the resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105701.
Villalpando-Rodriguez GE, Blankstein AR, Konzelman C, Gibson SB. Lysosomal destabilizing drug Siramesine and the dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor Lapatinib induce a synergistic ferroptosis through reduced Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) levels. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1–14.
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17):3221–47.
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Tew KD. Oxidative stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2020;38(2):167–97.
Forman HJ, Zhang H, Rinna A, Glutathione. Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 2009;30(1–2):1–12.
Bansal A, Simon MC. Glutathione metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J Cell Biol. 2018;217(7):2291–8.
Lu SC. Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 2009;30(1–2):42–59.
Zhang KR, Zhang YF, Lei HM, Tang YB, Ma CS, Lv QM, et al. Targeting AKR1B1 inhibits glutathione de novo synthesis to overcome acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(614):eabg6428.
Sharma N, Bhushan A, He J, Kaushal G, Bhardwaj V. Metabolic plasticity dehydrogenase. Cancer Metab. 2020;8(1):19.
Xu K. HIF-1α regulates cellular metabolism, and Imatinib resistance by targeting phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):586.
Meng L, Chen D, Meng G, Lu L, Han C. Dysregulation of the Sirt5/IDH2 axis contributes to sunitinib resistance in human renal cancer cells. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(3):921–31.
Li X, Zhang K, Hu Y, Luo N. ERRα activates SHMT2 transcription to enhance the resistance of breast cancer to lapatinib via modulating the mitochondrial metabolic adaption. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(1):BSR20192465.
Li X, Fan XX, Jiang ZB, Loo WT, Yao XJ, Leung ELH, et al. Shikonin inhibits gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting TrxR and activating the EGFR proteasomal degradation pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2017;115:45–55.
Prabhu KS, Siveen KS, Kuttikrishnan S, Jochebeth A, Ali TA, Elareer NR et al. Greensporone A, a fungal secondary metabolite suppressed constitutively activated AKT via ROS Generation and Induced apoptosis in leukemic cell lines. 2019;9(4):126.
Jiang H, Wang H, De Ridder M. Targeting antioxidant enzymes as a radiosensitizing strategy. Cancer Lett. 2018;438:154–64.
Park MH, Jo M, Kim YR, Lee CK, Hong JT. Roles of peroxiredoxins in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;163:1–23.
Lei HM, Zhang KR, Wang CH, Wang Y, Zhuang GL, Lu LM, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 confers erlotinib resistance via facilitating the reactive oxygen species-reactive carbonyl species metabolic pathway in lung adenocarcinomas. Theranostics. 2019;9(24):7122–39.
Kwon T, Kyung Rho J, Cheol Lee J, Park YH, Shin HJ, Cho S, et al. An important role for peroxiredoxin II in survival of A549 lung cancer cells resistant to gefitinib. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47(5):e165–165.
Vishnoi K, Ke R, Viswakarma N, Srivastava P, Kumar S, Das S, et al. Ets1 mediates sorafenib resistance by regulating mitochondrial ROS pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):581.
Głowacki S, Synowiec E, Szwed M, Toma M, Skorski T, Śliwiński T. Relationship between oxidative stress and Imatinib Resistance in Model Chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 2021;11(4):610.
Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX Family of ROS-Generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(1):245–313.
Hong SW, Park NS, Noh MH, Shim JA, Ahn BN, Kim YS, et al. Combination treatment with erlotinib and ampelopsin overcomes erlotinib resistance in NSCLC cells via the Nox2-ROS-Bim pathway. Lung Cancer. 2017;106:115–24.
Kim TW, Lee HG. 6-Shogaol overcomes Gefitinib Resistance via ER stress in Ovarian Cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2639.
Leung ELH, Fan XX, Wong MP, Jiang ZH, Liu ZQ, Yao XJ, et al. Targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by inducing epidermal growth factor receptor degradation via methionine 790 oxidation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016;24(5):263–79.
Dolmans DE, Fukumura D, Jain RK. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(5):380–7.
Agostinis P, Berg K, Cengel KA, Foster TH, Girotti AW, Gollnick SO, et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: an update. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(4):250–81.
Zhang M, Zhang X, Cai S, Mei H, He Y, Huang D, et al. Photo-induced specific intracellular release EGFR inhibitor from enzyme/ROS-dual sensitive nano-platforms for molecular targeted-photodynamic combinational therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(35):7931–40.
Huang K, Huo B, Li D, Xue J, Chen J. Enhanced efficacy of Gefitinib in Drug-Sensitive and Drug‐Resistant Cancer Cell lines after arming with a Singlet Oxygen releasing Moiety. ChemMedChem. 2020;15(9):794–8.
Gül EY, Karataş EA, Doğan HA, Karataş ÖF, Çoşut B, Eçik ET. Erlotinib-modified BODIPY photosensitizers for targeted photodynamic therapy. ChemMedChem. 2023;18(2):e202200439.
