Abstract
This study was focused on a specific blue‒green pigment applied on the edges of the green blocks of wall paintings in the Kizil Grottoes, the earliest Buddhist cave complex in China containing many wall paintings. Based on in situ portable XRF analyses, μ-Raman spectroscope, elemental analysis (SEM–EDS and EPMA-WDS) and μ-XRPD analyses, the pigment was proven to be lavendulan [NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl·5H2O], which has not been reported in ancient wall painting studies before. Lavendulan was found to coexist with atacamite [Cu2(OH)3Cl] in some of the samples in the study and showed a nanoneedle-like morphology. Further investigations of lavendulan revealed that it was probably not originally used as a pigment but was generated by the transformation of atacamite under the influence of arsenates [As(V)] and Na+. This phenomenon and the related mechanism were discovered in this study and are discussed in this paper. As an important cultural heritage site in the Silk Road, the Route Network of the Chang’an-Tianshan Corridor and the Kizil Grottoes are listed as UNESCO World and Natural Heritage sites. The pigment types and preservation conditions of wall paintings are similar to those of many wall paintings found along the Silk Road, and further attention should be given to this discolouration mechanism for heritage site conservation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Introduction
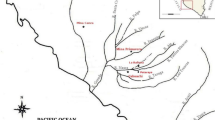
Ancient paintings, in which a range of media and techniques are used to depict the subjects of production, art, and spirituality, demonstrate the remarkable artistic talent of ancient civilizations. Paintings have the potential to reveal a great deal about historical techniques since the colours employed are derived from a range of natural sources, including plants, animals, mineral ores and also synthetic pigments such as Egyptian/Chinese blue. However, numerous types of pigments have tarnished or faded, yielding colours that differ from those of the original pigments [1,2,3]. In this investigation, we hope to learn more about the type, source, and manufacturing method of the unidentified material that was used to create the murals at the Kizil Grottoes ( ) in the Xinjiang region.
) in the Xinjiang region.
The Kizil Grottoes (3rd–8th century AD), which have numerous, scattered ancient Buddha temples and cave sites, are situated in the ancient Kucha ( ) region, which is on the main road of the ancient Silk Road (Fig. 1(a)). They also constitute the first major Buddhist cave complex in China, and the Mogao Grottoes (
) region, which is on the main road of the ancient Silk Road (Fig. 1(a)). They also constitute the first major Buddhist cave complex in China, and the Mogao Grottoes ( ) and other grottoes in the Hexi Corridor (
) and other grottoes in the Hexi Corridor ( ) greatly benefited from their artistic style, construction techniques, and painting methods. The Kizil Grottoes were included in the Chang’an–Tianshan Corridor’s Silk Road (
) greatly benefited from their artistic style, construction techniques, and painting methods. The Kizil Grottoes were included in the Chang’an–Tianshan Corridor’s Silk Road ( ), the Route Network of World Heritage, in 2014. Large expanses of green and blue colours are typical of the murals in the grottoes (Fig. 1(b) and (c)), and green is consistently the dominant colour. Ernst Waldschmidt stated that the use of brilliant green to provide a startling contrast with alternate tones was a hallmark of the first style (characterized by Grünwedel [4]). Blue was only used as a contrasting colour in the images in the second style [5]. Therefore, since the initial construction of the grottoes, the blue lapis lazuli pigment was used frequently in murals, and cold blue–green tones became an important artistic feature of the caves and influenced the artistic expression of the Buddhist grottoes in ancient China.
), the Route Network of World Heritage, in 2014. Large expanses of green and blue colours are typical of the murals in the grottoes (Fig. 1(b) and (c)), and green is consistently the dominant colour. Ernst Waldschmidt stated that the use of brilliant green to provide a startling contrast with alternate tones was a hallmark of the first style (characterized by Grünwedel [4]). Blue was only used as a contrasting colour in the images in the second style [5]. Therefore, since the initial construction of the grottoes, the blue lapis lazuli pigment was used frequently in murals, and cold blue–green tones became an important artistic feature of the caves and influenced the artistic expression of the Buddhist grottoes in ancient China.
The composition of the blue and green pigments found via analytical studies of the Kizil caves were limited to lapis lazuli (lazurite, (Na,Ca)4-8Al6Si6O24(S,SO4)1–2)) and atacamite [6, 7]. The vivid blue mineral chrysocolla [(Cu, Al)2H2Si2O5(OH)4 n(H2O)], which is occasionally present as gangue in the oxidation zone of copper deposits [8], was reportedly employed in the Kizil cave murals, according to some previous surveys. A study by Gettens revealed that when examined under a microscope, a sample from Kizil displayed certain optical properties of chrysocolla [9]. Riederer also described the use of chrysocolla in Cave 207 of the Kizil grottoes and Kumtura (库木吐喇石窟) South Monastery Cave 2 [10, 11]. However, the in situ examination revealed a watery blue–green colour in many caves, including in the Simsim (森木塞姆石窟) and Kizil Gaha (克孜尔尕哈石窟) grottoes, which was typically observed near the green borders as well as at the hooked edges of the paintings (Fig. 2). This hue is distinct from that of popular mural pigments consisting of atacamite, malachite, azurite, and lapis lazuli. Thus, we presume that this blue–green colour may have resulted from a combination of techniques; it might be the chrysocolla described by Riederer, it could be a pigment that has not been identified or studied, or it could be a degradation product.