Yamamoto S, Nakayama T, Seki H, Kawada C, Fukuhara H, Karashima T, et al. Sunitinib with photoirradiation-mediated reactive oxygen species generation induces apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021;35:102427.
Gautam M. Stealth Polymer-Coated Graphene Oxide Decorated Mesoporous Titania nanoplatforms for in vivo chemo-photodynamic Cancer therapy. Pharm Res. 2020;37(8):162.
Zong J, Peng H, Qing X, Fan Z, Xu W, Du X, et al. pH-Responsive Pluronic F127–Lenvatinib-encapsulated Halogenated Boron-Dipyrromethene nanoparticles for combined photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy of Liver Cancer. ACS Omega. 2021;6(18):12331–42.
Weiss A, Beijnum JR, Bonvin D, Jichlinski P, Dyson PJ, Griffioen AW, et al. Low-dose angiostatic tyrosine kinase inhibitors improve photodynamic therapy for cancer: lack of vascular normalization. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(3):480–91.
Yuan G, Yao M, Lv H, Jia X, Chen J, Xue J. Novel targeted Photosensitizer as an Immunomodulator for highly efficient therapy of T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Med Chem. 2020;63(24):15655–67.
Zhang J, Zhong Q. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and cell death. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(20):3885–901.
Ramaiah MJ, Tangutur AD, Manyam RR. Epigenetic modulation and understanding of HDAC inhibitors in cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2021;277:119504.
Carew JS, Giles FJ, Nawrocki ST. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: mechanisms of cell death and promise in combination cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2008;269(1):7–17.
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M, Hrabeta J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(7):1414.
Leone A, Roca MS, Ciardiello C, Terranova-Barberio M, Vitagliano C, Ciliberto G, et al. Vorinostat synergizes with EGFR inhibitors in NSCLC cells by increasing ROS via up-regulation of the major mitochondrial porin VDAC1 and modulation of the c-Myc-NRF2-KEAP1 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;89:287–99.
Park S, Kim D, Kim M, Lee J, Rho J, Jeong S, et al. Vorinostat enhances gefitinib–induced cell death through reactive oxygen species–dependent cleavage of HSP90 and its clients in non–small cell lung cancer with the EGFR mutation. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(1):525–33.
Wei D, Lu T, Ma D, Yu K, Li X, Chen B, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 reduces the sensitivity to imatinib through nonselective activation of histone deacetylases in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):5252–63.
Yu C, Rahmani M, Almenara J, Subler M, Krystal G, Conrad D, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote STI571-mediated apoptosis in STI571-sensitive and -resistant Bcr/Abl + human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2003a;63(9):2118–26.
Nimmanapalli R, Fuino L, Bali P, Gasparetto M, Glozak M, Tao J, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 both lowers expression and promotes proteasomal degradation of bcr-abl and induces apoptosis of Imatinib Mesylate-sensitive or -refractory chronic myelogenous Leukemia- Blast Crisis cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63(16):5126–35.
Dasmahapatra G, Patel H, Nguyen T, Attkisson E, Grant S. PLK1 inhibitors synergistically potentiate HDAC inhibitor lethality in Imatinib mesylate–sensitive or –resistant BCR/ABL + leukemia cells in Vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(2):404–14.
Nguyen T, Dai Y, Attkisson E, Kramer L, Jordan N, Nguyen N, et al. HDAC inhibitors potentiate the activity of the BCR/ABL kinase inhibitor KW-2449 in Imatinib-Sensitive or -resistant BCR/ABL + leukemia cells in Vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(10):3219–32.
Yu C, Rahmani M, Conrad D, Subler M, Dent P, Grant S. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl + cells sensitive and resistant to STI571. Blood. 2003;102(10):3765–74.
Tripathi SK, Pandey K, Rengasamy KRR, Biswal BK. Recent updates on the resistance mechanisms to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and resistance reversion strategies in lung cancer. Med Res Rev. 2020;40(6):2132–76.
Booth L, Roberts JL, Sander C, Lalani AS, Kirkwood JM, Hancock JF, et al. Neratinib and entinostat combine to rapidly reduce the expression of K-RAS, N-RAS, Gα q and Gα 11 and kill uveal melanoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(5):700–10.
Garcia E, Bhatti I, Henson E, Gibson S. Prostate Cancer cells are sensitive to Lysosomotropic Agent Siramesine through Generation reactive oxygen species and in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancers. 2022;14(22):5478.
Ma S, Henson ES, Chen Y, Gibson SB. Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(7):e2307–2307.
Cao X, Majidi M, Feng M, Shao R, Wang J, Zhao Y, et al. TUSC2(FUS1)-erlotinib Induced vulnerabilities in epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR) Wildtype Non-small Cell Lung Cancer(NSCLC) targeted by the Repurposed Drug Auranofin. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35741.
Liu Z, Li X, Gao J, Yin P, Teng Y, Yu P. The therapeutic inhibition of topoisomerase inhibitor and crizotinib combination in EGFR wild and mutant lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;205:115294.