Portable X-ray fluorescence (p-XRF) analysis was used for non-invasive confirmation. Then samples of green and blue–green pigments were collected, and the first step in the identification process was optical microscopy, which was followed by multispectral analysis, morphological and chemical composition analyses. Micro X-ray absorption near edge structure (μ-XANES) based on synchrotron radiation (SR) was used to determine the chemical state of the blue-green pigments.
Our goal was to learn more about the composition of this blue–green pigment. The findings we uncovered may explain rare local minerals, ancient chemical synthetic techniques, and the extraordinary craftsmanship of Central Asian mural paintings. In addition to aiding in restoration and conservation efforts, this study provides new information on archaeology, the history of pigment and murals technological innovations.
Methods
Mural painting samples
Five representative blue‒green micro-samples were collected for precise characterization and to attain an understanding of the pigment types and production processes. Figure 3 shows the collection locations and the optical micro-images of the samples. Table 1 provides comprehensive textural information on the locations and appearances of the samples.
In situ investigations with portable X-ray fluorescence (p-XRF)
A Niton XL3t 950 portable XRF analyser (Thermo Scientific™, USA) equipped with an X-ray tube (Ag anode) and a high-performance semiconductor detector was used for in situ experimental analyses. Soil analysis mode is settled with a voltage of 50 kV and a 200 μA current were applied for 60 s to acquire the XRF spectra.
Micro-Raman (μ-Raman) spectroscopy
The embedded samples were examined using μ-Raman spectroscopy before they were embedded to qualitatively assess the blue‒green pigment composition. The tests were conducted using a 532 nm laser on a Thermo Fisher Scientific DXR 2xi μ-Raman Spectrometer with an EM-CCD detector. The laser spot size ranged from 1 to 10 μm. The resolution was 2 cm−1. The Raman shift range was 100–3300 cm−1, the acquisition time was 2–10 s, the laser power was 0.1–2 mW, and the number of accumulations was 3–5 cycles.
Micro-X-ray powder diffraction (μ-XRPD)
An X-ray diffractometer (SmartLab 9 KW, Rigaku, X-ray diffractometer Japan) was used to identify the mineral phases using Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54059 Å) at room temperature at 45 kV and 100 mA with a scan rate of 2/min. The scanning range was 5–90 2theta. A mirror optic was employed to focus the beam, achieving a diameter of 0.5 mm. Ni beta-filters were used to reduce efflorescence. The angle of the parallel slit at the emission end was 5 degrees, and that of the parallel slit at the reception end was also 5 degrees. The emission end had a slit width of 0.25 mm, the first segment at the reception end had a slit width of 20 mm, and the second segment had a slit width of 10 mm. Identification of the crystalline phases was performed with the PDF database of the International Centre for Diffraction Data Powder Diffraction Files and Jade 6.5 software.
Scanning electron microscopy combined with energy dispersive spectrometry (SEM–EDS)
The samples were embedded in cold inlay epoxy resin, polished to form a cross-sectional surface, ground with 1000# to 7000# Si–C papers and polished with Micromesh® polishing cloths to a final mesh size of 12,000# mesh. The final polishing was performed using a 0.06 μm SiO2 suspension (liquid).
SEM and energy-dispersive X-ray analyses were used to observe the cross-sectional surfaces. A Phenom XL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) system with an EDS system (Amptek Fast SDD X123) was used, and the analysis was carried out in low vacuum mode (60 Pa). Cross-sectional backscattered electron (BSE) images were obtained with a 15 kV accelerating voltage.
Electron probe microanalysis with wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EPMA-WDS)
A JEOL JXA-iHP200F field emission electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) equipped with wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (WDS) was used for more accurate elemental mapping of the surface of the cross section, especially to determine the distribution and quantity of As, Pb, and S. Samples were pretreated with a gold sputter coating to increase conductivity. Elemental mapping of nine elements, i.e., O, Si, Cu, Ba, and Pb, was carried out under a voltage of 15 kV, a probe interval of 20 na, and a beam diameter of 0.3 μm.
Micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure (SR-μ-XANES)
The embedded cross-section samples were used for μ-XANES studies, which were conducted at the SSRF beamline BL15U1. The energy range of the X-ray absorption spectra around the As-K edge was 11.817–12.017 keV. Sodium arsenate dibasic heptahydrate (Na2HAsO4·7H2O) from Amadas (98%, China) was used as a reference. The Athena software package was used for the μ-XANES spectra.
Results
p-XRF study of the blue‒green pigment
We first investigated several caves where the blue–green hue was very pronounced. Cave 69 had a distinct blue‒green colouration at the edge of the main wall (Fig. 3a). Kα lines for Cu at 8.04 keV, Kβ lines for As at 11.73 keV, and Lβ lines for Pb at 12.61 keV were detected in the blue‒green region (Fig. 4b). These results suggested that Cu, As, and Pb were present in the area. The same results were obtained for the blue‒green pigments in several other caves, and the test locations and spectra are summarized in Fig. S1. Pb probably originated from the ground layer of the lead white. The well-known pigments containing both Cu and As, namely, Scheele’s Green [Cu(AsO2)OH] and emerald green (3Cu(AsO2)2Cu(CH3COO)2)), were invented in the nineteenth century [13, 14]. However, modern pigments were not used in the restoration of murals in the Kizil caves, and thus, the pigment compositions need to be confirmed by analyses.
μ-Raman spectra of the green–blue pigments
Micro-Raman spectroscopy was performed on the blue‒green pigments before the samples were embedded. Figure 5 displays the Raman spectra of the blue‒green pigments. Strong peaks centred at 856 cm−1 and 546 cm−1 were observed for all the blue‒green pigment samples taken from Caves 69, 80, 110, 207, and 227. These peaks were assigned to the symmetric stretching and bending vibrations of (AsO4)3− [15, 16]. The peaks at 209 cm−1 and 173 cm−1 are attributed to Cu–O stretching vibrations and O–Cu–O bending vibrations, respectively [13]. The comparison illustrated in Fig. 5(a) and (c) suggested that these blue–greenish samples were probably lavendulan [NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl·5H2O]. The peaks at 510 cm–1, attributed to Cu–O stretching vibrations, and those at 973 cm–1 and 910 cm–1, attributed to hydroxyl deformation modes, were also observed for the samples in Caves 110, 227, and 207, respectively [18]. Copper chloride was identified from Cu–Cl vibrations that generated bands below 140 cm–1, such as those at 120 cm–1 and 106 cm–1 [19]. Moreover, the peaks at 117 cm−1 in the spectra of the samples taken from Caves 69 and 80, which were attributed to Cu–Cl vibrations, displayed lower relative intensities than those of the samples from Caves 227, 207, and 110. This suggested that the intensity of the band at 120 cm−1 was connected to the reduced intensity of the Cu–Cl mode at 136 cm−1 for atacamite in the pigment mixtures. Other low-frequency bands associated with Cu–Cl stretching vibrations were observed at 172 cm−1 and 221 cm−1 for the other collected samples [15]. The presence of atacamite was indicated by bands at 510 cm−1, 973 cm−1, 910 cm−1, and 345 cm−1 (Fig. 5b). Atacamite [Cu2(OH)3Cl], a structural polymorph of copper trihydroxy chloride, was found in the Kizil grottoes [20] and Kumutura grottoes [21], indicating its widespread usage in the ancient Kucha region dating back to the fourth century AD. The findings showed that in the samples collected from caves 227, 207, and 110, lavendulan and atacamite were mixed. A strong peak was detected at approximately 1000 cm−1 for certain samples. This peak was attributed to the (SO4)2− symmetric stretching vibrations of calcium sulfate dihydrate [22], which is the primary constituent of the white ground layer. The peaks of the five samples taken from the Kizil grottoes differed from those of Scheele's green and emerald green [23, 24].
Raman spectra of the collected samples. a Raman spectra of blue‒green samples collected from five caves of the Kizil grottoes. b Comparison of the spectra of the samples with atacamite used as a reference. c Comparison of the sample spectra and the spectrum of lavendulan (reference data from https://rruff.info/)
μ-XRPD analysis of the green–blue pigment
Due to their relatively large sizes, the samples from Kizil Caves 69 and 227 were selected for μ-XRPD assessments, and Fig. 6 shows the results. Based on the μ-XRPD results, the samples from Cave 69 mainly consisted of lavendulan, quartz, and calcite. The samples from Cave 227 included gypsum (calcium sulfate (CaSO4·2H2O)), which likely originated from the ground layer, as many studies have mentioned that the ground layer of the Kizil Caves is made of gypsum [7, 20]. In addition, the identification of atacamite in Cave 227 is consistent with the Raman spectroscopy results. However, the detected phases did not include iron (Fe) or lead (Pb), possibly due to their low concentrations. Based on the appearance of the blue–greenish colour and the Raman spectra, we determined that the blue–green particles in the pigment were likely lavendulan and atacamite.