Wu Y, Zhang D, Wu B, Quan Y, Liu D, Li Y, et al. Synergistic activity of an Antimetabolite drug and tyrosine kinase inhibitors against breast Cancer cells. Chem Chem Pharm Bull. 2017;65(8):768–75.
Wang S, Chen J, Jiang Y, Lei Z, Ruan YC, Pan Y, et al. Targeting GSTP1 as therapeutic strategy against lung adenocarcinoma stemness and resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Adv Sci. 2023;10(7):2205262.
Zhang WC, Skiados N, Aftab F, Moreno C, Silva L, Corbilla PJA, et al. MicroRNA-21 guide and passenger strand regulation of adenylosuccinate lyase-mediated purine metabolism promotes transition to an EGFR-TKI-tolerant persister state. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022;29(12):1878–94.
Yuan Y, Gao H, Zhuang Y, Wei L, Yu J, Zhang Z, et al. NDUFA4L2 promotes trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2021;13:175883592110278.
He X, Hikiba Y, Suzuki Y, Nakamori Y, Kanemaru Y, Sugimori M, et al. EGFR inhibition reverses resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):8007.
Cheng Y, Hao Y, Zhang A, Hu C, Jiang X, Wu Q, et al. Persistent STAT5-mediated ROS production and involvement of aberrant p53 apoptotic signaling in the resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia to imatinib. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(1):455–63.
Dai C, Zhu L, Wang Y, Tang X, Du Y, Chen Y, et al. Celastrol acts synergistically with afatinib to suppress non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by inducing paraptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4538–54.
Li Y, Hu X, Li Q, Wang F, Zhang B, Ding K, et al. Shikonin sensitizes wild–type EGFR NSCLC cells to erlotinib and gefitinib therapy. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3882–90.
Panda M, Tripathi SK, Biswal BK. Plumbagin promotes mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in gefitinib sensitive and resistant A549 lung cancer cell line through enhancing reactive oxygen species generation. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(6):4155–68.
Tripathi SK, Rengasamy KRR, Biswal BK. Plumbagin engenders apoptosis in lung cancer cells via caspase-9 activation and targeting mitochondrial-mediated ROS induction. Arch Pharm Res. 2020;43(2):242–56.
Liu BN, Yan HQ, Wu X, Pan ZH, Zhu Y, Meng ZW, et al. Apoptosis Induced by Benzyl Isothiocyanate in Gefitinib-resistant Lung Cancer cells is Associated with Akt/MAPK pathways and generation of reactive oxygen species. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;66(1):81–92.
Lai X, Shi Y, Zhou M. Dihydroartemisinin enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity against lung adenocarcinoma cells by inducing ROS -dependent apoptosis and ferroptosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023;39(7):699–709.
Park S, Park JM, Park M, Ko D, Kim S, Seo J, et al. β-Escin overcomes trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by targeting cancer stem-like features. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22(1):289.
Wang LX, Aurora A, Kinase Inhibitor. AKI603 induces Cellular Senescence in Chronic myeloid leukemia cells harboring T315I mutation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35533.
Zhang H, Trachootham D, Lu W, Carew J, Giles F, Keating M, et al. Effective killing of Gleevec-resistant CML cells with T315I mutation by a natural compound PEITC through redox-mediated mechanism. Leukemia. 2008;22(6):1191–9.
Lin LC, Yeh CT, Kuo CC, Lee CM, Yen GC, Wang LS, et al. Sulforaphane potentiates the efficacy of Imatinib against Chronic Leukemia Cancer Stem Cells through enhanced abrogation of Wnt/β-Catenin function. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60(28):7031–9.
Cooper AJ, Sequist LV, Lin JJ. Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(8):499–514.
Eno MS, Brubaker JD, Campbell JE, De Savi C, Guzi TJ, Williams BD, et al. Discovery of BLU-945, a reversible, potent, and wild-type-sparing next-generation EGFR mutant inhibitor for treatment-resistant non-small-cell Lung Cancer. J Med Chem. 2022;65(14):9662–77.
Wang S, Song Y, Liu D. EAI045: the fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor overcoming T790M and C797S resistance. Cancer Lett. 2017;385:51–4.
Ou SHI, Nagasaka M, Brazel D, Hou Y, Zhu VW. Will the clinical development of 4th-generation double mutant active ALK TKIs (TPX-0131 and NVL-655) change the future treatment paradigm of ALK + NSCLC? Transl. Oncol. 2021;14(11):101191.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572277, 82072593).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: YM (Yunchong Meng), QL (Qinghong Long) and YL (Yongde Liao). Literatures collection: WL (Wei Lin) and XW (Xiaojun Wang). Manuscript revision: WL (Wei Lin) and MD (Mingxin Diao). Manuscript writing: WL (Wei Lin). Final approval of manuscript: All authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, W., Wang, X., Diao, M. et al. Promoting reactive oxygen species accumulation to overcome tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in cancer. Cancer Cell Int 24, 239 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-024-03418-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-024-03418-x