SEM–EDS/EPMA-WDS analysis
SEM was used to observe the internal morphology of the paint layers of the cross-sectioned samples. The results of the elemental distribution by SEM‒EDS (Fig. S2) showed that Cu, As, and Cl were mainly present in the pigment layer and did not overlap with Pb or S. The Fe content was not obvious and was located in some of the particles in the plaster layer. Since the energy of the Pb L alpha line is 10.55 keV and the energy of the As K alpha line is 10.53 keV, overlapping lines in the EDS spectra were likely present. To avoid misinterpretation, EPMA-WDS was applied in the elemental mapping analysis to further confirm the distribution of As, Pb and S. The WDS elemental mapping results for the sample of Cave 69 are illustrated in Fig. 7 and the others and shown in the Fig. S3. Cu, As, and Cl were present at the same positions in all the samples, where Na and Ca were also present, showing results similar to those of EDS (Fig. S2). Pb and S were also detected but their locations did not coincide with areas containing mainly Cu, As, and Cl. Pb was present in the form of small dots in samples taken from Cave 69 and Cave 227 or as layers attached to the base of the blue‒green layer of Cave 80. However, due to the low concentration of Pb, the type of lead-containing material could not be identified through μ-Raman spectroscopy and μ-XRPD. S and Ca were concentrated in the ground layer of samples from Cave 110, Cave 207, and Cave 227. Based on the μ-XRPD results, the ground layer in these three caves mainly consists of gypsum, which is also consistent with previously reported analyses [7, 16]. In addition, it is obvious that the distributions of Cu, As, and Cl in the surface particles were not uniform. For example, Cl levels were high in the sample from Cave 227, and As was located on the periphery of some particles in the sample from Cave 207. This suggests that there may have been a mixing of pigments or a migration of elements during the ageing process.
EPMA-WDS and SEM‒EDS elemental analyses clearly showed that the surface pigments contain mainly Cu, As, Cl, Na and Ca, which, in combination with the μ-Raman and μ-XRPD analyses, indicates that the blue–green pigment layer contains lavendulan [NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl·5H2O].
This was the first discovery of lavendulan in early nineteenth century murals. Lavendulan has also been found in murals and polychrome paintings as degradation product of emerald green [25, 26]. We verified that there was no pigment applied to the murals after the nineteenth century. Therefore, both natural and artificial lavendulan may have been utilized as a blue‒green pigment in the Kizil grottoes. Natural lavendulan is a secondary mineral in the oxidized zone of some copper deposits, and its sources are very rare [27], only being reported in Chile [28, 29], Australia, and Greece [30]. It is difficult to determine whether the mineral originated in the ancient Tang Dynasty or from a Central Asian source.
Morphological observations are powerful tools for distinguishing whether a blue–green pigment is natural or synthetic. Figure 8 displays the observed and morphology in BSE of the pigment, with enlarged details displayed in the right column. These blue‒green pigments feature unique morphological properties, primarily nanosized needle-like and radial shapes, as seen in the magnified images. The needle-like particles (Fig. S4) were tested by EDS and found to contain mainly Cu, As, Na, Ca, and Cl (Table S1), indicating that these needles are likely lavendulan. The reference form of the mineral lavendulan consists of rectangular particles [15, 30], which first ruled out the idea of a natural mineral origin for lavendulan due to the needle-like shapes of the collected samples. This is, however, similar to the particle shapes of the synthetic lavendulan analogue [31].
Further observations revealed that in the sample from Cave 207, external intrusion of arsenic into the atacamite pigment particles clearly occurred, and the high As, Na and Ca contents around the particles are demonstrated in Fig. 9. In particular, Fig. 9b shows a magnification of the dotted line area of Fig. 9a, with the left side area and the edges of the particles exhibiting a needle-like shape, similar to the shape that Fig. 7 illustrates. The elemental mapping results of the enlarged area (Fig. 9b) are shown in Fig. S5. From Fig. 9 and Fig. S5, it can be speculated that the edge of the particle contains more Na, As and Ca. Combined with the Raman analysis and μ-XRPD results, these results may lead to the conclusion that lavendulan is present. The middle-layer particles with relatively high Cu and Cl contents are likely atacamite. This elemental distribution is more akin to the natural formation of lavendulan around the grains rather than artificial mixing, indicating the transformation of atacamite to lavendulan from the outer edge.
EPMA-WDS elemental distribution analysis was conducted to obtain more accurate information on the distribution of elements and to exclude the possibility that As overlapped with S and Pb, and the results are shown in Fig. 10. Shows that the obtained distribution results were close to those from SEM‒EDS analysis. Although S was present at the particle edge, the content was very low, ruling out the possibility that the surrounding material was CaSO4. EPMA confirmed that the As content in the surrounding region was greater than that in the central region of the blue‒green particles. Compared to the central region, the Cl content decreased at the particle edges. Table 2 displays the corresponding element concentrations obtained from WDS analyses of specific spots of this particle. The scatter plot of the data points shows that the composition of this part was not uniform, and it showed a linear change. Na and As clearly showed a positive correlation (Fig. 10k), while Cl and As showed a negative correlation (Fig. 10j). It can be inferred that if atacamite was the original green pigment used, under the influence of arsenic-containing species and Na ions, Cl was consistently lost. The EDS test points (Fig. S6), elemental data (Table S2), and the atomic concentration plots also showed the same correlation and relatively close slopes (Fig. S7). The chemical reaction began in the areas surrounding atacamite, and during the process, As and Na species reacted with atacamite. The process may have been accompanied by a loss of Cl. The chloride concentration indicated a loss of chloride ions during the reaction. In the chemical structure of lavendulan, Cl is located at the vertices of the CuO4Cl tetrahedra, and Cl likely reacted with F and O [30, 32, 33].
The element concentrations of the blue‒green pigments in each sample were determined by averaging the WDS measurements from five points in the particles. Table 3 shows that Cu, As, Ca, Na, Ca and Cl constituted the majority of the blue‒green pigments. The WDS analysis had better resolution because the pigment sample had many micron holes and gaps that caused severe absorption and scattering effects with excited X-rays [34], resulting in high standard deviation. We also conducted semiquantitative analysis with SEM‒EDS, and the results are summarized in Table S3. Tests revealed that the Cu/As and Cu/Cl ratios varied from sample to sample. However, both the EDS and WDS data indicated relatively high As/Cu ratios and low Cl/Cu ratios in Cave 69, while the samples from caves 207 and 227 have relatively high Cl contents, which may have occurred due to the presence of atacamite. The samples from Cave 69 were all acicular in shape and no atacamite was detected by μ-XRPD, suggested that this sample had fully reacted, but the presence of atacamite alongside lavendulan in both Caves 227 and Cave 207 suggested that only a part of the pigment had reacted or that the reaction was ongoing.
μ-XANES
The edge energy, which is an indicator of the As oxidation state, was determined via μ-XANES experiments. Samples from Cave 69 and Cave 227 were selected for this analysis. The measurements performed on a cross section of the blue‒greenish pigment layer confirmed that lavendulan [NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl] formed at the top. The μ-XANES experiments established the edge energy, which indicated the oxidation state of As. The arsenate (V) white line energy is displayed in Fig. 11 for the reference sample. The associated energy was 11.874 keV, which is similar to the findings in reference [35]. According to these results, As(V) was present in the majority of the blue‒green pigment samples. The samples from Cave 227 underwent incomplete reactions, but no sulphides, arsenite, or arsenic oxides were found via μ-Raman analysis or μ-XRPD, which also suggests that there may be no intermediates. This implied that pentavalent As(V) ions, such as (HAsO4)2− and (AsO4)3−, were present between the atacamite particles.
Discussion
Most copper-containing pigments exhibit instability and susceptibility to environmental factors [36]. Therefore, copper-based green and blue pigments have been widely investigated and reviewed [37, 38]. As with the blackening of copper carbonate due to alkaline environments and heat [39]. Azurite (Cu3(CO3)3(OH)2) degrades into basic copper chloride when there is a source of chloride ions in outdoors environment [40, 41]. In addition, various degradation mechanisms for copper-based green pigments are strictly associated with the media in which they occur, and the influence of oxalic acid [42], which is excreted by some microorganisms, has also been studied [31]. Marc Vermeulen examined the relationship between orpiment and darkening verdigris (Cu(OH)2·(CH3COO)2·5H2O) and reported that darkening occurred due to the release of volatile sulphides or volatile sulfide or related species by the natural orpiment, which generated dark sulphide species such as chalcocite (Cu2S) [43]. Copper chloride biodegradation mechanisms that result in the production of copper oxalate on the surface have been reported [45, 46]. However, the secondary generation of lavendulan from As(V) ions (arsenate) or As(III) ions (arsenites) has not been reported.
The present study, however, revealed that the formation of blue‒green lavendulan occurred through the transformation of atacamite with the involvement of arsenic (As(V)). The presence of blue‒green lavendulan at the interface between green and the adjacent colour blocks suggested that the As within it likely originated from the neighbouring colour blocks including white (Fig. S8a, c, j, m), red (Fig. S8g) and yellow (Fig. S8c). To identify the source of the As ions, we investigated the elemental compositions of the pigments in the areas near the blue‒green pigments in Caves 69, 80, and 110 of the Kizil grottoes with a non-invasive p-XRF method to investigate the elemental compositions of the materials adjacent to the blue‒green samples (the findings are summarized in Fig. S8). Some grey‒white areas contain As (Fig. S8(l)), or red areas and black areas contain Pb and As (Fig. S8(i)), suggesting that As(V) may have a different pigment origin. Orpiment and realgar are inherently unstable, and their decomposition products often include white grey arsenolite (As2O3) [47,48,49,50], which closely matches the colouration of the surrounding pigment block (Fig. S8(l)). In addition, some rare arsenate minerals, such as mimetite (Pb5(AsO4)3Cl) and pyromorphite (Pb5(PO4,AsO4)3Cl), contain As in the + 5 oxidation state; these minerals were used in wall paintings found in northwestern China [51, 52] and also possibly represent the origins of As(V). The specific mineral source was preliminarily determined based on the Raman spectra of samples obtained from Cave 110 of the Kizil Grottoes. In Fig. 12, the peak at 819 cm−1 was attributed to (AsO4)3− stretching vibrations, strongly suggesting the presence of mimetite or hedyphane (Pb3Ca2(AsO4)3Cl) [53, 54].
Under conditions ranging from neutral to weakly alkaline, the transition of mimetite or hedyphane occurs as shown in Eq. 1, and under acidic conditions, it proceeds via Eq. 2. Additionally, at pH values above 9, [AsO43− (aq)] emerges as a significant species [55].
These interactions are expected to take place in aqueous environments that also contain Na and Ca ions, such as those found in the presence of alkaline copper chloride and arsenate (V) species. This reaction yields lavendulan (NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl·5H2O), as shown in Eq. 3
This discolouration of atacamite by arsenate has not been previously reported. Figure 13 shows the overall process. The arsenic-containing pigments produced arsenate ions, and in the presence of Na and Ca ions, atacamite gradually transformed into needle-like lavendulan. The Kizil Grottoes may have provided environments with groundwater containing high contents of sodium salts such as NaSO4 and NaCl. Therefore, this is probably the source of the Na+ ions.
Conclusions
This investigation was focused on the blue–green pigment located at the edges of the green regions on the murals of the Kizil grottoes. We aimed to clarify whether the colour resulted from the painting technique or an unidentified pigment.
The blue‒green pigments were investigated with multiple analyses, such as Raman spectroscopy, μ-XRPD and elemental analyses, as well as field investigations, and were identified as lavendulan.
Furthermore, lavendulan was confirmed to be a product of the original atacamite. The discolouration probably occurred as atacamite was affected by the diffusion of arsenate [As(V)] and sodium and calcium ions from the surrounding aqueous environment, after which nanosized, aggregated needle-like lavendulan crystals were produced. This mechanism was explored via micromorphological observations, regional elemental analyses and μ-XANES. In the case of Cave 110 of the Kizil grottoes, the lavendulan samples were collected at the edges between the atacamite and the As-containing pigments, which was confirmed to be mimetite and was considered the source of arsenate [As (V)]. These transformations could occur with other copper-containing pigments. The factors that cause the formation of lavendulan, such as the pH and the salinity of the environment, remain unknown.
This work also highlights the range of As-containing pigments found in Chinese cave paintings and presents the possibility that arsenic ions can discolour Cu-containing pigments. This tendency has been documented in Chinese wall paintings and polychrome artefacts from around the world. Therefore, all conservators and conservation scientists should have access to this information.
Availability of data and materials
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- OM:
-
Optical microscopy
- XRPD:
-
X-ray powder diffraction
- p-XRF:
-
Portable X-ray fluorescence
- SEM‒EDS:
-
Scanning electron microscopy combined with energy dispersive spectrometry
- BSE:
-
Backscattered electron
- μ-XANES:
-
Micro X-ray absorption near edge structure
- EM-CCD:
-
Electron-multiplying charge-coupled device
- SR:
-
Synchrotron radiation
- SSRF:
-
Shanghai synchrotron radiation facility
References
Daniels V, Stacey R, Middleton A. The blackening of paint containing Egyptian blue. Stud Conserv. 2013;49(4):217–30.
Aze S, Vallet J, Detalle V, Grauby O, Baronnet A. Chromatic alterations of red lead pigments in artworks: a review. Phase Transit. 2008;81(2–3):145–54.
de Seauve T, Detalle V, Semerok A, Aze S, Grauby O, Bosonnet S, et al. Continuous wave laser thermal restoration of oxidized lead-based pigments in mural paintings. Appl phys B Lasers Optics. 2021;127(12):1.
Grünwedel A. Altbuddhistische Kultstätten in Chinesisch-Turkistan bericht über archäologische Arbeiten von 1906 bis 1907 bei Kuča, Qarašahr und in der Oase Turfan. Berlin: De Gruyter; 1912.
Von Le CA, Waldschmidt E. Die buddhistische spätantike in mittelasien. Berlin: D. Reimer; 1922.
Schmidt BA, Ziemann MA, Pentzien S, Gabsch T, Koch W, Krüger J. Technical analysis of a Central Asian wall painting detached from a Buddhist cave temple on the Northern Silk road. Stud Conserv. 2016;61:113–22.
Su BM, Li ZX, Ma ZF, Li S, Ma QL. Studies on pigments of Kizil Grottoes. Dunhuang Res. 2000;63:65–75.
Castroviejo R, Chrysocolla A. Practical guide to ore microscopy. Cham: Springer; 2023.
Gettens RJ, Stout GL. Painting materials: a short encyclopedia. New York: D. Van Nostrand Company; 1942.
Riederer J. Technik und farbstoffe der frühmittelalterlichen Wandmalereien Ostturkistans. Berlin: Museum für Indische Kunst; 1977.
Taniguchi Y, Cotte M. The wall paintings of Bamiyan Afghanistan: technology and materials. London: Archetype; 2022.
Xinjiang Kucha Caved Research Institute. General catalogue of the contents of the Kizil Grottoes. Urumqi: Xinjiang Fine Arts and Photography Publishing House; 2000.
Eastaugh N, Walsh V, Chaplin T, Siddall R. Pigment compendium set pigment compendium a dictionary of historical pigments. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2005.
Fiedler I, Bayard M. Artists pigments a handbook of their history and characteristics 3. London: Archetype Publications; 2012.
Frost RL, Weier ML, Williams PA, Leverett P, Kloprogge JT. Raman spectroscopy of the sampleite group of minerals. J Raman Spectrosc. 2007;38:574–83.
Li J, Zha J, Pan X, Zhao T, Li J, Guo H. A study of song dynasty polychrome statue-making techniques and materials in the Sage Mother hall of the Jinci temple, Shanxi. China Crystals. 2022;12:1003.
Chen XL, Yang Q. Micro-raman spectroscopy study of three green pigments containing copper and arsenic. Sci Conserv Archaeol. 2015;27:84–9.
Frost RL. Raman spectroscopy of selected copper minerals of significance in corrosion. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2003;59:1195–204.
Tao WJ, Liu XD, Zheng XG, Meng DD, Guo QX. Mid-IR and Raman spectral properties of geometrically frustrated atacamite hydroxyl copper chloride. Adv Mater Res. 2010;146–147:972–5.
Zhou ZB. A study on the painting pigments from the cave of Kizil Grottoes. J Zhejiang Univ. 2022;49:726–32.
Wang Y, Zhang XT, Ye M, Zhou ZB, Wang LL. Raman analysis of lead pigments of Kumutula Grotto Murals, Xinjiang. China J Light Scatt. 2017;29:338–42.
Prieto-Taboada N, Gómez-Laserna O, Martínez-Arkarazo I, Olazabal MÁ, Madariaga JM. Raman spectra of the different phases in the CaSO4–H2O system. Anal Chem. 2014;86:10131–7.
Rosi F, Miliani C, Borgia I, Brunetti B, Sgamellotti A. Identification of nineteenth century blue and green pigments by in situ X-ray fluorescence and micro-raman spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc. 2004;35:610–5.
Herm C. Emerald green versus Scheele’s green: evidence and occurrence. In Acta Artis Academica the colour theme: proceedings of the 7th Interdisciplinary ALMA Conference 16th-18th october 2019 University Library Bratislava, Slovak Republic. Acad Fine Arts Prague. 2020;2020:189–202.
Li Z, Wang L, Chen H, Ma Q. Degradation of emerald green: scientific studies on multi-polychrome Vairocana Statue in Dazu Rock Carvings, Chongqing. China Herit Sci. 2020;8:64.
Lee NR, Kim SJ, Moon DH. Non-invasive mineral analysis of pigments of wall paintings in the Sungseonjeon hall. Geosci J. 2023;27:161–76.
Kruszewski Ł, Świerk M, Siuda R, Szełęg E, Marciniak-Maliszewska B. Third worldwide occurrence of juangodoyite, Na2Cu(CO3)2, and other secondary Na, Cu, Mg, and Ca minerals in the fore-sudetic monocline (lower Silesia, SW Poland). Minerals. 2020;10:190.
Zambra J, Kojima S, Espinoza S, Definis A. Angélica copper deposit: exotic type mineralization in the Tocopilla plutonic complex of the Coastal Cordillera. Northern Chile Resour Geol. 2007;57:427–34.
Kampf AR, Nash BP, Dini M, Donoso AAM. Torrecillasite, Na(As, Sb)43+O6Cl, a new mineral from the Torrecillas mine, Iquique Province, Chile: description and crystal structure. Mineral Mag. 2014;78:747–55.
Giester G, Kolitsch U, Leverett P, Turner P, Williams PA. The crystal structures of lavendulan, sampleite, and a new polymorph of sampleite. Eur J Mineral. 2007;19:75–93.
Antonov AA, Nikolaev AI. Production of analogs of the rare minerals sampleite and lavendulan as potential functional materials. Theor Found Chem Eng. 2022;56:541–4.
Kiriukhina G, Yakubovich O, Shvanskaya L, Volkov A, Dimitrova O, Simonov S, et al. A novel mineral-like copper phosphate chloride with a disordered guest structure: crystal chemistry and magnetic properties. Materials. 2022;15:1411.
Zubkova NV, Pekov IV, Chukanov NV, Kasatkin AV, Ksenofontov DA, Yapaskurt VO, et al. Redefinition of lemanskiite: new mineralogical data, crystal structure, and revised formula NaCaCu5(AsO4)4Cl3H2O. Geol Ore Depos. 2018;60:594–606.
Lyman CE, Goldstein JI Jr, Romig AD, Echlin P, Joy DC, Newbury DE, et al. Particle and rough surface microanalysis scanning electron microscopy, X-Ray microanalysis, and analytical electron microscopy. Boston: Springer; 1990.
Vermeulen M, Nuyts G, Sanyova J, Vila A, Buti D, Suuronen JP, et al. Visualization of As(III) and As(V) distributions in degraded paint micro-samples from Baroque- and Rococo-era paintings. J Anal At Spectrom. 2016;31:1913–21.
Castro K, Sarmiento A, Martínez-Arkarazo I, Madariaga JM, Fernández LA. Green copper pigments biodegradation in cultural heritage: from malachite to moolooite, thermodynamic modeling, X-ray fluorescence, and Raman evidence. Anal Chem. 2008;80:4103–10.
Švarcová S, Hradil D, Hradilová J, Čermáková Z. Pigments—copper-based greens and blues. Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2021;13:190.
Wiggins MB, Heath E, Booksh KS, Alcántara-García J. Multi-analytical study of copper-based historic pigments and their alteration products. Appl Spectrosc. 2019;73:1255–64.
Mattei E, De Vivo G, De Santis A, Gaetani C, Pelosi C, Santamaria U. Raman spectroscopic analysis of azurite blackening. J Raman Spectrosc. 2008;39:302–6.
Dei L, Ahle A, Baglioni P, Dini D, Ferroni E. Green degradation products of azurite in wall paintings: identification and conservation treatment. Stud Conserv. 1998;43:80–8.
Švarcová S, Hradil D, Hradilová J, Kočí E, Bezdička P. Micro-analytical evidence of origin and degradation of copper pigments found in Bohemian Gothic murals. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;395:2037–50.
Gunn M, Chottard G, Rivière E, Girerd JJ, Chottard JC. Chemical reactions between copper pigments and oleoresinous media. Stud Conserv. 2002;47:12–23.
Vermeulen M, Sanyova J, Janssens K, Nuyts G, De Meyer S, De Wael K. The darkening of copper- or lead-based pigments explained by a structural modification of natural orpiment: a spectroscopic and electrochemical study. J Anal At Spectrom. 2017;32:1331–41.
Taniguchi Y, Otake H, Maeda K. Constituent material analysis of the Bamiyan Buddhist mural paintings (I): examination of painting techniques from polished sections. Hozon Kagaku. 2006;45:1–8.
Cotte M, Dumas P, Taniguchi Y, Checroun E, Walter P, Susini J. Recent applications and current trends in cultural heritage science using synchrotron-based fourier transform infrared micro-spectroscopy. C R Phys. 2009;10:590–600.
Le Roux SG, Miller JA, Dunford AJ, Clarke CE. The dissolution kinetics of atacamite in the acid range and the stability of atacamite containing soils from Namaqualand. South Africa Appl Geochem. 2016;64:22–9.
Trentelman K, Stodulski L, Pavlosky M. Characterization of pararealgar and other light-induced transformation products from realgar by Raman microspectroscopy. Anal Chem. 1996;68:1755–61.
Ballirano P, Maras A. In-situ X-ray transmission powder diffraction study of the kinetics of the light induced alteration of realgar (α-As4S4). Eur J Mineral. 2006;18:589–99.
Gliozzo E, Burgio L. Pigments—arsenic-based yellows and reds. Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2021;14:4.
Macchia A, Campanella L, Gazzoli D, Gravagna E, Maras A, Nunziante S, et al. Realgar and light. Procedia Chem. 2013;8:185–93.
Shui B, Su B, Yu Z, Cui Q, Wang Z, Yin Z, et al. Analysis of mimetite-group minerals in mural paintings from the Wei and Jin Dynasty Tombs of Jiayuguan. Dunhuang Res. 2020;1:133–40.
Zhou GX. Lead-containing pigments in ancient murals and polychrome sculptures from the Northwest China. Sci Conserv Archaeol. 2012;24:95–103.
Frost RL, Bouzaid JM, Palmer S. The structure of mimetite, arsenian pyromorphite and hedyphane—a raman spectroscopic study. Polyhedron. 2007;26:2964–70.
Liu Z, Xu W, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li J. Identification of the pigments on the mural paintings from an ancient Chinese Tomb of Tang Dynasty using micro-Raman and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis. Minerals. 2023;13:1224.
Bajda T. Solubility of mimetite Pb5(AsO4)3Cl at 5–55°C. Environ Chem. 2010;7:268.
Yang J. Study on desalination of materials for the conservation and repair of mural paintings in the Kucha Caves. Identif Apprec Cult Relics. 2022;229(10):33–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China Program (23VJXG024) and the Academic Research Project of The Kizil Grottoes Institute of Xinjiang (QCX2302). Additionally, SSRF supported the research project (2022-SSRF-PT-501497) through assistance with micro-XANES analysis.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China Program (23VJXG024) and the Academic Research Project of The Kizil Grottoes Institute of Xinjiang (QCX2302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ling Shen: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing–original draft. Jie Yang: Resources, Formal analysis, Writing–review & editing. Jiakun Wang: Formal analysis. Shaoping Lin: Writing–review & editing. Hui Zhang: Supervision. Zhaozhao Liu: Writing-review & editing. Zhibo Zhou: Resources, Methodology, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
40494_2024_1406_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1. Results of p-XRF analysis in Cave 69, 80, 110; enlarged elemental mapping images of samples from Cave 227.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Yang, J., Wang, J. et al. Atacamite discolouration under the influence of arsenates in wall paintings in the Kizil Grottoes, Xinjiang, China. Herit Sci 12, 292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-024-01406-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-024-01406-y